Nqo1
-
Official Full Name
NAD(P)H dehydrogenase, quinone 1
-
Overview
This gene is a member of the NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (quinone) family and encodes a cytoplasmic 2-electron reductase. This FAD-binding protein forms homodimers and reduces quinones to hydroquinones. This proteins enzymatic activity prevents the one electron reduction of quinones that results in the production of radical species. Mutations in this gene have been associated with tardive dyskinesia (TD), an increased risk of hematotoxicity after exposure to benzene, and susceptibility to various forms of cancer. Altered expression of this protein has been seen in many tumors and is also associated with Alzheimers disease (AD). Alternate transcriptional splice variants, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
NQO1; NAD(P)H dehydrogenase, quinone 1; DTD; QR1; DHQU; DIA4; NMOR1; NMORI; NAD(P)H dehydrogenase [quinone] 1; azoreductase; diaphorase-4; DT-diaphorase; dioxin-inducible 1; menadione reductase; quinone reductase 1; phylloquinone reductase; NAD(P)H:quinone oxireductase; NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1; NAD(P)H:menadione oxidoreductase 1; NAD(P)H:Quinone acceptor oxidoreductase type 1; diaphorase (NADH/NADPH) (cytochrome b-5 reductase);
- Recombinant Proteins
- Cell & Tissue Lysates
- Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads
- Assay Kits
- Chicken
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Rhesus Macaque
- Zebrafish
- E. coli
- E.coli
- HEK293
- HEK293T
- Human
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Mammalian Cell
- Mammalian cells
- Wheat Germ
- Yeast
- Flag
- GST
- His
- His (Fc)
- Avi
- His|SUMO
- His|T7
- SUMO
- Myc
- DDK
- N/A
- Background
- Quality Guarantee
- Case Study
- Involved Pathway
- Protein Function
- Interacting Protein
- Nqo1 Related Articles
- Nqo1 Related Research Area
What is NQO1 protein?
NQO1 (NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 16 at locus 16q22. This gene is a member of the NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (quinone) family and encodes a cytoplasmic 2-electron reductase. This FAD-binding protein forms homodimers and reduces quinones to hydroquinones. This proteins enzymatic activity prevents the one electron reduction of quinones that results in the production of radical species. The NQO1 protein is consisted of 274 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 30.9 kDa.
What is the function of NQO1 protein?
NQO1 is a member of the NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (quinone) family and encodes a cytoplasmic 2-electron reductase. This protein apparently serves as a quinone reductase in connection with conjugation reactions of hydroquinons involved in detoxification pathways as well as in biosynthetic processes such as the vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylation of glutamate residues in prothrombin synthesis. NQO1 functions as an important part of cellular antioxidant defense by detoxifying quinines thus preventing the formation of reactive oxygen species.
NQO1 Related Signaling Pathway
NQO1 protein is mainly involved in the regulation of REDOX balance, anti-oxidative stress response and cell protection mechanism. It influences the activation and inhibition of intracellular signaling pathways by interacting with a variety of substrates. Specifically, NQO1 regulates the activity of transcription factors such as NF-κB and Nrf2, thereby affecting biological processes such as inflammatory response, antioxidant stress response, and apoptosis. In addition, NQO1 is also involved in the regulation of p53, β-catenin and other signaling pathways, and further affects the physiological processes of cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis.
NQO1 Related Diseases
The NQO1 protein has been implicated in a variety of diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, neurodegenerative diseases, and diabetes. In cancer, the abnormal expression of NQO1 may lead to the occurrence and development of tumors, and its polymorphism is also related to tumor susceptibility. In cardiovascular diseases, the anti-oxidative stress effect of NQO1 may be related to the occurrence and development of atherosclerosis. In neurodegenerative diseases, the antioxidant effect of NQO1 may be related to the occurrence and progression of the disease. In addition, NQO1 is also associated with the onset and development of diabetes, and its genetic polymorphism may increase the risk of developing diabetes.
