Ide
-
Official Full Name
insulin-degrading enzyme
-
Overview
This gene encodes a zinc metallopeptidase that degrades intracellular insulin, and thereby terminates insulins activity, as well as participating in intercellular peptide signalling by degrading diverse peptides such as glucagon, amylin, bradykinin, and kallidin. The preferential affinity of this enzyme for insulin results in insulin-mediated inhibition of the degradation of other peptides such as beta-amyloid. Deficiencies in this proteins function are associated with Alzheimers disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus but mutations in this gene have not been shown to be causitive for these diseases. This protein localizes primarily to the cytoplasm but in some cell types localizes to the extracellular space, cell membrane, peroxisome, and mitochondrion. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. Additional transcript variants have been described but have not been experimentally verified.[provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009] -
Synonyms
IDE; insulin-degrading enzyme; INSULYSIN; insulinase; insulin protease; Abeta-degrading protease;
- Recombinant Proteins
- Cell & Tissue Lysates
- Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Rhesus Macaque
- Zebrafish
- E. coli
- E.coli
- HEK293
- HEK293T
- Insect Cell
- Mammalian Cell
- Mammalian cells
- S.frugiperda
- Sf21 Insect Cell
- C
- His
- Flag
- His (Fc)
- Avi
- Myc
- DDK
- MYC
- N/A
- N
- Twin
- Strep
- Background
- Quality Guarantee
- Case Study
- Involved Pathway
- Protein Function
- Interacting Protein
- Ide Related Articles
- Ide Related Research Area
What is IDE protein?
IDE (insulin degrading enzyme) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 10 at locus 10q23. This gene encodes a zinc metallopeptidase that degrades intracellular insulin, and thereby terminates insulins activity. The preferential affinity of this enzyme for insulin results in insulin-mediated inhibition of the degradation of other peptides such as beta-amyloid. This protein localizes primarily to the cytoplasm but in some cell types localizes to the extracellular space, cell membrane, peroxisome, and mitochondrion. The IDE protein is consisted of 1019 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 118.0 kDa.
What is the function of IDE protein?
The main function of protein IDE is to degrade insulin and other bioactive peptides, such as beta-amyloid and α-amyloid. By regulating the concentration of these substances, protein IDE plays an important role in maintaining metabolic balance in the body and preventing the occurrence and development of diseases such as diabetes and Alzheimer's disease. In addition, the protein IDE is involved in biological processes such as extracellular matrix remodeling and immune response.
