Epha2
-
Official Full Name
EPH receptor A2
-
Overview
This gene belongs to the ephrin receptor subfamily of the protein-tyrosine kinase family. EPH and EPH-related receptors have been implicated in mediating developmental events, particularly in the nervous system. Receptors in the EPH subfamily typically have a single kinase domain and an extracellular region containing a Cys-rich domain and 2 fibronectin type III repeats. The ephrin receptors are divided into 2 groups based on the similarity of their extracellular domain sequences and their affinities for binding ephrin-A and ephrin-B ligands. This gene encodes a protein that binds ephrin-A ligands. Mutations in this gene are the cause of certain genetically-related cataract disorders. -
Synonyms
EPHA2; EPH receptor A2; ECK, EphA2; ephrin type-A receptor 2; soluble EPHA2 variant 1; tyrosine-protein kinase receptor ECK; epithelial cell receptor protein tyrosine kinase; ECK; CTPA; ARCC2; CTPP1;
- Recombinant Proteins
- Cell & Tissue Lysates
- Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads
- Assay Kits
- Dog
- Human
- Human
- Mouse
- Rhesus Macaque
- Baculovirus-Infected Sf9 Cells
- E.coli
- HEK293
- HEK293T
- Human Cell
- Human Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Insect Cell
- Insect Cells
- Mammalian Cell
- Mammalian cells
- NS0
- Sf21
- Sf9 Insect Cell
- Wheat Germ
- C
- 6×His
- Fc
- His
- Avi
- Myc
- DDK
- DDK|His
- DYKDDDDK
- Fc Chimera
- Flag
- GST
- His (Fc)
- His|Myc
- MYC
- Myc|DDK
- N/A
- No tag
- Background
- Quality Guarantee
- Case Study
- Involved Pathway
- Protein Function
- Interacting Protein
- Epha2 Related Articles
- Epha2 Related Gene Family
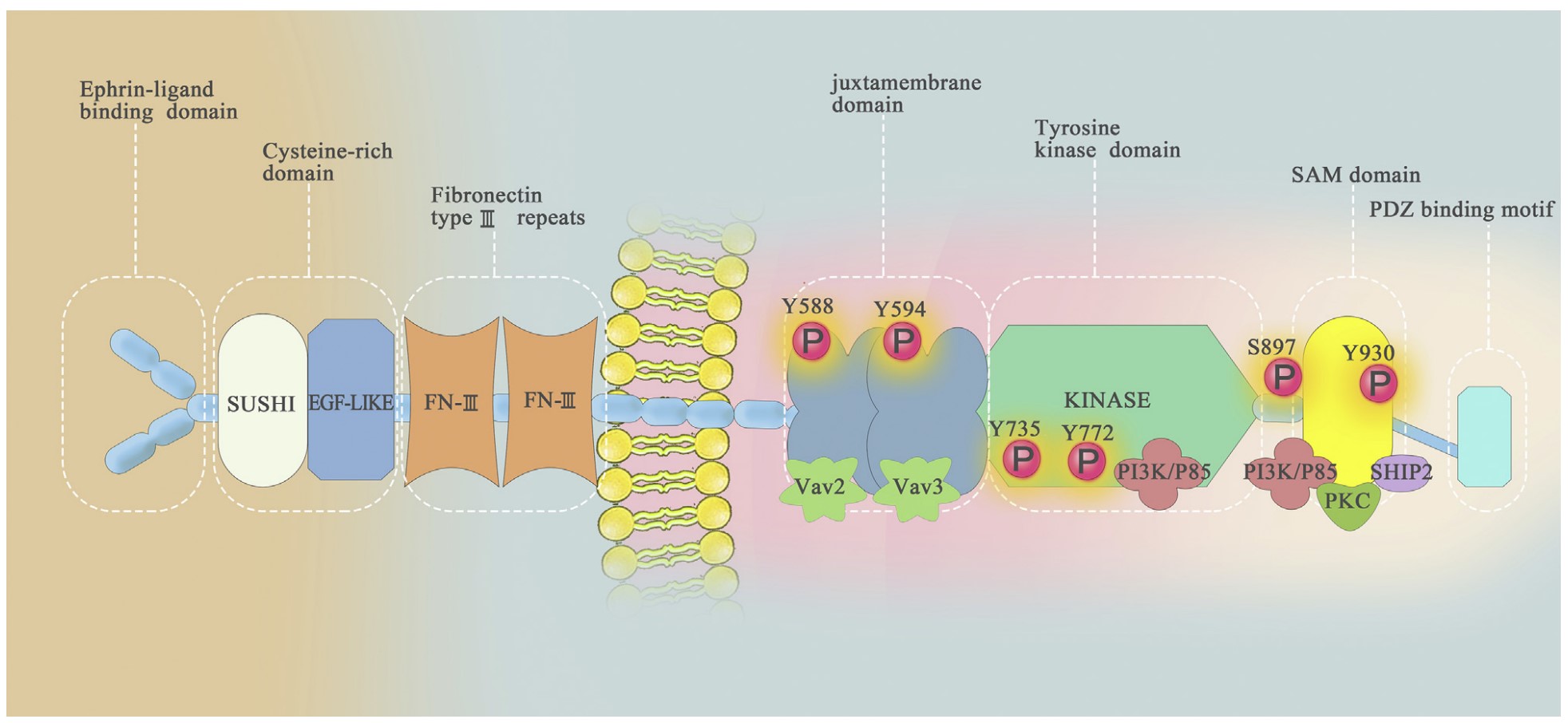
Fig1. Illustration of EphA2 protein structure and interacting proteins. (Ping Zhao, 2021)
What is EPHA2 protein?
