F11
-
Official Full Name
coagulation factor XI
-
Overview
Factor XI or plasma thromboplastin antecedent is the zymogen form of factor XIa, one of the enzymes of the coagulation cascade. Like many other coagulation factors, it is a serine protease. In humans, Factor XI is encoded by the F11 gene. -
Synonyms
coagulation factor XI; F11; FXI; MGC141891; PTA; OTTHUMP00000197033; plasma thromboplastin antecedent;
- Recombinant Proteins
- Cell & Tissue Lysates
- Transfected Stable Cell Lines
- Native Proteins
- Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- E. coli
- E.coli
- HEK293
- HEK293T
- Human Cell
- Human plasma
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Mammalian Cell
- Mammalian cells
- Wheat Germ
- C
- His
- GST
- His (Fc)
- Avi
- His|GST
- His|T7
- MYC
- DDK
- Myc|DDK
- N/A
- N
- Background
- Quality Guarantee
- Case Study
- Involved Pathway
- Protein Function
- Interacting Protein
- F11 Related Articles
- F11 Related Gene Family
- F11 Related Research Area
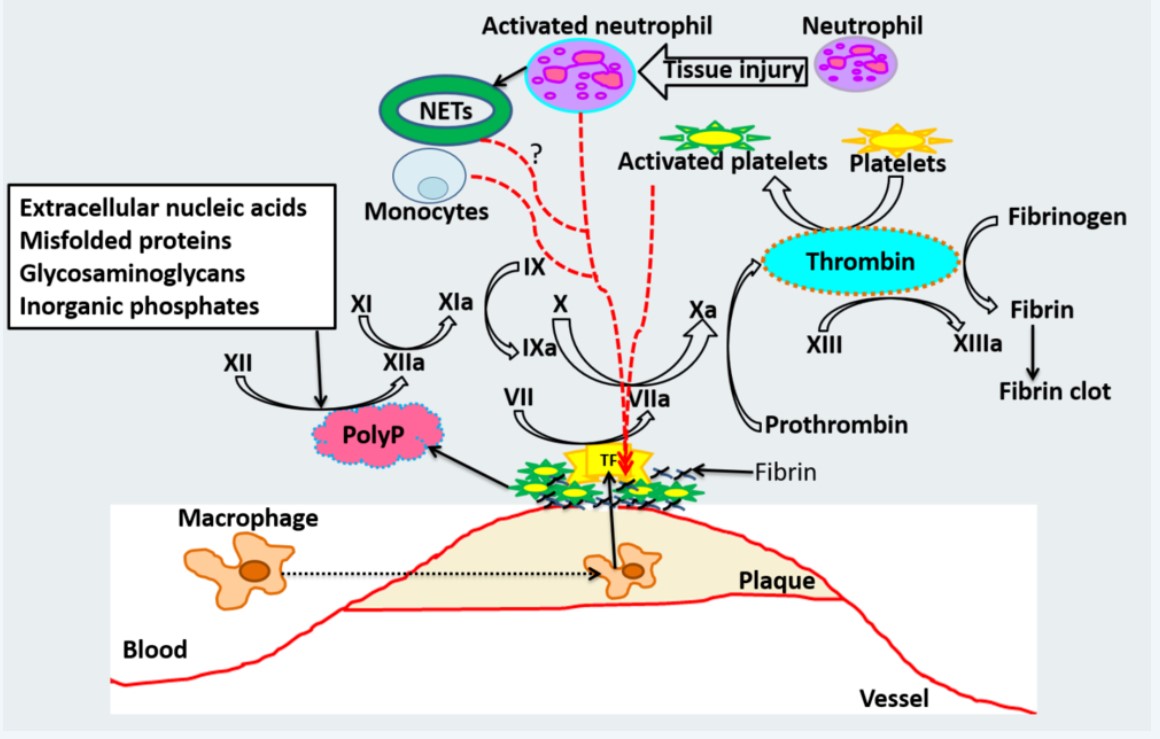
Fig1. Schematic model for Atherothrombosis after plaque rupture. (Vikrant Rai, 2019)
What is F11 protein?
F11 (coagulation factor XI) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 4 at locus 4q35. This gene encodes coagulation factor XI of the blood coagulation cascade. This protein is present in plasma as a zymogen, which is a unique plasma coagulation enzyme because it exists as a homodimer consisting of two identical polypeptide chains linked by disulfide bonds. The F11 protein is consisted of 625 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 70.1 kDa.
What is the function of F11 protein?