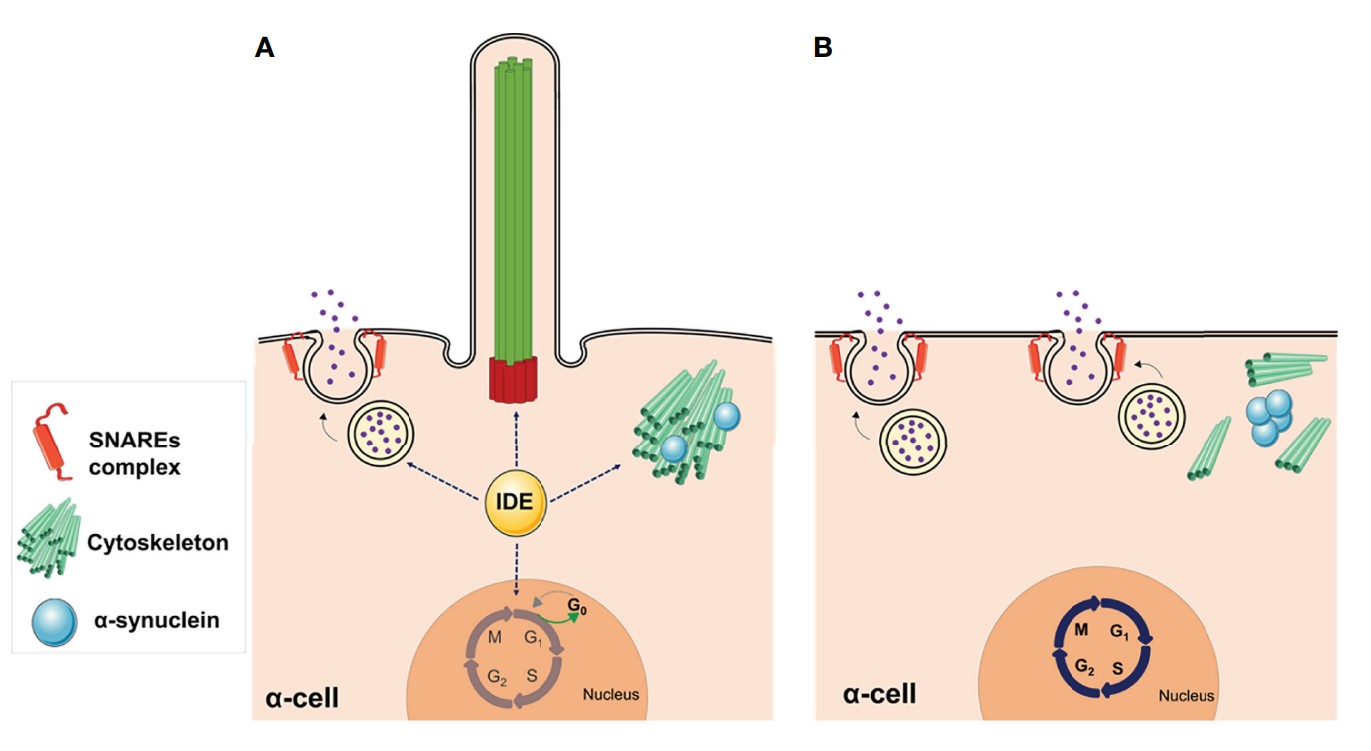
Fig1. Non-proteolytic functions of IDE in α-cells. (A) The abundance of IDE in pancreatic α-cells is relevant for maintaining several cellular functions. (B) Deletion of IDE in mouse α-cells revealed multiple phenotypes. (Marta Pablos, 2022)
IDE Related Signaling Pathway
1. insulin signaling pathway: protein IDE can degrade insulin, thereby regulating insulin levels and effects.
2. amyloid metabolic pathway: Protein IDE can degrade β-amyloid protein, thereby reducing neurotoxicity.
3. autophagy pathway: Protein IDE can participate in the process of autophagy, regulating the degradation and circulation of intracellular substances.
IDE Related Diseases
Abnormal or defective function of IDE may lead to accumulation of insulin and amyloid protein, which is closely related to the occurrence and development of neurodegenerative diseases such as diabetes and Alzheimer's disease (dysfunction of protein IDE may lead to accumulation of β-amyloid protein). In addition, dysfunction of the protein IDE may affect inflammatory responses and autophagy processes, thereby affecting cardiovascular health.
Bioapplications of IDE
The application of protein IDE in medical research and potential therapy is mainly focused on the treatment of diabetes and the study of neurodegenerative diseases, but also involves the regulation of cellular protein homeostasis. These applications demonstrate the importance of protein ides in biology and medicine, as well as their potential for future development.
High Purity
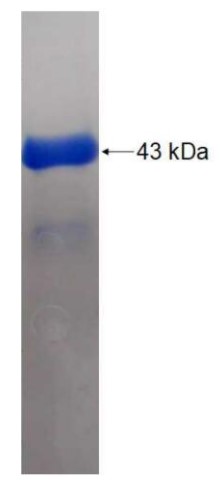
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (IDE-215H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
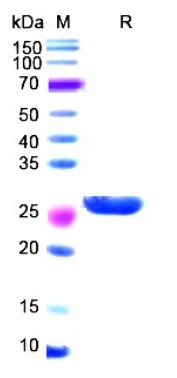
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (IDE-2818H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
Case study 1: Ayse Yilmaz, 2023
Insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE) is a highly conserved metalloprotease that is mainly localized in the cytosol. Although IDE can degrade insulin and some other low molecular weight substrates efficiently, its ubiquitous expression suggests additional functions supported by experimental findings, such as a role in stress responses and cellular protein homeostasis. The translation of a long full-length IDE transcript has been reported to result in targeting to mitochondria, but the role of IDE in this compartment is unknown.