EPHA2 (EPH receptor A2) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1p36. This gene belongs to the ephrin receptor subfamily of the protein-tyrosine kinase family. Receptors in the EPH subfamily typically have a single kinase domain and an extracellular region containing a Cys-rich domain and 2 fibronectin type III repeats. The ephrin receptors are divided into 2 groups based on the similarity of their extracellular domain sequences and their affinities for binding ephrin-A and ephrin-B ligands. This gene encodes a protein that binds ephrin-A ligands. The EPHA2 protein is consisted of 976 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 108.3 kDa.
What is the function of EPHA2 protein?
Unlike most Eph kinases, which are primarily expressed during development, EphA2 is primarily found in adult human epithelial cells. The cellular functions of EphA2 may be regulating cell growth, survival, migration, and angiogenesis. EphA2 has been demonstrated to critically regulate tumor cell growth, migration and invasiveness. It is frequently overexpressed and functionally altered in aggressive tumor cells, and that these changes promote metastatic character.
EPHA2 Related Signaling Pathway
EPHA2 protein activated multiple signaling pathways such as PI3K/AKT, MAPK/ERK, Wnt/β-catenin through binding with Ephrin-A1, A5 and other ligands. These signaling pathways play key roles in physiological and pathological processes such as cell growth, migration, differentiation, and angiogenesis.
EPHA2 Related Diseases
EPHA2 is overexpressed in many types of cancer, such as breast, prostate, glioma, and melanoma, and it promotes cancer progression by promoting tumor growth, invasion, and metastasis. In addition, EPHA2 also plays a role in neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease, where overactivation of EPHA2 can lead to neuronal damage and cognitive dysfunction. Other studies have shown that EPHA2 is also involved in cardiovascular diseases, such as atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction, and it may play a role by affecting endothelial cell function and angiogenesis.
Bioapplications of EPHA2
The application of EPHA2 protein is mainly in the field of tumor therapy, by targeting EPHA2 in a variety of ways to inhibit tumor growth and spread, such as through antibody drug conjugations or peptide drug conjugations, inhibitors or cell therapies.