Coagulation Factor XI (Coagulation Factor XI) is a serine protease precursor in the blood coagulation system, which is part of the intrinsic coagulation pathway. Its main function is to participate in the process of thrombosis, specifically, when the clotting system is activated, Factor XI is activated on the surface of platelets and transformed into an activated form of Factor XIa. Factor XIa then activates Factor IX, which triggers a cascade of reactions that ultimately lead to the formation of blood clots. In addition to its role in blood clotting, research in recent years has suggested that Factor XI may also be involved in physiological processes such as inflammatory responses and wound healing.
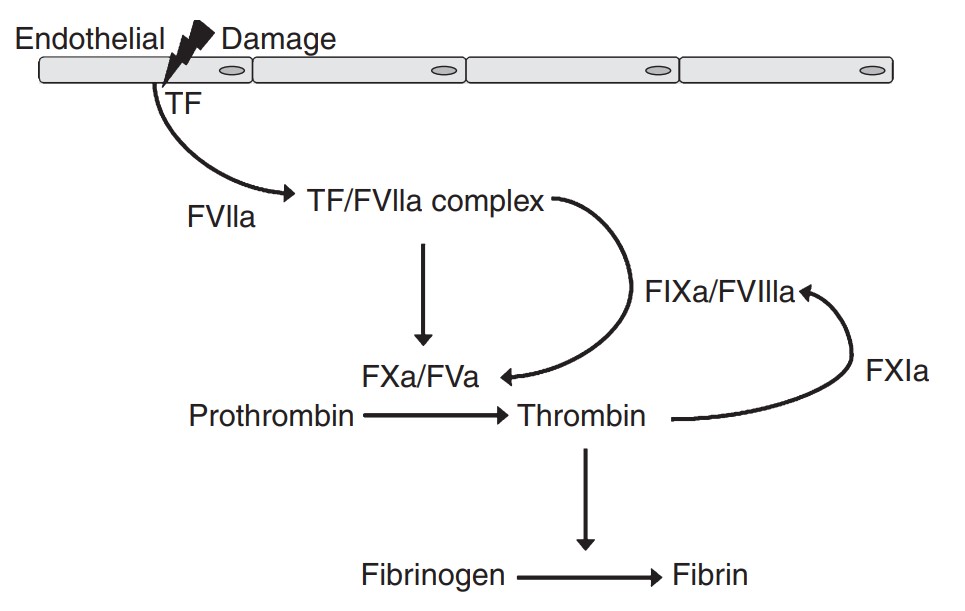
Fig2. Simplified schematic presentation of coagulation activation in vivo. (E C Löwenberg, 2010)
F11 Related Signaling Pathway
F11 is a protease involved in the blood clotting process, and its activation is part of the intrinsic clotting pathway, which further activates clotting factor IX, thus initiating a series of reactions that lead to thrombosis and ultimately converting soluble fibrinogen into an insoluble fibrin network to seal the wound and facilitate damage repair. F11 is also involved in signaling the inflammatory response. The FXIa produced by its activation can promote the activation and chemotaxis of inflammatory cells through protease-activated receptors (PARs), especially PAR2, and thus affect the inflammatory response. In addition, the activation of PARs can also induce a variety of intracellular signaling pathways, such as MAPK, NF-κB and PI3K/Akt pathways, which play a key role in regulating cell proliferation, survival and migration.
F11 Related Diseases
F11 is a component of the contact activation pathway in the blood clotting system. Diseases associated with coagulation factor XI mainly involve coagulation dysfunction, the most typical of which is coagulation factor XI deficiency, a rare hereditary bleeding disorder characterized by lower than normal activity of coagulation factor XI. In addition, some studies suggest that abnormal activation of clotting factor XI may be associated with thrombosis.
Bioapplications of F11
Concentrated preparations of F11 can be used to treat bleeding disorders caused by deficiency of clotting factor XI, such as hemophilia C. Due to the role of clotting factor XI in blood clotting, antibodies or small molecule drugs that inhibit its activity may serve as an anticoagulant strategy for the prevention and treatment of thrombosis related diseases, such as deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events.