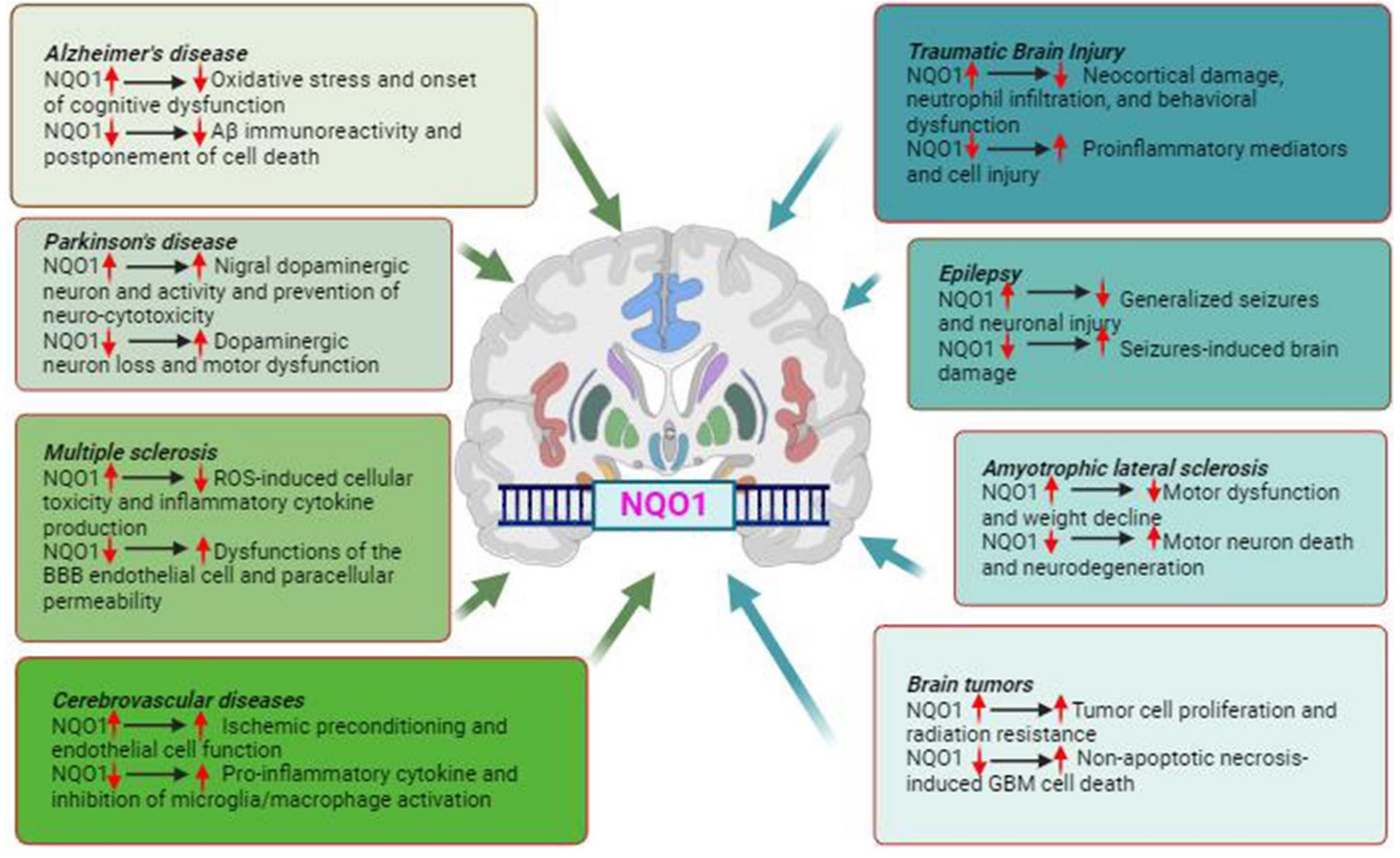
Fig1. An overview of the potential effects of NQO1 alterations on the pathophysiology of various neurological disorders. (Li Yuhan, 2024)
Bioapplications of NQO1
Because NQO1 is highly expressed in a variety of tumors and is closely related to the occurrence and development of tumors, it has become an important target for anti-tumor drug research and development. Several small molecule inhibitors targeting NQO1 have been developed and are in clinical trials. In addition, genetic polymorphisms of NQO1 have been linked to susceptibility to a variety of diseases and are therefore also used for genetic risk assessment and individualized treatment of diseases.