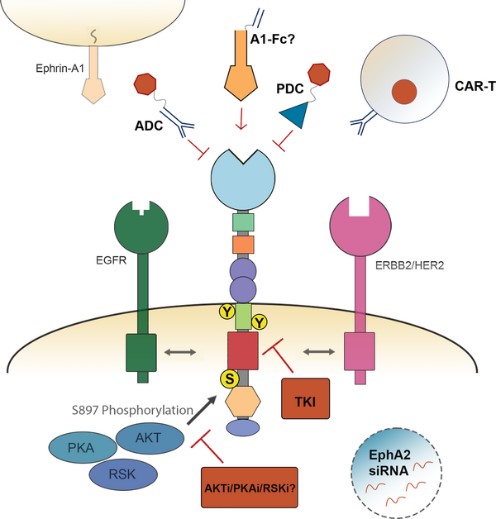
Fig2. EphA2 therapeutic targeting strategies. (Kalin Wilson, 2021)
High Purity
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (EPHA2-3378H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.

Fig2. SDS-PAGE (EPHA2-698HFL) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
Case study 1: Zhongwen Chen, 2021
Clustering of ligand:receptor complexes on the cell membrane is widely presumed to have functional consequences for subsequent signal transduction. However, it is experimentally challenging to selectively manipulate receptor clustering without altering other biochemical aspects of the cellular system. Here, the researchers develop a microfabrication strategy to produce substrates displaying mobile and immobile ligands that are separated by roughly 1 μm, and thus experience an identical cytoplasmic signaling state, enabling precision comparison of downstream signaling reactions. Applying this approach to characterize the ephrinA1:EphA2 signaling system reveals that EphA2 clustering enhances both receptor phosphorylation and downstream signaling activity. Single-molecule imaging clearly resolves increased molecular binding dwell times at EphA2 clusters for both Grb2:SOS and NCK:N-WASP signaling modules.
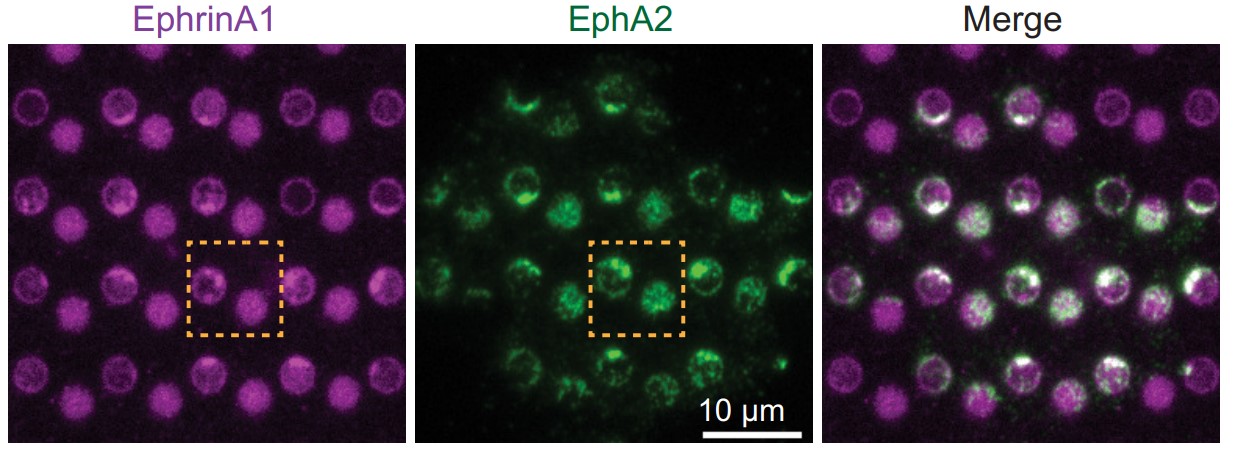
Fig1. Representative immunofluorescence images of EphA2 in MDA-MB-231 cells fixed after 45 min spread on the substrate. The yellow square marked region is enlarged in bottom panel.
