FEN1
-
Official Full Name
flap structure-specific endonuclease 1
-
Overview
Flap endonuclease-1 (FEN-1) is a structure-specific nuclease with multiple functions in DNA processing pathways. The replication and DNA repair activities of FEN-1 are critical for genomic stability in the eukaryotic cell. Through interaction with prolife -
Synonyms
FEN1; flap structure-specific endonuclease 1; RAD2; flap endonuclease 1; DNase IV; FEN 1; maturation factor 1; MF1; maturation factor-1; FEN-1;
- Recombinant Proteins
- Cell & Tissue Lysates
- Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads
- Chicken
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Rhesus Macaque
- Zebrafish
- E. coli
- E.coli
- HEK293
- HEK293T
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Mamanlian cells
- Mammalian Cell
- Wheat Germ
- C
- His
- Flag
- GST
- His (Fc)
- Avi
- Myc
- Strep
- DDK
- Myc|DDK
- N/A
- N
- No tag
- Background
- Quality Guarantee
- Case Study
- Involved Pathway
- Protein Function
- Interacting Protein
- FEN1 Related Research Area
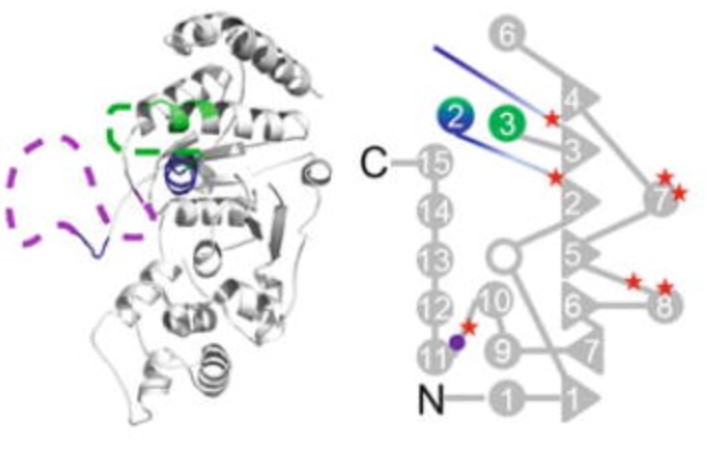
Fig1. Structures of hFEN1 without DNA. (L David Finger, 2012)
What is FEN1 protein?
FEN1 (flap structure-specific endonuclease 1) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 11 at locus 11q12. FEN-1, also known as Flap structure-specific endonuclease 1, removes 5" overhanging flaps in DNA repair and processes the 5" ends of Okazaki fragments in lagging strand DNA synthesis. The protein is a member of the XPG/RAD2 endonuclease family and is one of ten proteins essential for cell-free DNA replication. The FEN1 protein is consisted of 380 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 42.6 kDa.
What is the function of FEN1 protein?
The FEN1 protein is a key DNA repair enzyme that plays an important role in cell division and DNA replication. The main functions of FEN1 include: excision of RNA primers, excision of single-stranded DNA ends, participation in long patch base excision repair, and maintenance of genome stability.
FEN1 Related Signaling Pathway
The signaling pathways involved in FEN1 protein mainly include DNA repair pathway and apoptosis pathway. On the one hand, it is involved in DNA repair pathways such as nucleotide excision repair (NER) and subcutaneous cleavage (SSB), helping to remove damaged bases or DNA forks on the DNA and restore the normal structure of the DNA. On the other hand, FEN1 is involved in the cleavage of nuclear DNA and the repair of DNA fragments during apoptosis.
FEN1 Related Diseases
The abnormal expression or mutation of FEN1 is associated with the occurrence and development of various malignant tumors such as breast cancer, liver cancer and colorectal cancer. It is also associated with neurodegenerative and immune diseases, liver disease, lung disease, and cardiovascular diseases, and FEN1 gene mutations are associated with the occurrence of some genetic diseases such as Xeroderma pigmentosum.
