PTPN13
-
Official Full Name
protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 13 (APO-1/CD95 (Fas)-associated phosphatase)
-
Overview
A novel protein tyrosine phosphatase, FAP-1 (for FAS-associated phosphatase) (originally designated PTP-BAS), has been shown to associated with the carboxy terminus fifteen amino acids of FAS. Three isoforms of the protein result from alternative RNA splicings, the longest of which encodes a protein 2485 amino aicds in lenghth. Although lacking a transmembrane region, FAP-1 does contain a membrane-binding domain, similar to that found in cytoskeleton-associated proteins such as ezrin. FAP-1 does not seem to associate with CD40 or death domain proteins such as TNF-RI and TNF-RII. -
Synonyms
PTPN13; protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 13 (APO-1/CD95 (Fas)-associated phosphatase); tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 13; PTP BAS; PTP BL; PTP1E; PTPL1; hPTPE1; protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1E; protein-tyrosine phosphatase PTPL1; fas-associated protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1; PNP1; FAP-1; PTPLE; PTP-BL; hPTP1E; PTP-BAS; DKFZp686J1497;
- Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Zebrafish
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cell
- GST
- His
- His|T7
- N/A
| Species | Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human | PTPN13-463H | Recombinant Human PTPN13,GST-tagged,Active | E.coli | GST |
|
|
| Human | PTPN13-8097H | Recombinant Human PTPN13 protein, His & T7-tagged | E.coli | His/T7 | Met1~Asn161 (Accession # Q12923) |
|
| Human | PTPN13-3728H | Recombinant Human PTPN13 protein, His-tagged | E.coli | His | 1-350 aa | |
| Mouse | Ptpn13-337M | Active Recombinant Mouse Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase, Non-receptor Type 13 | E.coli | N/A |
|
|
| Mouse | Ptpn13-8098M | Recombinant Mouse Ptpn13 protein, His & T7-tagged | E.coli | His/T7 | Met1~Asn161 (Accession # G5E8B1) |
|
| Rat | Ptpn13-8099R | Recombinant Rat Ptpn13 protein, His & T7-tagged | E.coli | His/T7 | Met1~Asn161 (Accession # G3V9S3) |
|
| Zebrafish | PTPN13-5628Z | Recombinant Zebrafish PTPN13 | Mammalian Cell | His |
|
- Background
- Quality Guarantee
- Case Study
- Involved Pathway
- Protein Function
- Interacting Protein
- PTPN13 Related Research Area
- PTPN13 Related Signal Pathway
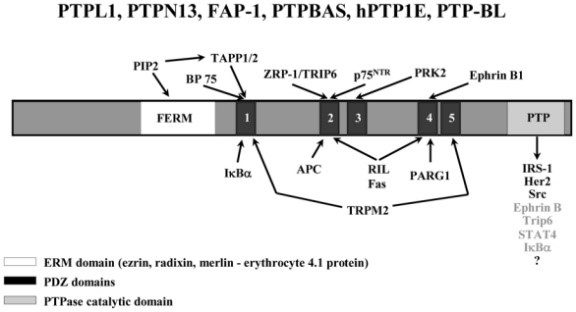
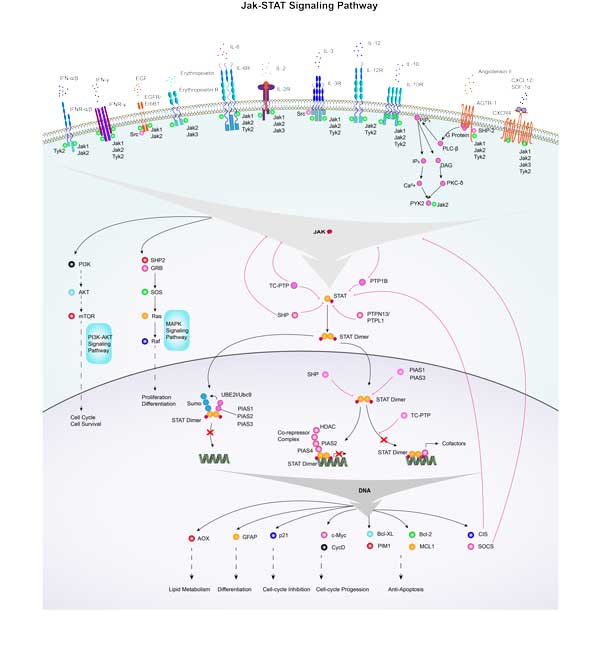
Fig1. Scheme of PTPL1domains and interacting partners. Arrow from the catalytic domain points direct substrates (black) and putative substrates (grey). (Gilles Freiss, 2011)
What is PTPN13 protein?
