Vsig4
-
Official Full Name
V-set and immunoglobulin domain containing 4
-
Overview
This gene encodes a v-set and immunoglobulin-domain containing protein that is structurally related to the B7 family of immune regulatory proteins. The encoded protein may be a negative regulator of T-cell responses. This protein is also a receptor for the complement component 3 fragments C3b and iC3b. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. -
Synonyms
VSIG4; V-set and immunoglobulin domain containing 4; V-set and immunoglobulin domain-containing protein 4; Z39IG; protein Z39Ig; Ig superfamily protein; complement receptor of the immunoglobulin superfamily; CRIg;
- Recombinant Proteins
- Cell & Tissue Lysates
- Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads
- Human
- Mouse
- CHO
- E.coli
- HEK293
- HEK293 cells
- HEK293T
- Human Cell
- Mammalian cells
- C
- His
- Fc
- Avi
- GST
- hFc
- His (Fc)
- HlgG1 Fc
- Myc
- DDK
- Myc|DDK
- N/A
- Background
- Quality Guarantee
- Case Study
- Involved Pathway
- Protein Function
- Interacting Protein
- Vsig4 Related Research Area
What is VSIG4 protein?
VSIG4 (V-set and immunoglobulin domain containing 4) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome X at locus Xq12. This gene encodes a v-set and immunoglobulin-domain containing protein that is structurally related to the B7 family of immune regulatory proteins. The encoded protein may be a negative regulator of T-cell responses. This protein is also a receptor for the complement component 3 fragments C3b and iC3b. The VSIG4 protein is consisted of 399 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 44.0 kDa.
What is the function of VSIG4 protein?
VSIG4 is a transmembrane protein whose structure contains a V-set immunoglobulin variable region and a constant immunoglobulin region. This structure enables it to participate in a variety of protein-protein interactions. Studies have shown that VSIG4 can be used as a co-stimulatory molecule to promote the activation and proliferation of T cells. In addition, VSIG4 can also regulate immune response and maintain immune homeostasis by interacting with receptors or ligands on the surface of other immune cells.
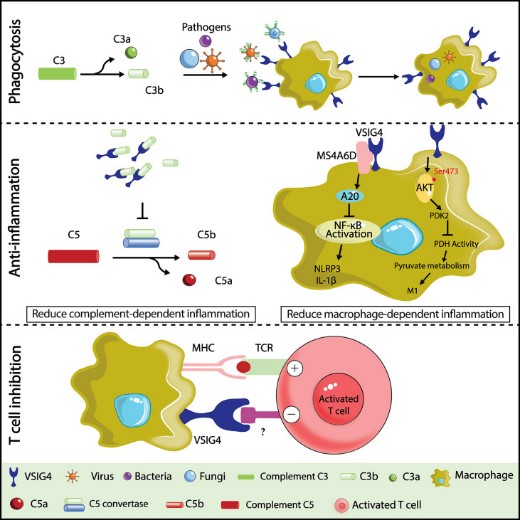
Fig1. Illustration of VSIG4 functions. (Xia Zhou, 2022)
VSIG4 Related Signaling Pathway
Through its extracellular immunoglobulin domain, VSIG4 recognizes and binds to specific ligands, such as activated inducible T cell immune receptors (AITR), which initiate a series of signal transduction events. These signaling pathways are involved in the activation, proliferation and survival of T cells, as well as the regulation of immune responses. In particular, VSIG4 plays an important role in co-stimulation and inhibition of T cells, thereby influencing T-cell-mediated immune responses.
VSIG4 Related Diseases
VSIG4 plays a key role in a variety of physiological and pathological processes, especially in inflammatory responses. It has been found to be abnormally expressed in a variety of inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and asthma. Abnormal VSIG4 expression is closely related to the regulation of inflammatory response and the development of disease.
Bioapplications of VSIG4
VSIG4 is also considered as a potential immunotherapeutic target that can influence the activity of the immune system and the tumor microenvironment by modulating its function, providing new ideas and methods for the treatment of related diseases.