High Purity

Fig1. SDS-PAGE (NQO1-6062H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
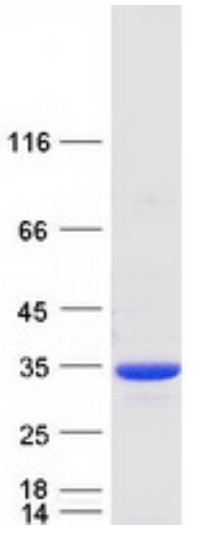
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (NQO1-4163H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
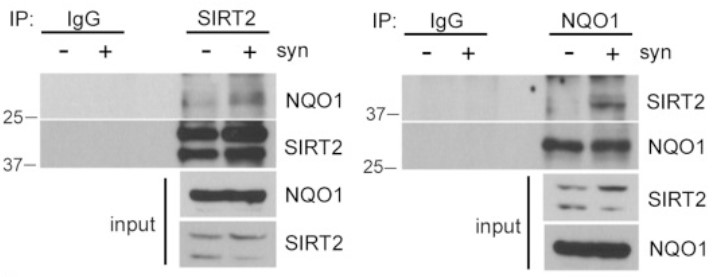
Case study 1: Hong-Jun Kang, 2018
Previous studies have shown that SIRT2 plays a role in mitosis through deacetylating specific downstream targets. However, the upstream regulation of SIRT2 activity has been relatively unexplored. In this study, the researchers provide evidence that NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) interacts with and activates SIRT2 in an NAD-dependent manner. Strong protein-protein interaction and co-localization of the two proteins during mitosis is required to maintain an active NQO1-SIRT2 axis which is critical for successful completion of mitosis. In this regard, both pharmacologic and genetic NQO1 inhibition increases sensitivity to anti-mitotic drugs functioning as microtubule poisons by inducing mitotic arrest and allowing cells to accumulate cell death signals. Therefore, the significant prognostic value of NQO1 in predicting outcome of cancer patients might be explained in part due to the functional contribution of NQO1-SIRT2 axis to mitotic stress.
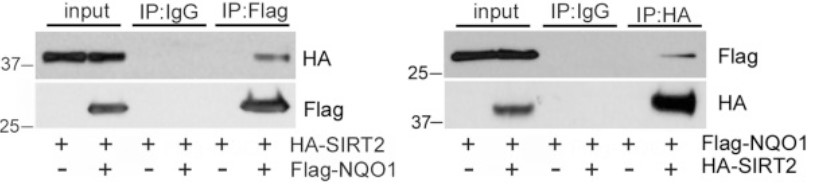
Fig1. MCF-7 cells were transiently transfected with Flag-NQO1 and HA-SIRT2.
Case study 2: Duojun Qiu, 2023
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is one of the main complications of diabetes, and inflammation and fibrosis play an important role in its progression. NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) protects cells from oxidative stress and damage caused by toxic quinones. In the present study, the researchers aimed to investigate the protective effects of NQO1 against diabetes-induced renal inflammation and fibrosis and the underlying mechanisms.
In vitro, human renal tubular epithelial (HK-2) cells transfected with NQO1 pcDNA3.1(+) were cultured under high-glucose (HG) conditions. Gene and protein expression was assessed by quantitative real-time PCR, Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemical staining. Overexpression of NQO1 suppressed proinflammatory cytokine (IL-6, TNF-α, MCP-1) secretion, extracellular matrix (ECM) (collagen IV, fibronectin) accumulation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) (α-SMA, E-cadherin) in the db/db mouse kidneys and HG-cultured HK-2 cells. Furthermore, NQO1 overexpression ameliorated HG-induced TLR4/NF-κB and TGF-β/Smad pathways activation. This study suggest that NQO1 alleviates diabetes-induced renal inflammation and fibrosis by regulating the TLR4/NF-κB and TGF-β/Smad signaling pathways.
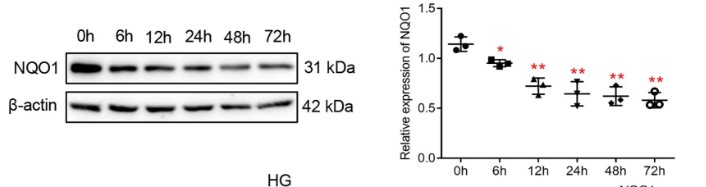
Fig3. NQO1 overexpression blocked HG-induced fibronectin and collagen IV expression in HK-2 cells.