PTPN13 (protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 13) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 4 at locus 4q21. PTPs are known to be signaling molecules that regulate a variety of cellular processes including cell growth, differentiation, mitotic cycle, and oncogenic transformation. PTPN13 also known as PTPL1, is a large protein that possesses a PTP domain at C-terminus, and multiple noncatalytic domains, which include a domain with similarity to band 4.1 superfamily of cytoskeletal-associated proteins, a region consisting of five PDZ domains, and a leucine zipper motif. The PTPN13 protein is consisted of 2485 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 276.9 kDa.
What is the function of PTPN13 protein?
PTPN13 is a protein tyrosine phosphatase that regulates intracellular signaling by dephosphorylation of specific signaling molecules. PTPN13 plays a role in multiple biological processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, and apoptosis. It is particularly important in the immune response, regulating the activation of T and B cells as well as the inflammatory response. In addition, PTPN13 is involved in bone development and metabolism, as well as signaling pathways associated with tumorigenesis and development.
PTPN13 Related Signaling Pathway
PTPN13 is involved in several signaling pathways, including EGFR, NF-κB, Wnt/β-catenin, etc. In these signaling pathways, PTPN13 regulates the activity of several key regulatory factors through dephosphorylation, thereby affecting biological processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation, survival, and migration.
PTPN13 Related Diseases
In terms of immune diseases, abnormal activity of PTPN13 is associated with the occurrence of autoimmune diseases, for example, defects or dysfunction of PTPN13 may lead to inadequate or excessive immune response, which can trigger diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. In the skeletal system, PTPN13 is involved in regulating the function of bone cells and bone metabolism, and its dysfunction may be associated with the development of diseases such as osteoporosis. In addition, the role of PTPN13 in tumorigenesis and development has also attracted the attention of researchers, including a variety of malignant tumors such as breast cancer, colorectal cancer, stomach cancer and lung cancer.
Bioapplications of PTPN13
Due to its important role in the immune and skeletal systems, PTPN13 is seen as a potential therapeutic target for diseases such as autoimmune disorders and osteoporosis. Small molecule inhibitors or activators targeting PTPN13 are being investigated to evaluate their potential value for disease treatment.
High Purity
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PTPN13-8097H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (Ptpn13-8099R) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
Case study 1: Jing Wang, 2022
To reveal the function of protein tyrosine phosphatase-L1 (PTPL1) in lung adenocarcinoma. Lung cancer cell lines were transfected with short hairpin RNA against PTPL1 (shPTPL1 group) or negative control (shmock group). Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and western blotting were used to verify the transfection efficacy. Cell proliferation was analyzed and colony formation assay after PTPL1 or PTPL1 and yes-associated protein (YAP1) knockdown.
PTPL1 was downregulated in various types of lung cancer cell lines. PTPL1 knockdown increased the proliferation of lung cancer cells. Mechanistically, PTPL1 knockdown induced the activation of the Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase SRC (Src)/Extracellular regulated MAP kinase (ERK) pathway and thereby promoted yes-associated protein (YAP1) nuclear translocation and activation.
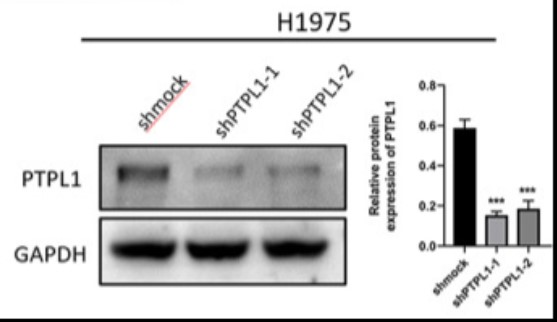
Fig1. Knockdown of PTPL1 was validated via western blot analyses. PTPL1, protein-tyrosine phosphatase-L1; shmock, negative control; shPTPL1, short hairpin RNA against PTPL1.
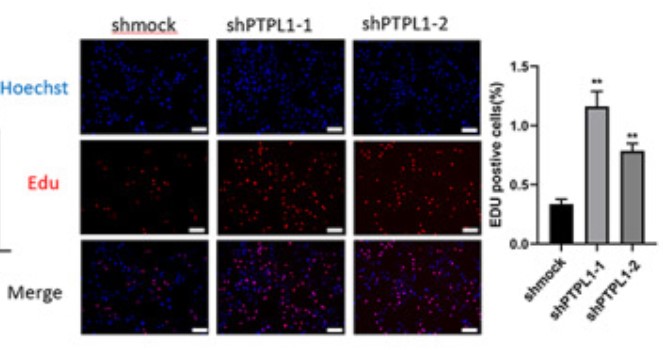
Case study 2: Mohamed Hamyeh, 2020
Clinical data suggest that the protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPN13 exerts an anti-oncogenic effect. Its exact role in tumorigenesis remains, however, unclear due to its negative impact on FAS receptor-induced apoptosis.