To obtain initial leads on the function of IDE in mitochondria, the researchers used a proximity biotinylation approach to identify proteins interacting with wild-type and protease-dead IDE targeted to the mitochondrial matrix. IDE interacts with multiple mitochondrial ribosomal proteins as well as with proteins involved in the synthesis and assembly of mitochondrial complex I and IV. The mitochondrial interactomes of wild type and mutant IDE are highly similar and do not reveal any likely proteolytic IDE substrates. IDE may adopt similar additional non-proteolytic functions in mitochondria as in the cytosol, acting as a chaperone and contributing to protein homeostasis and stress responses.
Fig1. The expression of TurboID fusion proteins in HEK293 cells.
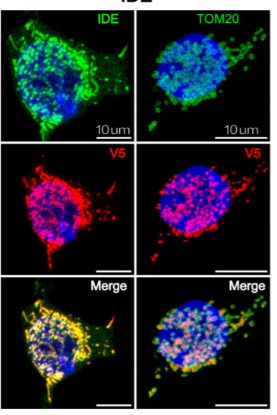
Case study 2: Helen A Rowland, 2023
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is characterised by the aggregation and deposition of amyloid-β (Aβ) peptides in the human brain. In age-related late-onset AD, deficient degradation and clearance, rather than enhanced production, of Aβ contributes to disease pathology. In the present study, the researchers assessed the contribution of the two key Aβ-degrading zinc metalloproteases, insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE) and neprilysin (NEP), to Aβ degradation in human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived cortical neurons.
Using an Aβ fluorescence polarisation assay, inhibition of IDE but not of NEP, blocked the degradation of Aβ by human neurons. When the neurons were grown in a 3D extracellular matrix to visualise Aβ deposition, inhibition of IDE but not NEP, increased the number of Aβ deposits. Inhibition of the Aβ-forming β-secretase prevented the formation of the IDE-inhibited Aβ deposits. These data indicate that inhibition of IDE in live human neurons grown in a 3D matrix increased the deposition of Aβ derived from the proteolytic cleavage of the amyloid precursor protein.
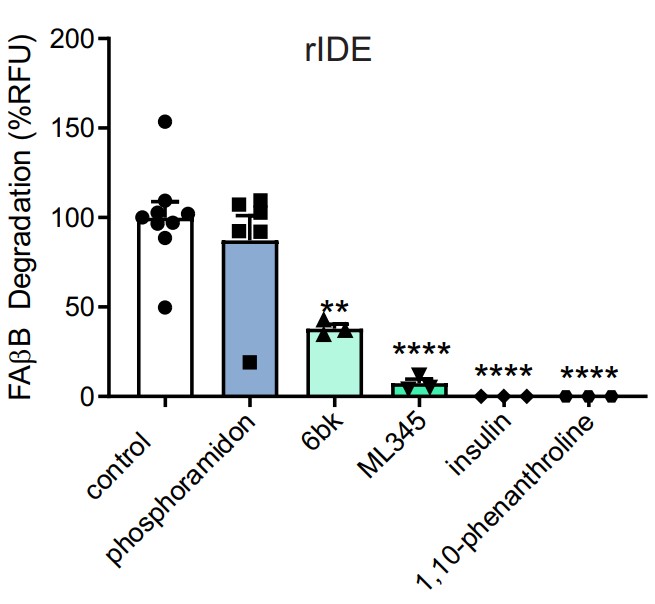
Fig3. Incubation of the Aβ substrate (500 nM) with 25 ng recombinant IDE (rIDE) in the absence or presence of the general metalloprotease inhibitor 1,10-phenanthroline (1 mM), the IDE inhibitors 6bK (10 μM), ML345 (10 μM) and insulin (100 μM).
