PLG
-
Official Full Name
plasminogen
-
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a secreted blood zymogen that is activated by proteolysis and converted to plasmin and angiostatin. Plasmin dissolves fibrin in blood clots and is an important protease in many other cellular processes while angiostatin inhibits angiogenesis. Defects in this gene are likely a cause of thrombophilia and ligneous conjunctivitis. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. -
Synonyms
PLG; plasminogen; EC 3.4.21.7; DKFZp779M0222; plasmin; EC 3.4.21;
- Recombinant Proteins
- Native Proteins
- Cell & Tissue Lysates
- Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads
- Transfected Stable Cell Lines
- Bovine
- Chicken
- Dog
- Human
- Mouse
- Pig
- Rabbit
- Rat
- Rhesus Macaque
- Zebrafish
- Chicken Plasma
- Dog Plasma
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Human
- human plasma
- Human plasma
- Human Plasma
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Insect Cell
- Mammalian Cell
- Mammalian cells
- Mouse Plasma
- P.pastoris
- Plasma
- Rabbit Plasma
- Rat plasma
- Wheat Germ
- Yeast
- C
- His
- Fc
- GST
- His (Fc)
- Avi
- Myc
- His|GST
- N/A
- N
- Background
- Quality Guarantee
- Case Study
- Involved Pathway
- Protein Function
- Interacting Protein
- PLG Related Articles
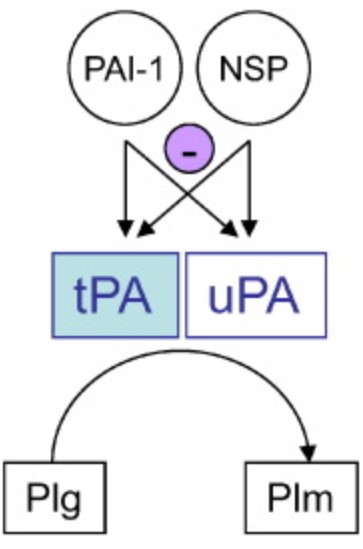
Fig1. The plasminogen activator system. Tissue-type- and Urokinase- plasminogen activators (tPA and uPA) activate the inactive zymogen plasminogen (Plg) into active plasmin (Plm). (Anupriya Mehra, 2016)
What is PLG protein?
PLG (plasminogen) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 6 at locus 6q26. The protein encoded by this gene is a secreted blood zymogen that is activated by proteolysis and converted to plasmin (PLM) and angiostatin. PLM dissolves fibrin in blood clots and is an important protease in many other cellular processes while angiostatin inhibits angiogenesis. PLG is also named plasminogen kringles 1-4 and PK1-4. The PLG protein is consisted of 810 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 90.6 kDa.
What is the function of PLG protein?
PLG interacts with PLG receptors which results in the retention of plasmin on cell surfaces and in plasmin-induced cell signaling. The localization of PLG on cell surfaces plays a role in the degradation of extracellular matrices, cell migration, inflamation, wound healing, oncogenesis, metastasis, myogenesis, muscle regeneration, neurite outgrowth, and fibrinolysis. This protein may also play a role in acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) which, in part, is caused by enhanced clot formation and the suppression of fibrinolysis.
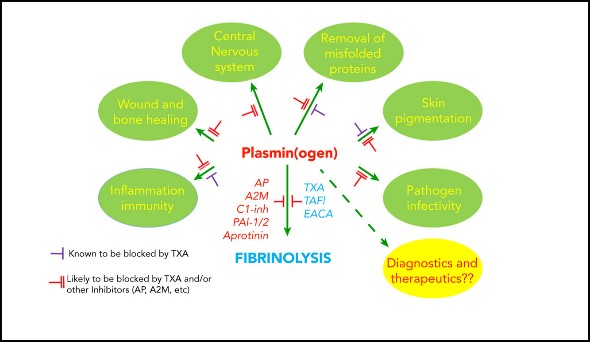
Fig2. The broadening role of the plasminogen-activating system in physiology and pathophysiology. (Charithani B Keragala, 2021)
PLG Related Signaling Pathway
Plasminogen activation system: In the plasminogen activation system, PLG participates in the process of fibrinolysis by binding to its receptor, such as tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA), and being activated by tPA as plasmin.