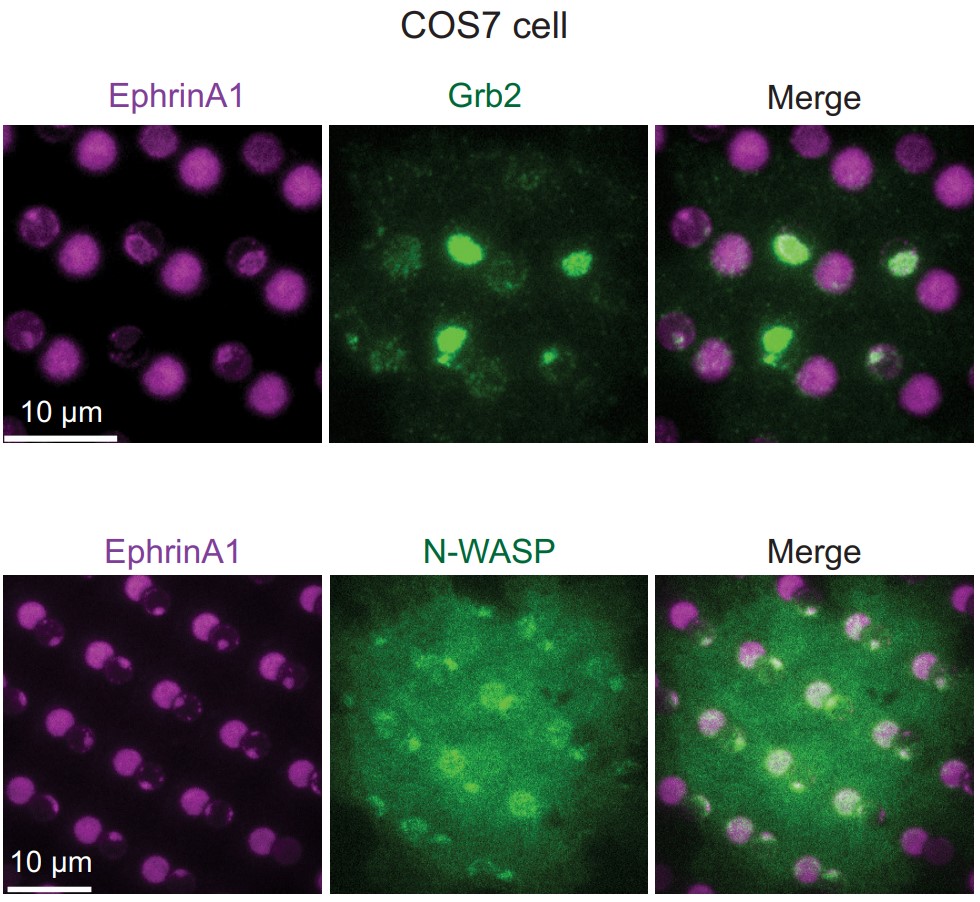
Case study 2: Zicong Gao, 2021
Tumor metastasis induced by drug resistance is a major challenge in successful cancer treatment. Nevertheless, the mechanisms underlying the pro-invasive and metastatic ability of drug resistance remain elusive. Exosome-mediated intercellular communications between cancer cells and stromal cells in tumor microenvironment are required for cancer initiation and progression. Recent reports have shown that communications between cancer cells also promote tumor aggression. However, little attention has been regarded on this aspect.
Quantitative proteomic analysis showed that EphA2 was rich in exosomes from drug-resistant cells. Exosomal EphA2 conferred the invasive/metastatic phenotype transfer from drug-resistant cells to sensitive cells. Moreover, exosomal EphA2 activated ERK1/2 signaling through the ligand Ephrin A1-dependent reverse pathway rather than the forward pathway, thereby promoting breast cancer progression. Theses findings indicate the key functional role of exosomal EphA2 in the transmission of aggressive phenotype between cancer cells that do not rely on direct cell-cell contact.