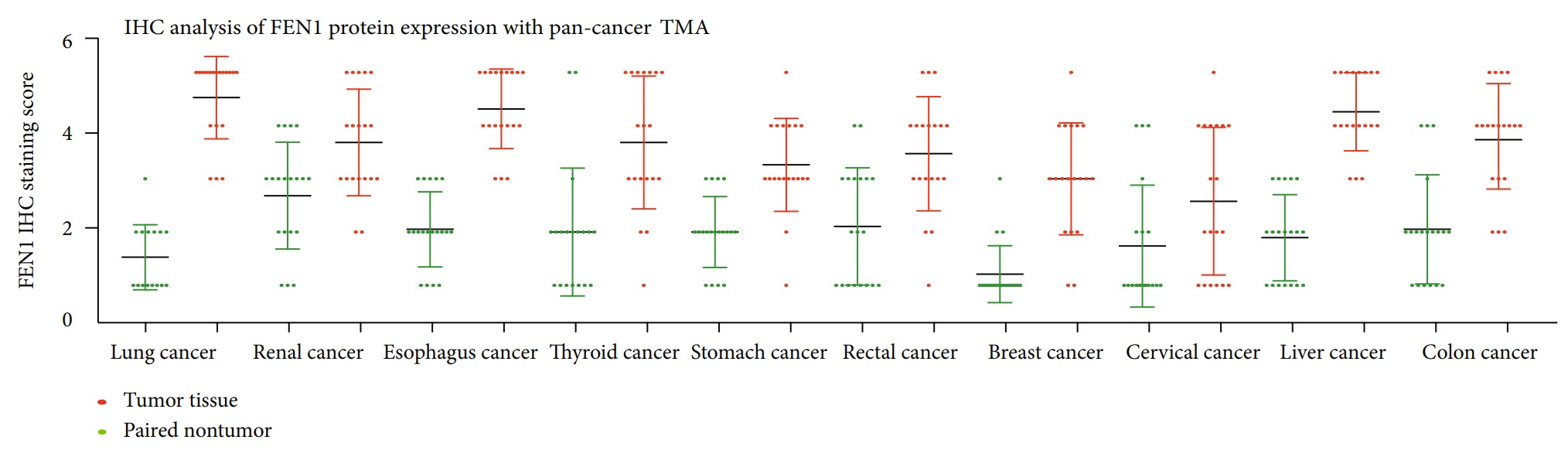
Fig2. FEN1 protein expression in pan-cancer tissues and paired nontumor samples. FEN1 protein was upregulated in tumor tissues. (Yingying Zhang, 2020)
Bioapplications of FEN1
FEN1 exhibits weak exonuclease activity in vitro, but is primarily dependent on its endonuclease activity for its function in the cell. This property can be exploited to develop highly sensitive bioassays for diagnosing diseases or monitoring specific DNA sequences in environmental samples. In addition, it plays an important role in gene editing, DNA repair mechanism research, DNA synthesis and modification.
High Purity
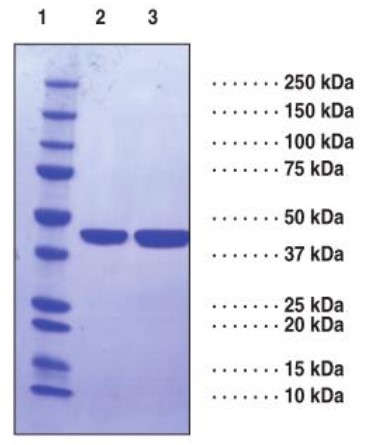
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (FEN1-013H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
High Bioactivity
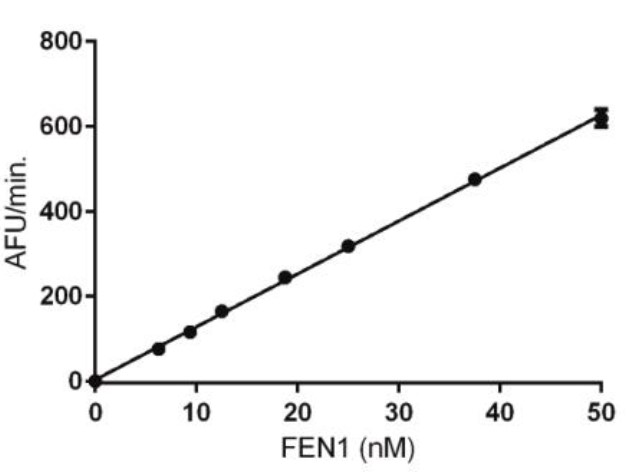
Fig2. Activity Data. (FEN1-013H)
Case study 1: Lu Xu, 2020
Flap endonuclease‑1 (FEN1), a structure‑specific nuclease participating in DNA replication and repair processes, has been confirmed to promote the proliferation and drug resistance of tumor cells. However, the biological functions of FEN1 in cancer cell migration and invasion have not been defined. In the present study, using online database analysis and immunohistochemistry of the specimens, it was found that FEN1 expression was associated with a highly invasive triple‑negative breast cancer (TNBC) subtype in both breast cancer samples from the Oncomine database and from patients recruited into the study. Furthermore, FEN1 was an important biomarker of lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in patients with TNBC. FEN1 promoted migration of TNBC cell lines and FEN1 knockdown reduced the number of spontaneous lung metastasis in vivo. PLK4 was further identified as a critical target of FEN1 mediating TNBC cell migration, by regulating actin cytoskeleton rearrangement.