Plasminogen receptor signaling pathway: PLG can bind to plasminogen receptors (such as annexin A2) on the cell surface and participate in cell migration, proliferation and transformation by activating the signaling pathway on the receptor.
Fibrinogen interaction signaling pathway: In the process of platelet activation and thrombosis, the interaction between plasminogen and fibrinogen can regulate platelet aggregation and thrombosis formation through the participation of PLG.
PLG Related Diseases
Defects in this gene are likely a cause of thrombophilia and ligneous conjunctivitis. Diseases associated with PLG include plasminogen deficiency and angioedema. PLG plays an important role in fibrinolytic systems. Its abnormal function can lead to abnormal degradation of blood vessel walls and clotting factors, resulting in bleeding or hemostasis disorders. Or participate in the invasion and metastasis of tumor cells.
Bioapplications of PLG
Treatment of thrombotic diseases: PLG can be used to treat thrombotic diseases such as deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. By injecting PLG, it can promote the dissolution of thrombus and restore blood circulation. Anticoagulant therapy: PLG can be used as an anticoagulant therapy to prevent blood clotting. For example, PLG can be used for prophylactic anticoagulant therapy in heart surgery, vascular surgery and other surgeries that need to prevent thrombosis.
High Purity
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PLG-9029H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (Plg-573R) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
Case Study 1: Claire S Whyte, 2015
The interaction of plasminogen with platelets and their localization during thrombus formation and fibrinolysis under flow are not defined. Using a novel model of whole blood thrombi (Thrombi were perfused with 0.8 μM glu-plasminogen labeled with DyLight 633 (DL633)), formed under flow, the dose-dependent fibrinolysis using fluorescence microscopy was examined. The article indicates that different subpopulations of platelets harbor plasminogen by diverse mechanisms and provide an essential scaffold for the accumulation of fibrinolytic proteins that mediate fibrinolysis under flow.
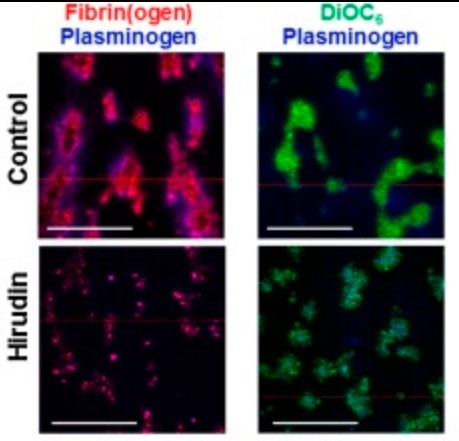
Fig1. Plasminogen localization within thrombi.