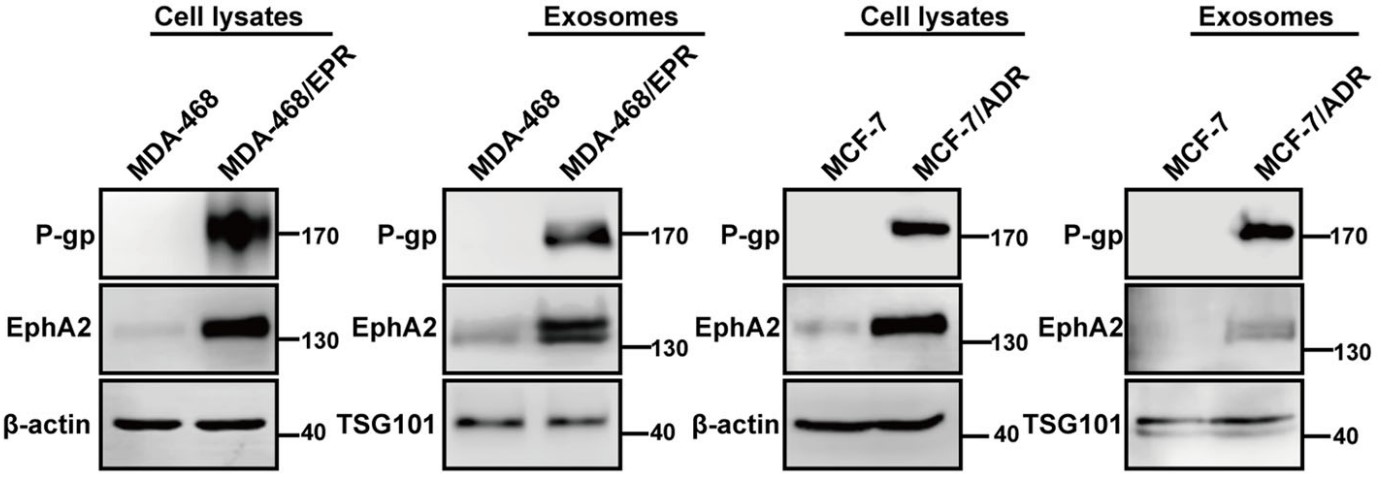
Fig3. The expression of EphA2, ABCB1 (encode P-glycoprotein) in exosomes, and cell lysates were analyzed by using Western blotting; β-actin was used as the loading control.
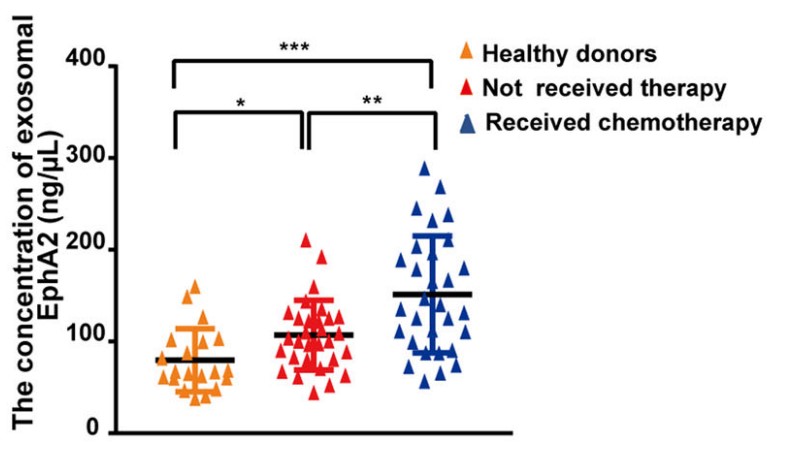
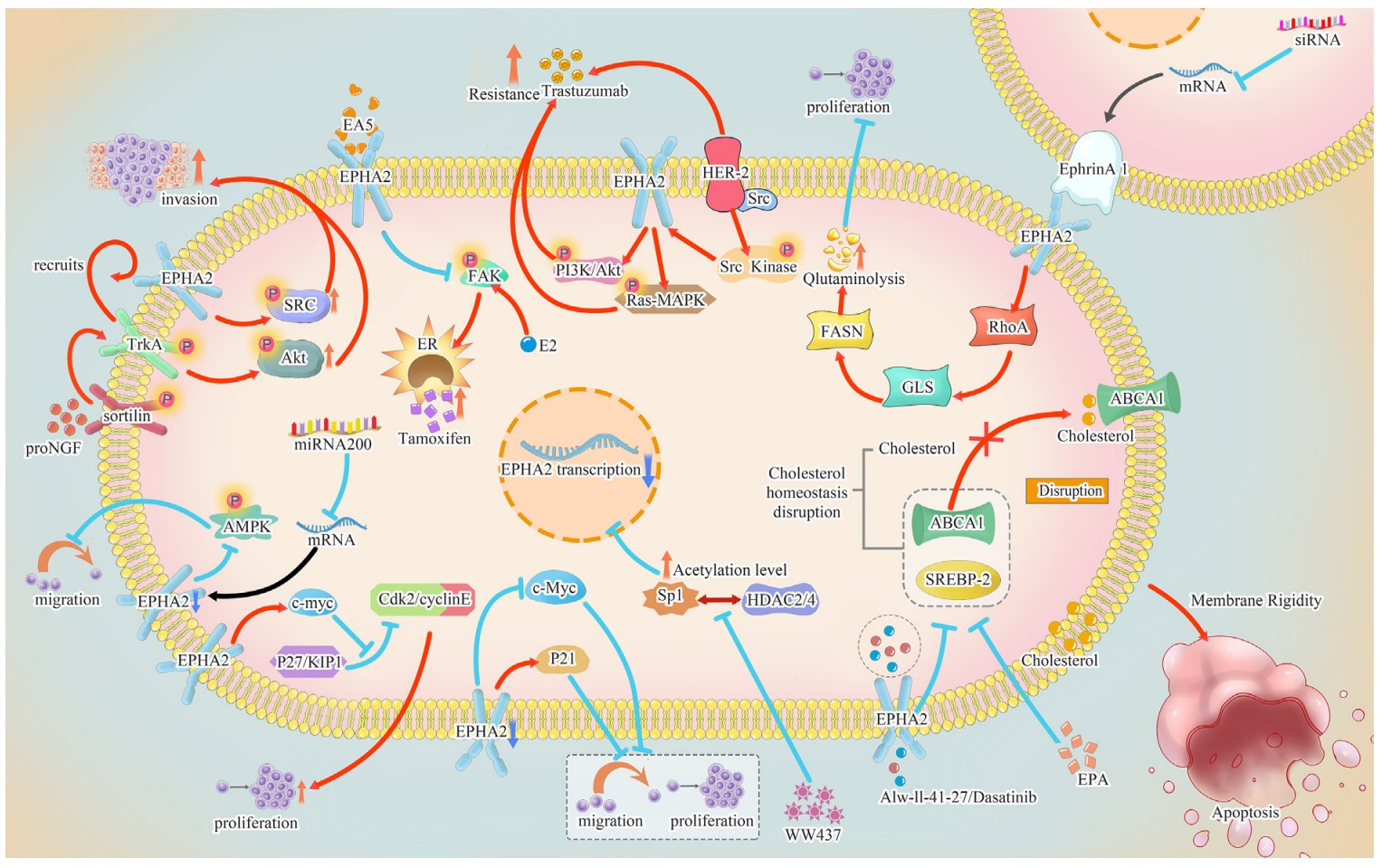
Fig1. Function and regulation of EphA2 in breast cancer and its targeting therapeutics. (Ping Zhao, 2021)
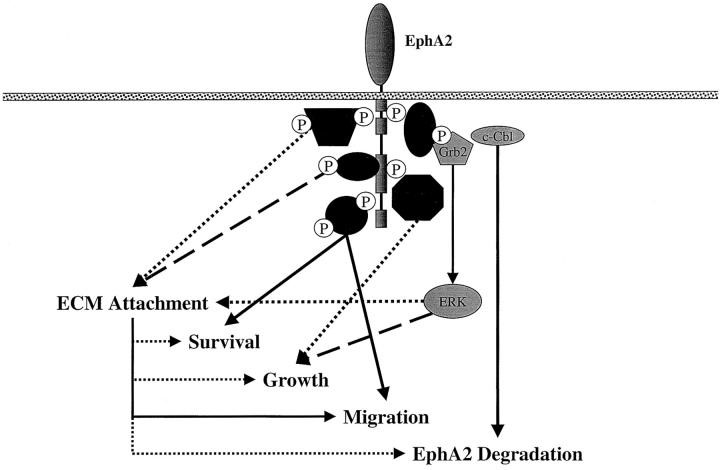
Fig2. Biological and biochemical pathways linked with EphA2. (Jennifer Walker-Daniels, 2003)
Epha2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Epha2 participated on our site, such as Arf6 signaling events, Axon guidance, Developmental Biology, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Epha2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Arf6 signaling events | USP6;EGF;EFNA1;AGTR1;KIF13B;EGFR;ADRB2;GULP1;IPCEF1 |
| Axon guidance | DPYSL3;AP2S1;SEMA6A;COL9A1A;NCK2;UNC5A;KBTBD7;MYL12B;SLIT2 |
| Developmental Biology | MED26;FRS2A;PSPN;MEF2B;PEA15;CSNK2A2;FOXH1;AP2B1;EFNB3B |
| Direct p53 effectors | DUSP5;SMARCA4;CEBPZ;CTSD;BNIP3L;FOXA1;EDN2;DGCR8;S100A2 |
| EPH-Ephrin signaling | ACTR2B;MYL12A;CLTC;EPHA4A;ACTR3;EPHB3A;CLTB;EFNB1;SHB |
| EPH-ephrin mediated repulsion of cells | AP2B1;EFNA4;EFNB2A;EFNB3;AP2A2;EFNA2A;EPHA2A;EFNA5;EFNB2 |
| EPHA forward signaling | ARHGEF15;EPHA2;CRKL;EFNA3;BLK;EFNA2;EFNA5;EFNA1 |
| EPHA-mediated growth cone collapse | EFNA3;EFNA1A;EFNA2A;EPHA4A;EFNA4;EPHA2A;EPHA2;SHB;MYL12B |