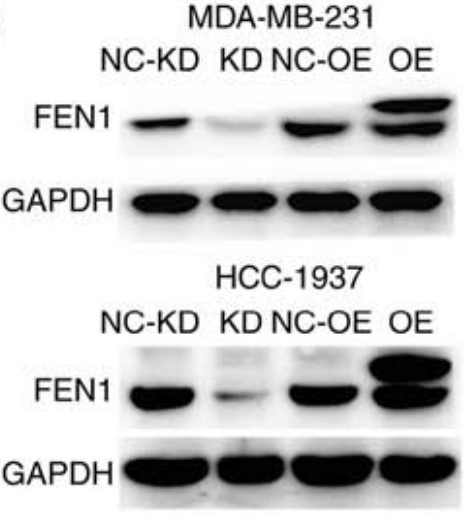
Fig1. The efficiency of FEN1 knockdown and overexpression was confirmed using western blot analysis
Case study 2: Yingying Zhang, 2020
Studies show that patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) have poor prognosis, particularly when patients are diagnosed at late stages of the disease development. The flap endonuclease 1 (FEN1) gene is overexpressed in multiple malignant tumors and may promote tumor aggressiveness. However, its expression profile and functional roles in HCC are still unclear.
The expression of FEN1 in HCC was evaluated using HCC mRNA expression data from TCGA and GEO databases. Kaplan-Meier analysis and univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses were used to determine the correlation between FEN1 expression and survival rate of HCC patients. The molecular mechanism and biological functions of FEN1 in HCC were predicted using functional and pathway enrichment analysis in vitro experiments. The results showed that FEN1 was overexpressed in multiple HCC cohorts at both mRNA and protein levels. Furthermore, knocking down FEN1 resulted in suppressed cell proliferation and migration in vitro. This could have been due to regulation expressions of c-Myc, survivin, and cyclin D1 genes, indicating that FEN1 may function as an oncogene through its role in the cell cycle and DNA replication pathway.
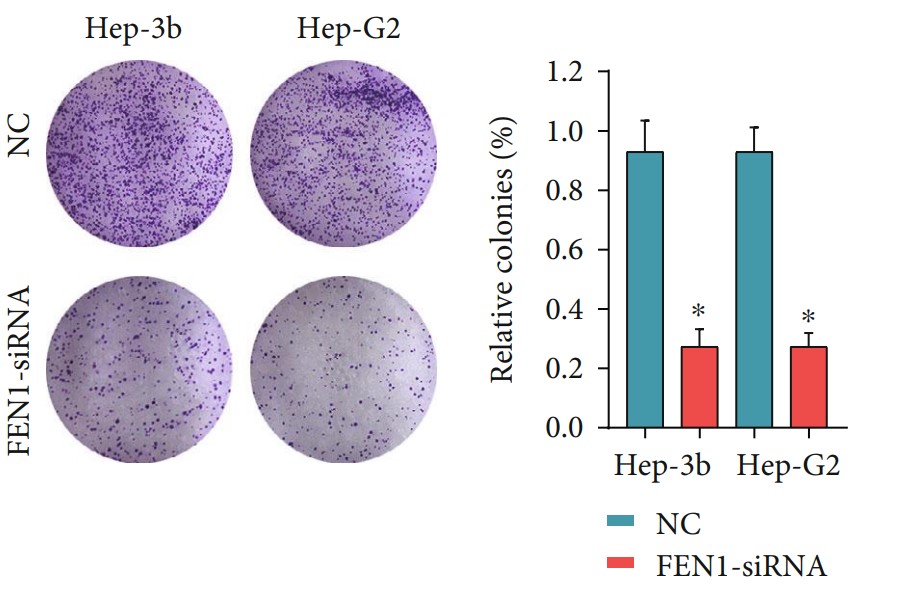
Fig3. Knockdown of FEN1 in Hep-3b and Hep-G2 significantly decreased cell proliferation compared with si-NC cells, performed by the CCK-8 assay
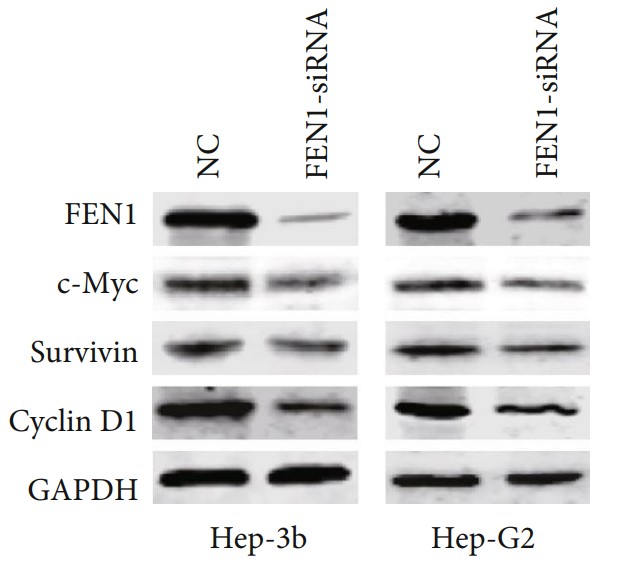
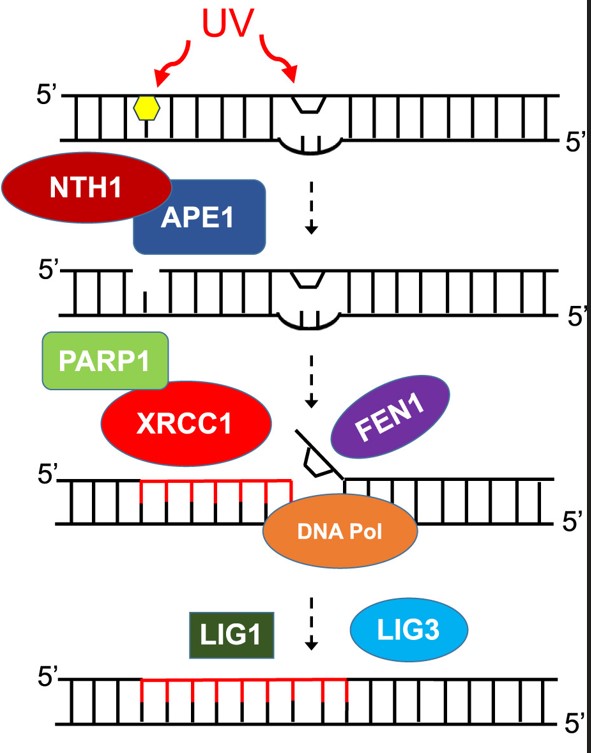
Fig1. Model for BER-mediated photodimer repair. (Amit Gautam, 2023)