The team crossed transgenic mice deleted for PTPN13 phosphatase activity with mice that overexpress human HER2 to assess the exact role of PTPN13 in tumor development and aggressiveness. They also developed isogenic clones of the aggressive human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 overexpressing either wild type or a catalytically-inactive mutant PTPN13. The results showed that observed that PTPN13 phosphatase activity is required to inhibit cell motility and invasion in the MDA-MB-231 cell line overexpressing PTPN13. Phosphoproteomic and gene ontology analyses indicated a role of PTPN13 in the regulation of intercellular junction-related proteins. Finally, protein localization studies in MDA-MB-231 cells and HER2-overexpressing mice tumors confirmed that PTPN13 stabilizes intercellular adhesion and promotes desmosome formation. These data provide the first evidence for the negative role of PTPN13 in breast tumor invasiveness and highlight its involvement in cell junction stabilization.
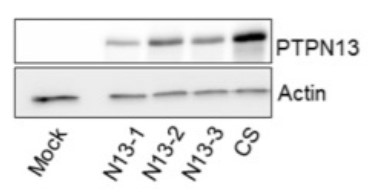
Fig3. Expression of wt (N13-1, N13-2, N13-3) or catalytically inactive (CS) PTPN13 in the indicated cell clones was monitored by western blotting using anti-PTPN13 antibodies.
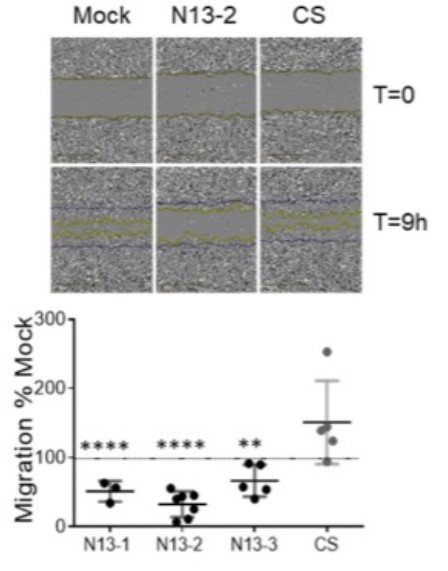
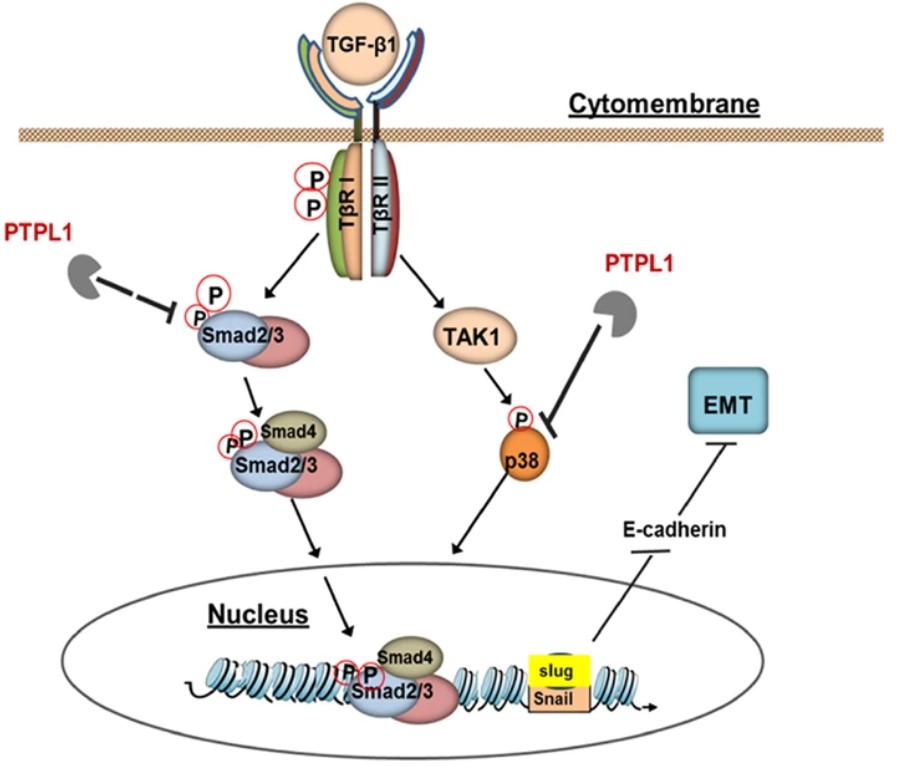
Fig1. Schematic diagram for PTPL1 regulation of TGF-β signaling in Epithelial-mesenchymal transition of non-small cell lung cancer cells. (Ning Zhu, 2021)
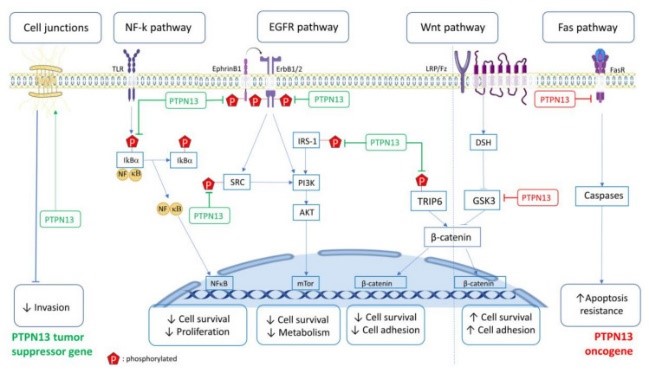
Fig2. PTPN13 is involved in multiple signaling pathways. PTPN13 in green: Tumor suppressor role; PTPN13 in red: Pro-tumoral role. (Soha Mcheik, 2020)
PTPN13 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PTPN13 participated on our site, such as Apoptosis Modulation and Signaling, Ephrin B reverse signaling, Fc-epsilon receptor I signaling in mast cells, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PTPN13 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Apoptosis Modulation and Signaling | BOK;CASP2;HRK;DIABLO;CRADD;HN1;PTRH2;PTPN13;DFFA |
| Ephrin B reverse signaling | EFNB2;EFNB1;PTPN13 |
| Fc-epsilon receptor I signaling in mast cells | DOK1;ITK;S1PR1;PTPN13;LAT2 |
PTPN13 has several biochemical functions, for example, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit binding, protein binding, protein tyrosine phosphatase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PTPN13 itself. We selected most functions PTPN13 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PTPN13. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit binding | FAM83B;PIK3R1;XBP1;PIK3AP1;FAM83A;DNM2;PTPN13 |
| protein binding | NTSR1;RNF175;PLEKHM1;GLS;ZZZ3;NUP62CL;ELMO3;IGFBP5;CREB1 |
| protein tyrosine phosphatase activity | PTPRJ;PTENA;CDC25C;MTMR6;DUSP15;PTPMT1;CDC25B;PTPN14;CDC14C |
PTPN13 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PTPN13 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PTPN13.