High Purity
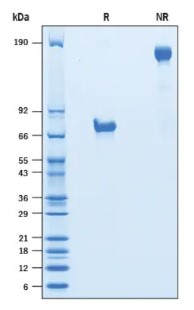
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (VSIG4-051H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
High Bioactivity
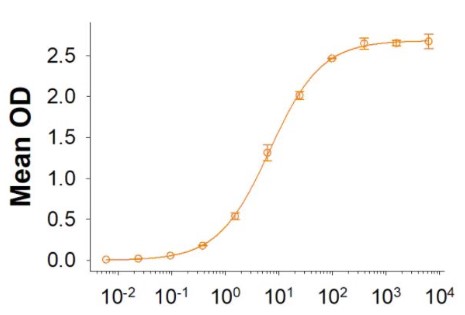
Fig2. Activity Data. (VSIG4-051H)
Case study 1: Zhutian Zeng, 2016
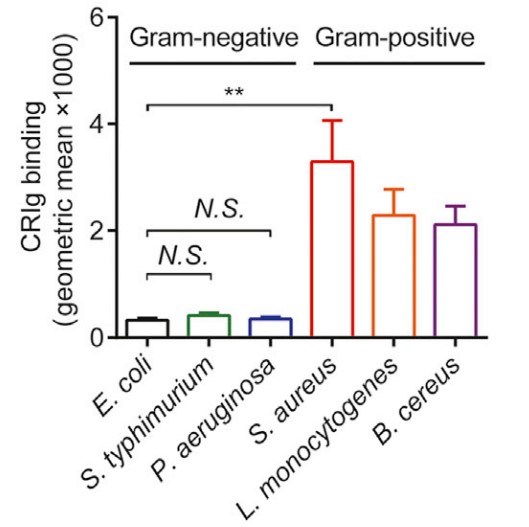
Kupffer cells (KCs), the vast pool of intravascular macrophages in the liver, help to clear blood-borne pathogens. The mechanisms by which KCs capture circulating pathogens remain unknown. Here the researchers use intra-vital imaging of mice infected with Staphylococcus aureus to directly visualize the dynamic process of bacterial capture in the liver. Circulating S. aureus were captured by KCs in a manner dependent on the macrophage complement receptor CRIg, but the process was independent of complement. CRIg bound Staphylococcus aureus specifically through recognition of lipoteichoic acid (LTA), but not cell-wall-anchored surface proteins or peptidoglycan. Blocking the recognition between CRIg and LTA in vivo diminished the bacterial capture in liver and led to systemic bacterial dissemination. All tested Gram-positive, but not Gram-negative, bacteria bound CRIg in a complement-independent manner. These findings reveal a pattern recognition role for CRIg in the direct capture of circulating Gram-positive bacteria from the bloodstream.
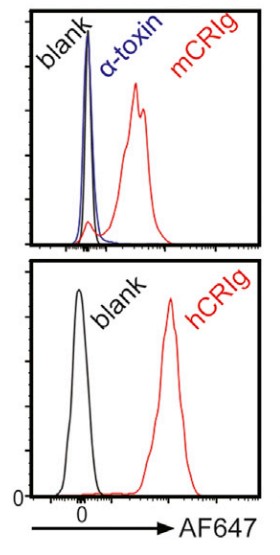
Fig1. Recombinant mouse (upper) or human (below) CRIg were labeled with AF-647.
Case study 2: Yunmei Liao, 2014
Tumor-associated macrophages are a prominent component of lung cancer stroma and contribute to tumor progression. The protein V-set and Ig domain-containing 4 (VSIG4), a novel B7 family-related macrophage protein that has the capacity to inhibit T-cell activation, has a potential role in the development of lung cancer. Results showed massive VSIG4(+) cell infiltration throughout the samples. Immunofluorescent double staining showed that VSIG4 was present on CD68(+) macrophages, but absent from CD3(+) T cells, CD31(+) endothelial cells, and CK-18(+) epithelial cells. Moreover, VSIG4 was coexpressed on B7-H1(+) and B7-H3(+) cells in these tumor specimens.
Transfection of the VSIG4 gene into 293FT cells demonstrated that the VSIG4 signal could inhibit cocultured CD4(+) and CD8(+) T-cell proliferation and cytokine (IL-2 and IFN-γ) production in vitro. Interestingly, in a murine tumor model induced by Lewis lung carcinoma cell line, the researchers found that tumors grown in VSIG4-deficient (VSIG4(-/-)) mice were significantly smaller than those found in wild-type littermates. All of these results demonstrate that macrophage-associated VSIG4 is an activator that facilitates lung carcinoma development. Specific targeting of VSIG4 may prove to be a novel, efficacious strategy for the treatment of this carcinoma.
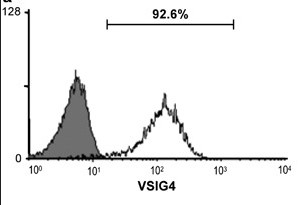
Fig3. The 293FT cells were transfected with lentivirus-expressing VSIG4 or empty lentivirus (gray shadow), and VSIG4 expression was confirmed by fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS).