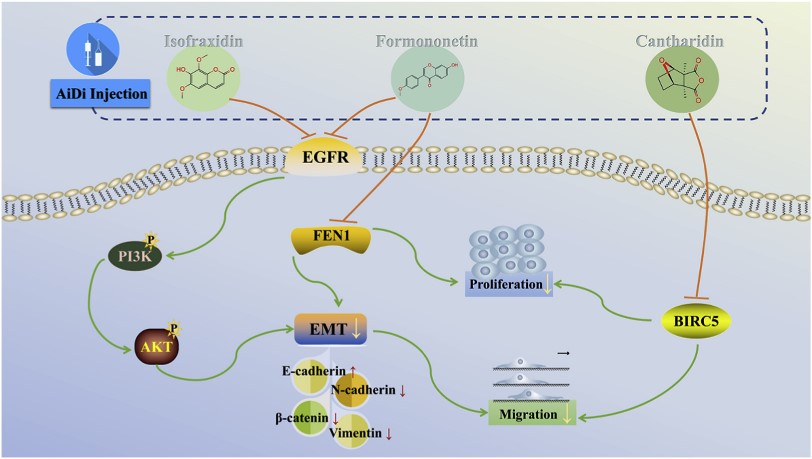
Fig2. Diagram of the potential mechanism of ADI suppressing HCC. (Shan Lu, 2024)
FEN1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways FEN1 participated on our site, such as DNA replication, Base excision repair, Non-homologous end-joining, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with FEN1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| DNA replication | RNASEH2B;POLA2;PRIM2;MCM7;RNASEH2A;RPA1;POLE4;RFC1;RFC4 |
| Base excision repair | TDG.1;XRCC1;POLB;xthA;APEX2;HMGB1;POLE;POLE4;POLL |
| Non-homologous end-joining | XRCC6;FEN1;DCLRE1C;POLM;XRCC4;LIG4;XRCC5;POLL;PRKDC |
FEN1 has several biochemical functions, for example, 5-3 exonuclease activity, 5-flap endonuclease activity, DNA binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by FEN1 itself. We selected most functions FEN1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with FEN1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| 5-3 exonuclease activity | DCLRE1C;XRN2;POLN;DXO;DOM3Z;FAN1;EXO1;FEN1;CPSF3 |
| 5-flap endonuclease activity | DNA2;FAN1;SLX1B;FEN1 |
| DNA binding | ZNF625;NFYA;HOXC4A;HMGB3A;ZNF507;GCM1;GTF2A1;PRKRIR;ZFP322A |
| RNA-DNA hybrid ribonuclease activity | FEN1;RNASEH1;RNASEH2A;APEX1;RNASEH2B;EXO1;RNASEH2C |
| damaged DNA binding | TP53;NEIL1;TDG;RAD1;FEN1;POLB;TRP63;EP300;REV1 |
| double-stranded DNA binding | RAD51AP1;TRP63;TARDBP;CGGBP1;AIM2;SETMAR;TEF;NEIL3;MTERFD3 |
| double-stranded DNA exodeoxyribonuclease activity | |
| endonuclease activity | SMG6;ZC3H12A;PMS2;EAR3;DROSHA;EAR4;RNASEKB;EAR14;RNASEKA |
| exonuclease activity | MEIOB;ISG20L2;CNOT6L;REX1;AEN;FEN1;WRN;REXO1;DOM3Z |
| magnesium ion binding | NT5C3B;TDP2;NT5C1A;ATP10A;NLK;IDH1;ITPK1A;OPA1;ENO4 |