RAPGEF6; PKN2; FAS; PLEKHA1; PDCD10
- Q&As
- Reviews
Q&As (7)
Ask a questionThe expression of PTPN13 can be regulated at the transcriptional level by various factors, including transcription factors, epigenetic modifications, and signaling pathways. For example, the tumor suppressor p53 can transcriptionally upregulate PTPN13 expression. Additionally, growth factors, cytokines, and oncogenic signals can modulate PTPN13 expression through their downstream effectors.
There are no specific inhibitors or activators targeting PTPN13 available. However, further research is underway to identify small molecules or compounds that can modulate PTPN13 activity selectively.
PTPN13 binds to its substrates through its phosphatase domain and regulates their activities by dephosphorylation. It acts as a negative regulator of signaling pathways by dephosphorylating tyrosine residues on target proteins, thereby modulating their enzymatic activity, protein-protein interactions, and subcellular localization.
PTPN13 shows diverse expression patterns in different cancer types, and its potential as a prognostic marker or therapeutic target remains to be fully elucidated. Further studies are needed to determine its clinical significance in specific cancer types and its potential for personalized treatment approaches.
As PTPN13 functions as a tumor suppressor, restoring its activity or expression could be a potential therapeutic strategy. However, direct targeting of PTPN13 is challenging. Alternatively, targeting downstream signaling pathways that are dysregulated in PTPN13-deficient tumors, such as the PI3K/AKT pathway, may provide potential therapeutic opportunities.
PTPN13 acts as a tumor suppressor in various cancers. Its loss or inactivation is associated with increased cell proliferation, survival, and metastasis. PTPN13 regulates key signaling pathways involved in cancer progression, such as the PI3K/AKT and MAPK pathways, and its dysregulation contributes to tumor growth, invasion, and resistance to therapies.
PTPN13, also known as Fas-associated phosphatase-1 (FAP-1), plays critical roles in various cellular processes, including cell adhesion, migration, proliferation, and survival. It is involved in regulating multiple signaling pathways such as the PI3K/AKT, MAPK, and Wnt pathways.
Customer Reviews (3)
Write a reviewThe performance of this reagent during the experiment is remarkable, providing the optimal sample preparation conditions.
I am truly grateful for this product as it has successfully resolved protein interference issues that I encountered.
Utilizing this protein reagent, my gel electrophoresis results for experimental samples are clearer, enabling better comparison and analysis.
Ask a Question for All PTPN13 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All PTPN13 Products
Required fields are marked with *