Epha2 has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding, ephrin receptor activity, protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Epha2 itself. We selected most functions Epha2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Epha2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | CTPS2;DDX18;UCK2B;PTK2AB;KIF22;MAPK15;CAMK2B1;HSPA12A;GMPS |
| ephrin receptor activity | EPHB6;EPHA6;EPHB4B;EPHA2;EPHA10;EPHA2A;EPHA4A;EPHA5;EPHB4 |
| protein binding | SAMHD1;HGF;KCNJ9;OAS2;FCGR2A;ARAP1;FSHB;RTP2;PYURF |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity | ERBB3A;NTRK2B;EPHA4A;FLT4;FGFR1B;DDR1;LTK;INSRR;ROR2 |
Epha2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Epha2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Epha2.
EFNA1; EPHA7; HSP90AB1; PTK2; saicar; PKM; PTPN11; KPNA3
- Q&As
- Reviews
Q&As (6)
Ask a questionTherapeutic strategies for EPHA2 include inhibition of its expression, blocking its signal transduction pathway, and modulating its interaction with ligands. These strategies may involve the use of small molecule inhibitors, antibodies, or other types of therapeutics.
The expression level of EPHA2 is associated with the occurrence and progression of a variety of diseases. For example, in tumors such as lung, breast, and colorectal cancer, EPHA2 expression levels may be elevated and correlated with the degree of malignancy and poor prognosis of the tumor.