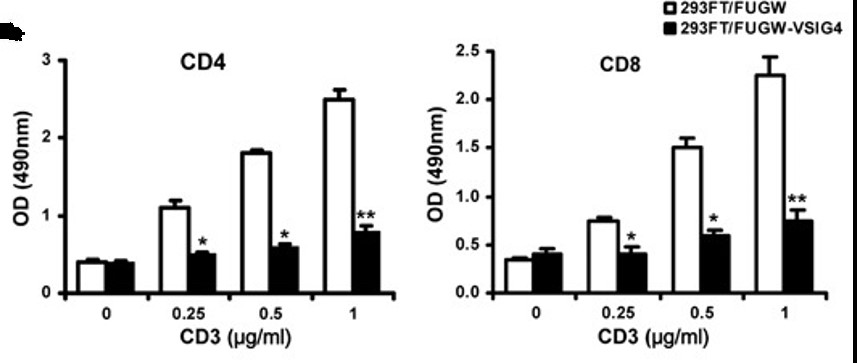
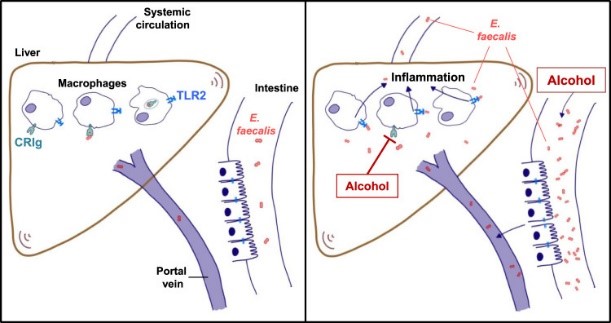
Fig1. Alcohol reduces the clearance of pathobionts by Kupffer cells and contributes to liver disease. (Yi Duan, 2021)
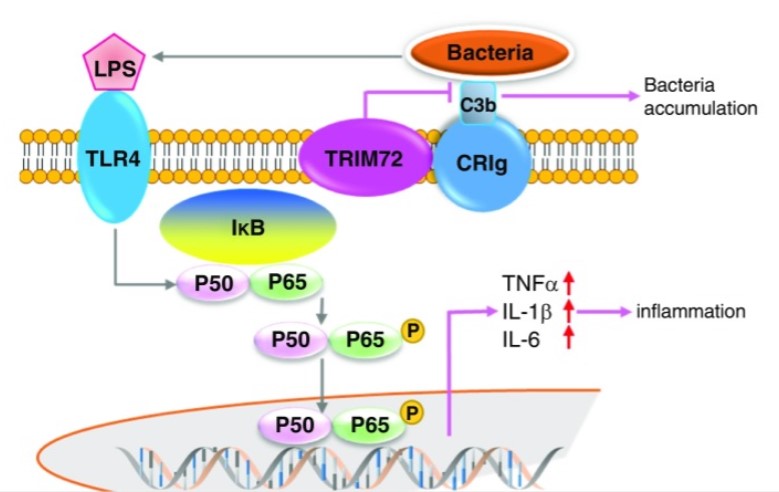
Fig2. Working model for the role of TRIM72 in regulating bacterial phagocytosis and inflammation. (Nagaraja Nagre, 2018)
Vsig4 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Vsig4 participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Vsig4 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
Vsig4 has several biochemical functions, for example, protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Vsig4 itself. We selected most functions Vsig4 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Vsig4. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | CSTF1;BMP2;ITCH;C17orf28;FIS1;KLF11;BAD;CMTM5;TES |
Vsig4 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Vsig4 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Vsig4.
PDK2
- Q&As
- Reviews
Q&As (6)
Ask a questionVSIG4 has a complex relationship with other genes or proteins, and can interact with other genes or proteins and participate in a variety of biochemical reactions.
There are no drugs that directly regulate VSIG4 levels, but they can affect VSIG4 expression and function by modulating the immune system.
Mutations in VSIG4 can be detected and analyzed by methods such as whole-genome sequencing or target region sequencing to understand the impact of mutations on protein structure and function.
VSIG4 plays an important role in tumor immunity, which can inhibit the activation and function of T cells and NK cells, thereby promoting tumor growth and metastasis.
Studying the regulatory mechanism of VSIG4 requires a combination of various experimental methods and techniques, such as gene knockout, transcriptome analysis, and protein-protein interactions.
The types of mutations in VSIG4 include point mutations, insertions/deletions, duplications, etc., which can cause structural and functional abnormalities of the protein.
Customer Reviews (3)
Write a reviewStable performance, excellent performance in a variety of experiments.
No side effects, high safety.
It has good antigenicity and can induce target immune response.
Ask a Question for All Vsig4 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All Vsig4 Products
Required fields are marked with *