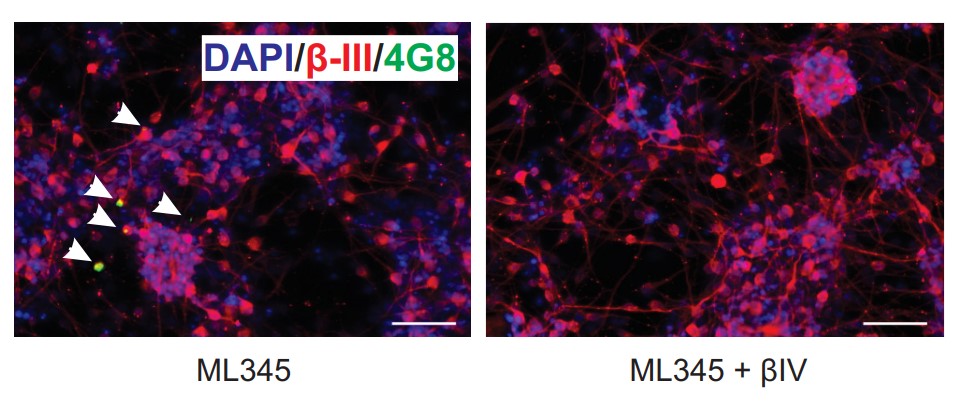
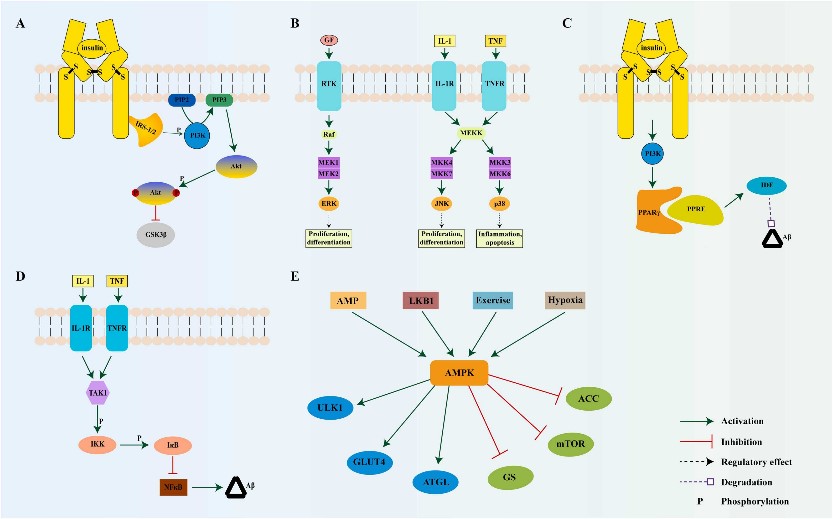
Fig1. Schematic illustration of possible signaling pathways involved in the improvement of AD-related cognitive impairment by IDE. (Yue Tian, 2023)
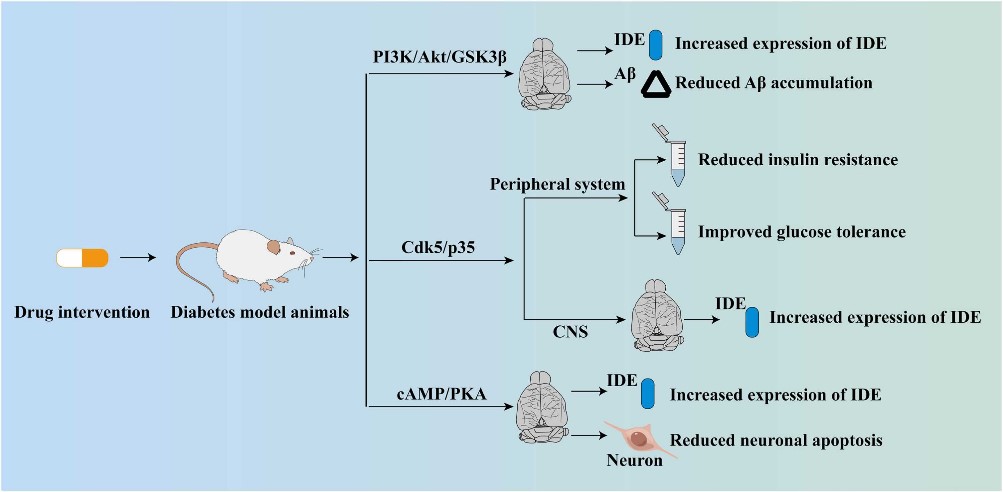
Fig2. Possible signaling pathways involved in IDE-mediated improvement in cognitive impairment in diabetes models. (Yue Tian, 2023)
Ide involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Ide participated on our site, such as Alzheimers disease, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Ide were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Alzheimers disease | CASP12;COX8C;PSENEN;PPP3R2;GRIN1;GNAQ;ATP5G3;Atp5g2;CHP |
Ide has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding, ATPase activity, beta-amyloid binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Ide itself. We selected most functions Ide had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Ide. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | TGFBR1B;MYO1A;UBE2D1A;RFC4;ATRX;SNRKB;NOLC1;DHX36;SNRNP200 |
| ATPase activity | INO80;ATAD1A;ABCC8;PMS1;TOR1A;KIF9;MLH1;WRNIP1;KIF6 |
| beta-amyloid binding | ITM2C;ARMCX5-GPRASP2;LDLRAP1;IDE;APBB1;NGFR;APOEB;Apba1;HSD17B10 |
| beta-endorphin binding | |
| glycoprotein binding | VLDLR;LCK;APOH;VWF;OS9;PIP;FOXRED2;ERLEC1;PTBP3 |
| insulin binding | IGF1R;C2CD2L;INSR;PIK3R1;HSPD1;IDE |
| metalloendopeptidase activity | ADAMTS18;ADAM28;NLN;PITRM1;MMP2;YBEY;ECEL1;PAPPAB;ADAMTS9 |
| peptide binding | ANG;GPR37L1;BDKRB1;ANPEP;TPP1;QRFPR;CCKAR;PLOD1;AVPR2L |
| protein binding | GATA1;PTPN22;FAM117B;MED1;POLDIP2;ZC3H14;NAT8B;CCBL1;EDA2R |
| protein homodimerization activity | CSF1R;FLT3;SLC30A8;LRP4;MTMR2;AMICA1;IRAK3;SLK;RABEP1 |
| receptor binding | GDNF;PLG;IDE;PRDX5;UCN2;ANXA1;HLA-B;CXADR;F2 |
| ubiquitin binding | UBE2N;USP16;RBCK1;FAF2;PARK2;NSFL1C;VPS36;USP25;OTUB1A |
| virus receptor activity | CR1;PVRL4;LDLR;EFNB3;RPSA;GYPA;AXL;MRC1;DPP4 |