High Purity
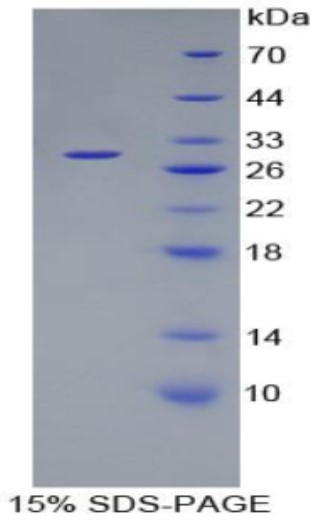
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (F11-1861H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
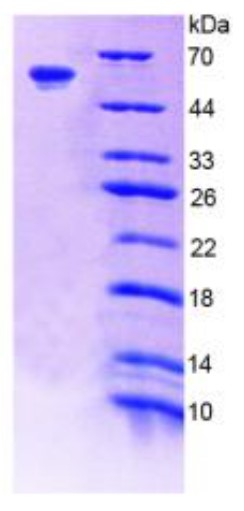
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (F11-1862R) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
Case study 1: Yipeng Geng, 2013
Factor XI (fXI) is a homodimeric zymogen that is converted to a protease with 1 (1/2-fXIa) or 2 (fXIa) active subunits by factor XIIa (fXIIa) or thrombin. It has been proposed that the dimeric structure is required for normal fXI activation. Consistent with this premise, fXI monomers do not reconstitute fXI-deficient mice in a fXIIa-dependent thrombosis model. FXI activation by fXIIa or thrombin is a slow reaction that can be accelerated by polyanions. Phosphate polymers released from platelets (poly-P) can enhance fXI activation by thrombin and promote fXI autoactivation. Poly-P increased initial rates of fXI activation 30- and 3000-fold for fXIIa and thrombin, respectively. FXI monomers were activated more slowly than dimers by fXIIa in the presence of poly-P. However, this defect was not observed when thrombin was the activating protease, nor during fXI autoactivation. The data suggest that fXIIa and thrombin activate fXI by different mechanisms.
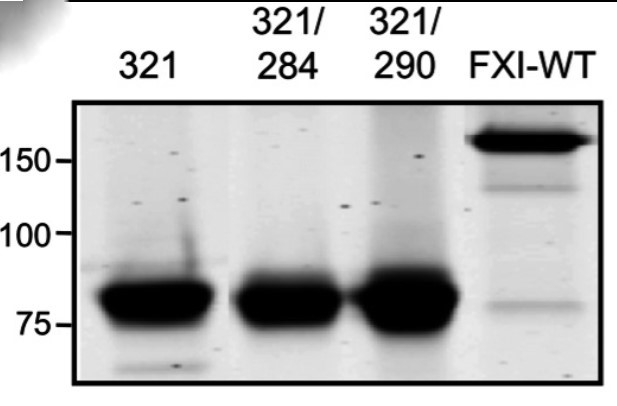
Fig1. Recombinant fXIC321S (321), fXIC321S,L284A (321/284), and fXIC321S,I290A (321/290) appear as 80-kDa monomers on 7.5% nonreducing SDS-PAGE because they lack the Cys321-Cys321 interchain disulfide bond that connects the 2 subunits of the dimer in fXIWT (160-kDa band at right).
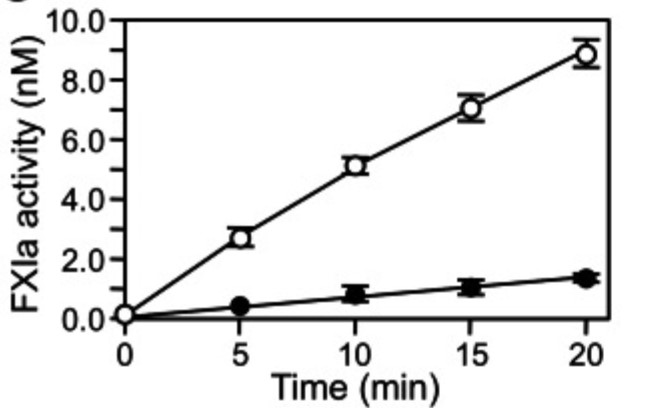
Case study 2: Dmitri V Kravtsov, 2009
During surface-initiated blood coagulation in vitro, activated factor XII (fXIIa) converts factor XI (fXI) to fXIa. Whereas fXI deficiency is associated with a hemorrhagic disorder, factor XII deficiency is not, suggesting that fXI can be activated by other mechanisms in vivo. Thrombin activates fXI, and several studies suggest that fXI promotes coagulation independent of fXII. However, a recent study failed to find evidence for fXII-independent activation of fXI in plasma. Using plasma in which fXII is either inhibited or absent, we show that fXI contributes to plasma thrombin generation when coagulation is initiated with low concentrations of tissue factor, factor Xa, or alpha-thrombin. The results could not be accounted for by fXIa contamination of the plasma systems. Replacing fXI with recombinant fXI that activates factor IX poorly, or fXI that is activated poorly by thrombin, reduced thrombin generation. The results support a model in which fXI is activated by thrombin or another protease generated early in coagulation, with the resulting fXIa contributing to sustained thrombin generation through activation of factor IX.
