Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinases (MEKs/MKKs)
About Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinases (MEKs/MKKs)
Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases (MEKs, also known as MKKs) play a key role in regulating cellular signaling as an important component of the MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) signaling pathway.
MEKs belong to a family of protein kinases that includes two main members, MEK1 (also known as MAP2K1) and MEK2 (also known as MAP2K2). They have similar structural features, including phosphorylation activation sites (Ser/Thr) at the N-terminal end and kinase-active regions at the C-terminal end.MEK1 and MEK2 have some structural and functional differences, but both of them are able to phosphorylate and activate specific MAPKs.
MEKs play a key regulatory role as an important component of the MAPK signaling pathway. They are involved in the regulation of a variety of cellular processes by phosphorylating and activating MAPK and converting extracellular signals into intracellular biological responses. The study of MEKs can help to gain a deeper understanding of signaling mechanisms and their role in disease development, thus providing potential targets and strategies for the treatment of related diseases.
Mechanism of Action of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinases (MEKs/MKKs)
MEKs/MKKs regulate physiological processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation, survival and cell cycle by activating downstream MAPK through phosphorylation and initiating downstream signaling cascade reactions. The following are the basic steps of the mechanism of action of MEKs:
- Activation of MEKs
MEKs are usually phosphorylated and activated through the upstream activation of MAP3K (Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase).After MAP3K is activated by an external stimulus (e.g., growth factors, cellular stress, or inflammatory factors), it phosphorylates specific MEKs sites, leading to conformational changes in MEKs and enhanced kinase activity.
- MEKs Phosphorylate MAPKs
Activated MEKs phosphorylate downstream MAPKs, which usually occurs at the Thr and Tyr residues of MAPK. Different MEKs correspond to different MAPKs, e.g., MEK1 and MEK2 mainly phosphorylate extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs), MEK4 and MEK7 mainly phosphorylate c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and MEK3 and MEK6 mainly phosphorylate p38 MAPK.
- MAPK Activation
Phosphorylation of MEKs activates downstream MAPKs, transforming them from a non-activated to an activated state. Activated MAPKs can further signal and regulate a variety of cellular biological processes.
- Downstream Effects
Activated MAPKs can further phosphorylate transcription factors, nuclear proteins, and other downstream effector proteins, thereby affecting gene expression, cell proliferation, differentiation, survival and apoptosis, cell migration, and inflammatory responses. The combination of different MAPKs and downstream effector proteins determines the specific effects of cell signaling.
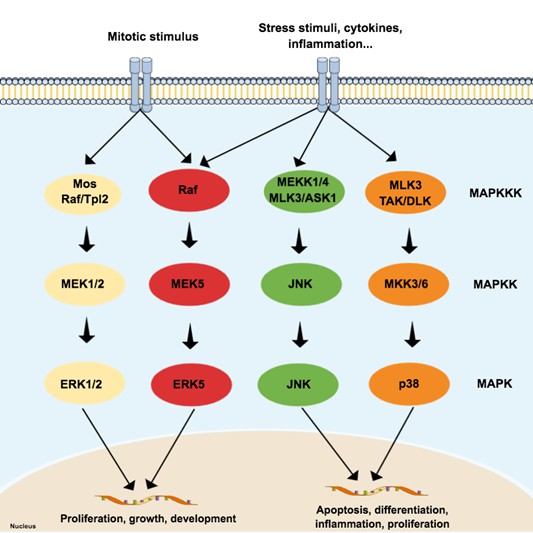 Fig.2 Schematic representation of the typical mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) pathway, composed of three levels (three-tier module) and four subfamilies: extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK) 1/2, p38, c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and ERK5. (Hepp Rehfeldt S C, et al., 2020)
Fig.2 Schematic representation of the typical mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) pathway, composed of three levels (three-tier module) and four subfamilies: extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK) 1/2, p38, c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and ERK5. (Hepp Rehfeldt S C, et al., 2020)
Functions of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinases (MEKs/MKKs)
MEKs/MKKs have multiple functions in cells and participate in various cellular biological processes mainly by regulating downstream MAPKs. Here are the main functions of MEKs:
- Signal Transduction Regulation
MEKs are important components of the MAPK signaling pathway, and they transmit extracellular signals by phosphorylating and activating MAPKs. These signals can come from a variety of stimuli, such as growth factors, cellular stress, or inflammatory factors.MEKs translate these signals into biological responses within the cell and regulate cellular physiological and pathological processes.
- Cell Proliferation and Differentiation
MEKs and their downstream MAPKs play important roles in cell proliferation and differentiation. Activated MEKs are able to phosphorylate and activate MAPKs, which in turn regulate the activity of multiple transcription factors and affect gene expression. This regulatory action promotes cell growth and differentiation and is involved in embryonic development, tissue regeneration, and the process of cell proliferation and differentiation.
- Cell Survival and Apoptosis
The MEKs-MAPK signaling pathway also plays an important role in cell survival and apoptosis. Activated MAPKs can affect cell survival signaling and apoptosis signaling by phosphorylating and regulating multiple downstream effector proteins. In some cases, the MEKs-MAPK signaling pathway can promote cell survival, while in other cases it can induce apoptosis, depending on the specific regulation of the signaling pathway and the cell type.
- Cell migration and Invasion
MEKs and MAPKs play important roles in cell migration and invasion. Activated MAPKs can phosphorylate and activate multiple downstream effector proteins to regulate cytoskeletal reorganization, cell adhesion and extracellular matrix degradation, thereby promoting cell migration and invasion. This is critical for processes such as embryonic development, tissue repair, and tumor metastasis.
- Regulation of Inflammatory Response
The MEKs-MAPK signaling pathway plays an important role in the inflammatory response. Activated MAPKs can regulate the activity of inflammatory cells and the production of inflammatory mediators, participating in the regulation of immune and inflammatory responses. This is important for maintaining the immune homeostasis of the body and coping with infections and inflammatory diseases.
Available Resources for Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinases (MEKs/MKKs)
MEKs, as key components of the MAPK signaling pathway, regulate cellular physiological and pathological processes. They are involved in a variety of biological processes and have an important impact on the normal function of cells and the development of diseases. An in-depth study of the functions of MEKs can help to understand the complexity of cell signaling and provide potential targets and strategies for the treatment of related diseases. Creative BioMart offers a variety of MEKs/MKKs-related research products, such as recombinant proteins, cell and tissue lysates, and protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, as well as customizable services and other resources to support your research in the field of MEKs/MKKs. The following MEKs/MKKs are displayed, click to view all related molecules/targets and research reagents. For further information or to purchase products, please contact us. We are committed to providing the highest quality resources and support for your research to help you succeed.
References:
- Hepp Rehfeldt S C, Majolo F, Goettert M I, et al. c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitors as potential leads for new therapeutics for Alzheimer's diseases[J]. International journal of molecular sciences, 2020, 21(24): 9677
- Grewal S, Molina DM, Bardwell L. Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)-docking sites in MAPK kinases function as tethers that are crucial for MAPK regulation in vivo. Cell Signal. 2006;18(1):123-134.
- Sinha A K, Jaggi M, Raghuram B, et al. Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in plants under abiotic stress[J]. Plant signaling & behavior, 2011, 6(2): 196-203.