In some tumors, EPHA2 expression levels are associated with poor prognosis in patients. For example, patients with lung cancer who express EPHA2 often have shorter survival. Therefore, the expression level of EPHA2 may be one of the indicators to predict tumor prognosis.
Some diseases can be diagnosed by measuring EPHA2 expression levels, such as immunohistochemistry, western blotting, and real-time PCR.
Yes, EPHA2 can be used as a target for the treatment of certain diseases. For example, inhibition of EPHA2 expression can inhibit tumor growth and spread, so EPHA2 can serve as a potential therapeutic target. In addition, regulating the expression level of EPHA2 may also be helpful in the treatment of diseases such as the nervous system and cardiovascular system.
EPHA2 can promote cancer metastasis and affect the spread and spread of cancer by regulating processes such as invasion and migration of tumor cells. Therefore, inhibition of EPHA2 expression or blocking its signal transduction pathway may have a potential therapeutic effect on inhibiting cancer metastasis.
Customer Reviews (3)
Write a reviewThe protein has low cytotoxicity.
EPHA2 has good stability, and the test results of heat resistance, acid and alkali resistance and protease degradation resistance are good.
Kinetic parameters such as enzymatic reaction rate and binding affinity were tested, and the protein performed well.
Ask a Question for All Epha2 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All Epha2 Products
Required fields are marked with *