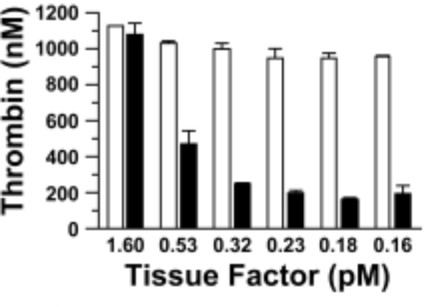
Fig3. Effect of fXI on thrombin generation in fXI-deficient plasma. Coagulation was initiated with TF and Ca2+ in the presence (□) or absence (■) of fXI.
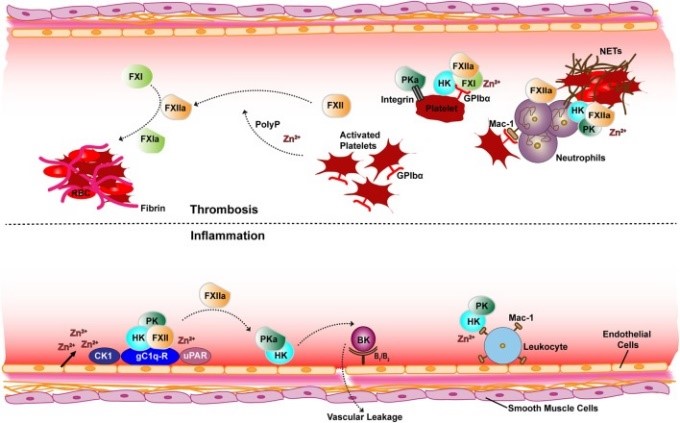
Fig1. Schematic overview of receptor and cofactor interactions of the contact factors for thrombotic (top) and inflammatory (bottom) pathways. (Monika Pathak, 2018)
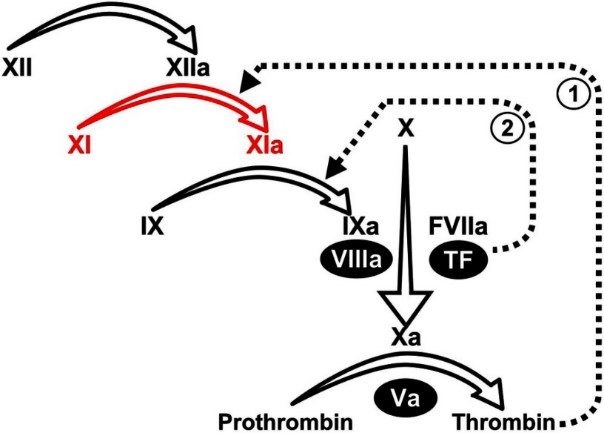
Fig2. Plasma coagulation protease reactions. (Jonas Emsley, 2010)
F11 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways F11 participated on our site, such as Complement and coagulation cascades, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with F11 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Complement and coagulation cascades | F2;PLAUR;PLAT;CR1L;F3;MBL2;SERPINF2;SERPING1;C5 |
F11 has several biochemical functions, for example, heparin binding, protein binding, serine-type endopeptidase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by F11 itself. We selected most functions F11 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with F11. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| heparin binding | SLIT2;NOV;ECM2;LAMC2;PF4V1;HSD17B12;Epy;SLIT3;MDK |
| protein binding | TCF7;SNX31;RPL7A;LGALS14;TXLNA;ZHX1;RXFP1;CSF2;TEX14 |
| serine-type endopeptidase activity | PARL;PRSS52;PRSS48;PLAT;MASP1;KLK1B1;KLK15;RHBDD2;TYSND1 |
F11 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with F11 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of F11.
eco
- Q&As
- Reviews
Q&As (6)
Ask a questionF11 plays an important role in diabetes, and abnormal levels may lead to insulin resistance and lipid metabolism disorders, which can lead to diabetes.
The mutation types of F11 include point mutations, insertions/deletions, duplications, etc., which may cause structural and functional abnormalities of the protein.
Studying the regulatory mechanism of F11 requires the comprehensive use of various experimental methods and techniques, such as gene knockout, transcriptome analysis, protein interaction, etc.
Abnormal F11 levels may indicate some diseases related to lipid metabolism, such as diabetes, obesity, hyperlipidemia, etc.
There are no drugs that directly regulate F11 levels, but they can be affected by lifestyle adjustments such as diet and exercise.
F11 has a complex relationship with other genes or proteins, and can interact with other genes or proteins and participate in a variety of biochemical reactions.
Customer Reviews (3)
Write a reviewThe structure of the recombinant protein was analyzed by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), X-ray crystallography or electron microscopy, and the results showed that the protein was stable.
In the process of purification, the removal of impurities is good.
There are no structural or functional defects.
Ask a Question for All F11 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All F11 Products
Required fields are marked with *