| zinc ion binding | TRIM59;RABIF;PYGO1;APOBEC3C;ADAMTS15;ISL1L;PCGF5A;ESR1;MMP30 |
Ide has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Ide here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Ide.
CCL3; SIRT4; CCL4; Cdk1; NES; IFIH1
- Q&As
- Reviews
Q&As (6)
Ask a questionSide effects of IDE treatment include pain at the implant site, displacement or rupture of the electrodes, and irritation discomfort. However, these side effects are usually rare and can be relieved by adjusting stimulation parameters or procedures.
The principle of IDE pain treatment is to inhibit or regulate the transmission of pain signals by sending electrical stimulation signals to the spinal cord or peripheral nerves, thereby reducing pain sensation.
The advantages of IDE treatment include non-drug, non-surgical, reversible, etc. It is effective in relieving pain, improving quality of life, and does not require long-term medication or surgical treatment.
A detailed physical examination and evaluation is required prior to IDE treatment to ensure that the patient is suitable for IDE treatment. At the same time, it is also necessary to prepare relevant surgical instruments and drugs.
IDE treatment process involves implanting electrodes, connecting the stimulator, adjusting the stimulation parameters and procedures, and regular check-ups and adjustments.
After IDE treatment, you need to pay attention to maintaining good lifestyle habits and avoid overwork and strenuous exercise. In addition, regular check-ups and adjustments to stimulation parameters and procedures are required to ensure optimal treatment outcomes.
Customer Reviews (3)
Write a reviewIDE protein has a long shelf life, which facilitates the continuity of subsequent experiments.
IDE has shown good biocompatibility and safety in relevant experiments.
The IDE shows excellent stability and repeatability under certain experimental conditions.
Ask a Question for All Ide Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All Ide Products
Required fields are marked with *