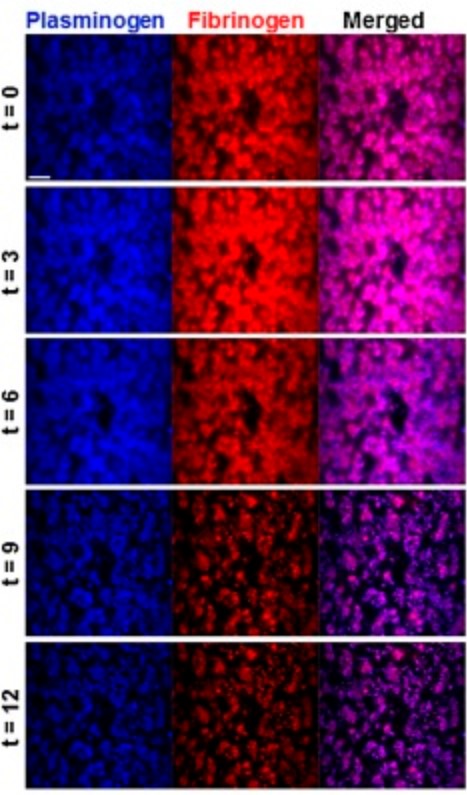
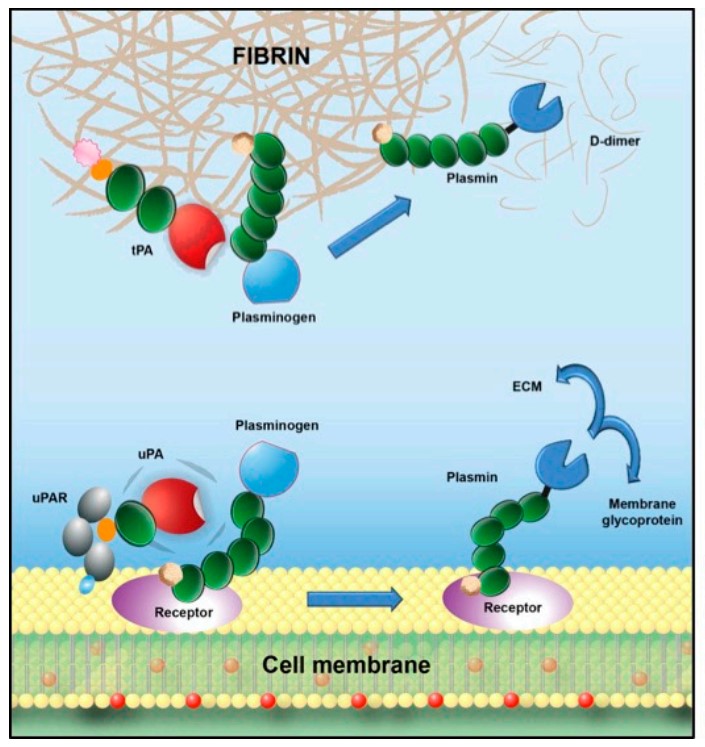
Fig2. Canonical mechanism for plasminogen activation; assemblage of both plasminogen and its activator on the same surface is required for plasmin generation. (Laurent Plawinski, 2023)
PLG involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PLG participated on our site, such as Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction, Complement and coagulation cascades, Staphylococcus aureus infection, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PLG were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | GRIN2A;PTGER3;CNR2;GABBR2;MC3R;GRIA2;GRIA3A;NPY6R;TAAR14B |
| Complement and coagulation cascades | VWF;FGA;FGB;KLKB1;CFB;C8G;C8A;F8;TFPI |
| Staphylococcus aureus infection | HLA-DQA2;FCGR4;MBL1;FPR2;FCGR3A;C3AR1;HLA-DPB1;C1RA;DSG1 |
| Influenza A | OAS1A;PRSS3;MAPK11;TYK2;CPSF4;HLA-DQA1;BMA1;H2-AB1;STAT2 |
PLG has several biochemical functions, for example, apolipoprotein binding, protein binding, protein domain specific binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PLG itself. We selected most functions PLG had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PLG. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| apolipoprotein binding | VLDLR;LRP1;LPA;LPL;LRP4;LRP6;ABCA1;SCARB1;LIPC |
| protein binding | SHFM1;AIMP1;NR2C1;CINP;NAE1;SMURF2;ARL13B;CLCN1;C9orf100 |
| protein domain specific binding | ARFIP2B;TNNI3;RCC2;HIST1H4B;ARHGEF4;STAMBP;XPO1;YWHAE;TFDP2 |
| receptor binding | Icosl;H2-Q10;AMH;CCL17;AKAP9;LEPROT;CAT;FASLG;ECI2 |
| serine-type endopeptidase activity | KLK7;PCSK6;PREPL;AZU1;KLK6;F9B;KLK4;TMPRSS11B;TMPRSS11G |
| serine-type peptidase activity | GM5077;KLK7;GZME;TMPRSS11B;MCPT2;CMA1;SEC11A;MCPT1;PRSS16 |
PLG has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PLG here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PLG.
q6v4l1_strpy; q6v4l4_strpy; q6v4l5_strpy; q6v4l9_strpy; sak; ATP2; ATP1; ATP15
- Q&As
- Reviews
Q&As (7)
Ask a questionPLG has been investigated as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for various diseases. For instance, altered PLG levels have been observed in cancer patients, serving as a potential marker for tumor progression and prognosis. Additionally, PLG has been implicated in cardiovascular diseases, where its levels can reflect the severity of certain conditions, such as thrombosis. Moreover, PLG may have utility as a biomarker in inflammatory disorders and neurological diseases. Further research is needed to validate the clinical utility of PLG as a biomarker and develop specific assays for its detection.