| manganese ion binding | LARGE;SOD2;PEPD;GALNT3;NPEPL1;NUDT7;DCP2;SLC11A2;WRN |
| protein binding | TSC22D3;SMN2;GNAQ;NMB;EIF4EBP2;SIGLEC5;ZNF286A;SERP2;SH3BP4 |
FEN1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with FEN1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of FEN1.
WRN; PCNA; BLM; MUS81
- Q&As
- Reviews
Q&As (6)
Ask a questionMutations in the FEN1 protein can be detected and analyzed by methods such as whole-genome sequencing or target region sequencing to understand the impact of mutations on protein structure and function.
The FEN1 protein can be used as a biomarker in medical therapy to help monitor disease progression and treatment efficacy. In addition, therapeutics targeting the FEN1 protein, such as inhibiting its activity or regulating its expression, are also being investigated.
Abnormal levels of the FEN1 protein may suggest a genetic disorder such as cancer or neurofibroma, but it may also be associated with other diseases.
Studying the regulatory mechanism of FEN1 protein requires a combination of various experimental methods and techniques, such as gene knockout, transcriptome analysis, and protein-protein interactions.
Deficiency or aberrant expression of FEN1 protein may be associated with some cancers and genetic diseases, such as lung cancer, bowel cancer, neurofibromas, etc.
The types of mutations in the FEN1 protein include point mutations, insertions/deletions, duplications, etc., which may cause structural and functional abnormalities of the protein.
Customer Reviews (3)
Write a reviewFEN1 has strong stability.
It shows excellent stability in production.
FEN1 is easy to operate.
Ask a Question for All FEN1 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All FEN1 Products
Required fields are marked with *