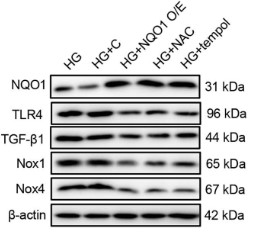
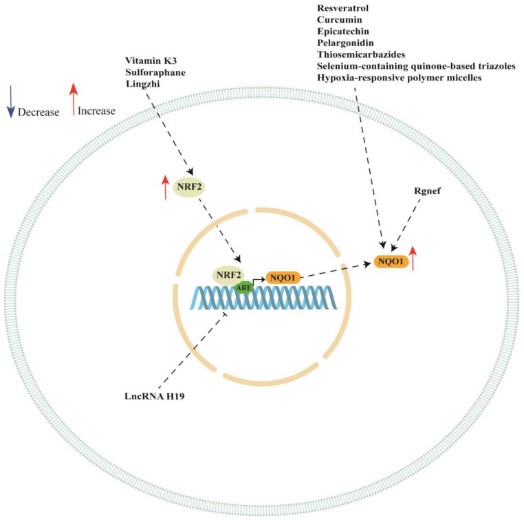
Fig1. Schematic representation of NQO1 regulation in ovarian cancer cells. (Giovanni Tossetta, 2023)
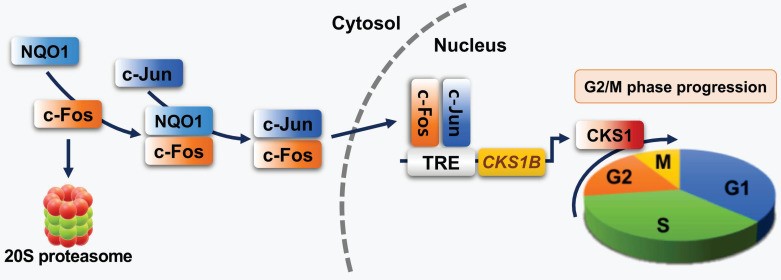
Fig2. Schematic model showing how NQO1 regulates cell cycle progression at the G2/M phase in cancer cells. (Eun-Taex Oh, 2023)
Nqo1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Nqo1 participated on our site, such as AhR pathway, Dopamine metabolism, Estrogen metabolism, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Nqo1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| AhR pathway | AHRR;JUN;PTGES3;EGFR;CDC37;FLG;AIP;CDKN1A;JUND |
| Dopamine metabolism | NQO1;DDC;COMT |
| Estrogen metabolism | CYP1B1;CYP1A1;NQO1;COMT;ARSE;ARSD |
| Keap1-Nrf2 Pathway | NQO1;AIMP2 |
| Metabolism | TIMMDC1;SLC25A1;YY2;CYP4T8;CYP4F22;SLC25A15;SLC4A1A;PDK4;INSIG2 |
| Metabolism of amino acids and derivatives | IDO2;SLC25A10;ALDH9A1A.2;ACMSD;CRYM;OAZ2;OAZ3;AZIN1A;IVD |
| Metabolism of polyamines | CKM;AMD2;CKMT2;AZIN1A;CKMB;AZIN1;SLC25A15A;OAZ3;OAZ1A |
| Oxidative Stress | NOX4;TXN2;NFIX;JUNBA;TXNRD2;NQO1 |
Nqo1 has several biochemical functions, for example, NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (quinone) activity, cytochrome-b5 reductase activity, acting on NAD(P)H, identical protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Nqo1 itself. We selected most functions Nqo1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Nqo1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (quinone) activity | NQO1;CBR4 |
| cytochrome-b5 reductase activity, acting on NAD(P)H | CYB5R3;CYB5R1;CYB5R4;CYB5R2;NQO1;POR;CYB5RL |
| identical protein binding | ZDHHC17;CCT7;THG1L;L3MBTL1;Serpina1b;PYCARD;NQO1;REG3B;USP4 |
| poly(A) RNA binding | WDR43;USP10;RPL14;FBL;FUS;HIST1H4C;XRCC6;NSUN2;RPL27A |
| protein binding | ALOX12B;DLL1;FAM107A;PVRL1;DYNLL1;CWC15;LOX;RNF144B;TALDO1 |
| superoxide dismutase activity | NQO1;SOD1;SOD3A;CCS;SOD2;PRNPA |
Nqo1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Nqo1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Nqo1.
ING1; Tp63; Tp63; NDUFS7; VCAM1
- Q&As
- Reviews
Q&As (6)
Ask a questionMutations in NQO1 can be detected and analyzed by methods such as whole-genome sequencing or target region sequencing to understand the impact of mutations on protein structure and function.
The types of mutations in NQO1 include point mutations, insertions/deletions, duplications, etc., which can cause structural and functional abnormalities of the protein.
Abnormal NQO1 levels may indicate cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and oxidative stress-related diseases.
Studying the regulatory mechanism of NQO1 requires a combination of various experimental methods and techniques, such as gene knockout, transcriptome analysis, and protein-protein interactions.
This protein can be used as a biomarker in medical treatment to help monitor disease progression and treatment efficacy. In addition, therapeutics targeting NQO1, such as gene therapy or modulating its expression, are also being studied.
NQO1 has a complex relationship with other genes or proteins, and can interact with other genes or proteins and participate in a variety of biochemical reactions.
Ask a Question for All Nqo1 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All Nqo1 Products
Required fields are marked with *