Dysregulation of PLG has been associated with several pathological conditions. Decreased PLG levels or impaired activation can lead to impaired fibrinolysis, resulting in the formation of excessive blood clots. On the other hand, increased PLG activation or excessive Plasmin activity can promote tissue degradation, contributing to diseases such as chronic inflammation, cancer metastasis, and tissue damage. Moreover, PLG has been implicated in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disorders and cardiovascular diseases. Understanding the mechanisms underlying PLG dysregulation is crucial for designing therapeutic strategies to counteract its pathological implications.
PLG-targeted therapeutic strategies have shown promise in various diseases. For example, agents that enhance PLG activation, such as tPA and uPA, have been employed to promote fibrinolysis and dissolve blood clots in conditions such as heart attacks and ischemic strokes. Conversely, inhibitors of PLG activation, such as PAIs, can be used to prevent excessive fibrinolysis and subsequent bleeding complications. Additionally, targeting PLG receptors or manipulating PLG interactions with other molecules may offer potential therapeutic avenues. However, further research is required to optimize these strategies and assess their efficacy and safety in clinical settings.
The PLG protein, also known as Plasminogen, is a single-chain glycoprotein composed of 790 amino acids. It consists of several domains, including a signal peptide, five kringle domains (K1-K5), and a serine protease domain. The signal peptide mediates protein secretion, while the kringle domains have numerous functions, such as binding to receptors and ligands. The serine protease domain is responsible for the conversion of Plasminogen to active Plasmin, a crucial enzyme in fibrinolysis and extracellular matrix remodeling processes.
PLG plays a vital role in several physiological processes. Its primary function is as a precursor to Plasmin, which is involved in the degradation of blood clots (fibrinolysis). Plasmin also participates in tissue remodeling, wound healing, and cell migration. Additionally, PLG has been implicated in immune responses, angiogenesis, and cell adhesion. Its ability to interact with various receptors and bind to components of the extracellular matrix highlights its diverse and important functions in maintaining normal physiological homeostasis.
PLG, also known as plasminogen, plays a crucial role in the fibrinolytic system. Its main biological function is to be converted into plasmin, an enzyme that breaks down fibrin clots. Plasminogen is activated by tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), which cleaves it into active plasmin. Plasmin then degrades fibrin clots, preventing the formation of thrombi and promoting the dissolution of existing blood clots. Additionally, PLG is involved in various physiological processes, such as wound healing, tissue remodeling, cell migration, and inflammation.
The activation of PLG is tightly regulated to prevent undesired fibrinolysis. Activation can occur through two main pathways: the tissue-type Plasminogen Activator (tPA)-dependent pathway and the urokinase-type Plasminogen Activator (uPA)-dependent pathway. In the tPA-dependent pathway, tPA binds to a specific receptor on the cell surface and catalyzes the conversion of PLG to Plasmin. The uPA-dependent pathway involves uPA binding to a receptor, followed by the activation of PLG. Additionally, various regulatory proteins, such as Plasminogen Activator Inhibitors (PAIs), control PLG activation by inhibiting the activity of tPA and uPA.
Customer Reviews (3)
Write a reviewThe tightly sealed packaging of this protein reagent ensures optimal preservation of its activity.
I highly recommend this reagent for its simplified experimental workflow, saving time and experimental costs.
Catering to diverse experimental needs, its outstanding performance facilitates diversity in scientific research.
Ask a Question for All PLG Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All PLG Products
Required fields are marked with *


