vWF
-
Official Full Name
von Willebrand factor
-
Overview
The glycoprotein encoded by this gene functions as both an antihemophilic factor carrier and a platelet-vessel wall mediator in the blood coagulation system. It is crucial to the hemostasis process. Mutations in this gene or deficiencies in this protein result in von Willebrands disease. An unprocessed pseudogene has been found on chromosome 22. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
VWF; von Willebrand factor; VWD; F8VWF; coagulation factor VIII VWF;
- Recombinant Proteins
- Cell & Tissue Lysates
- Native Proteins
- Transfected Stable Cell Lines
- Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads
- Dog
- Human
- Mouse
- Pig
- Rat
- Rhesus Macaque
- Zebrafish
- CHO
- E. coli
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Human plasma
- Mamanlian cells
- Mammalian Cell
- Sf9 Insect Cell
- Yeast
- C
- His
- DDK
- Flag
- His (Fc)
- Avi
- Myc
- His|Myc
- Met|His
- N/A
- N
- Background
- Quality Guarantee
- Case Study
- Involved Pathway
- Protein Function
- Interacting Protein
- vWF Related Articles
- vWF Related Research Area
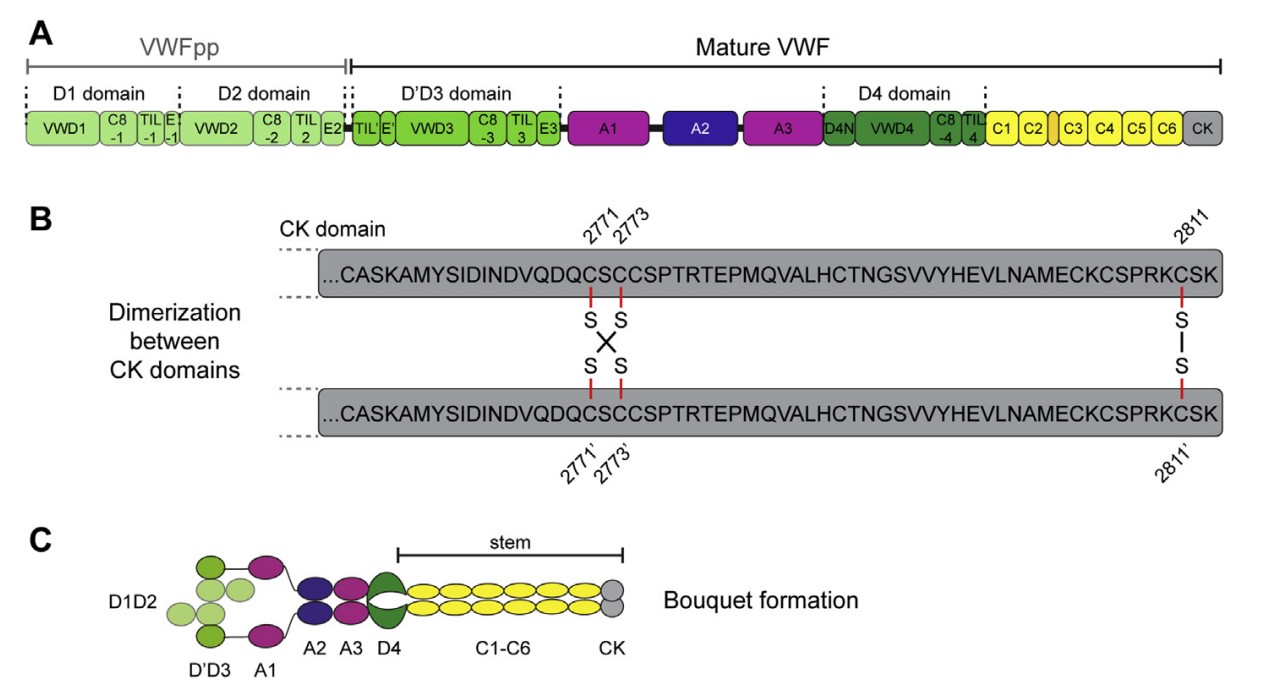
Fig1. VWF domain structure. (A) Schematic representation of VWF's domain structure, (B) dimerizing disulfide bonds between the CK domains of two VWF monomers and (C) dimeric bouquet formation. (Achim Löf, 2017)
What is VWF protein?
VWF (von Willebrand factor) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 12 at locus 12p13. This gene encodes a glycoprotein involved in hemostasis. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed following assembly into large multimeric complexes. These complexes function in the adhesion of platelets to sites of vascular injury and the transport of various proteins in the blood. The VWF protein is consisted of 2813 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 309.3 kDa.
What is the function of VWF protein?
This protein is important in the maintenance of hemostasis, it promotes adhesion of platelets to the sites of vascular injury by forming a molecular bridge between sub-endothelial collagen matrix and platelet-surface receptor complex GPIb-IX-V. Also it acts as a chaperone for coagulation factor VIII, delivering it to the site of injury, stabilizing its heterodimeric structure and protecting it from premature clearance from plasma.
VWF Related Signaling Pathway
VWF is a glycoprotein associated with blood clotting disorders and plays a role in the clotting process. VWF binds to the GPIb-IX-V complex on platelets and promotes platelet adhesion and agglutination, thus initiating the signaling pathway for thrombosis. It can also bind to platelet membrane glycoprotein (GP) complexes and subcutaneous collagen, and this interaction mediates platelet adhesion at the site of vascular injury. It is also involved in reticulum formation and thrombosis.
VWF Related Diseases
VWF protein abnormalities can cause a variety of diseases, von Willebrand disease (VWD) is a group of hereditary bleeding disorders that can be divided into three types based on their severity and the degree of functional deficiency of VWF. When VWF function may also be affected, resulting in bleeding tendencies that can cause thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP). It can also cause von Willebrand Disease Type A. When the VWF protein is abnormal, patients may experience symptoms such as easy bruising and difficulty in hemostasis.
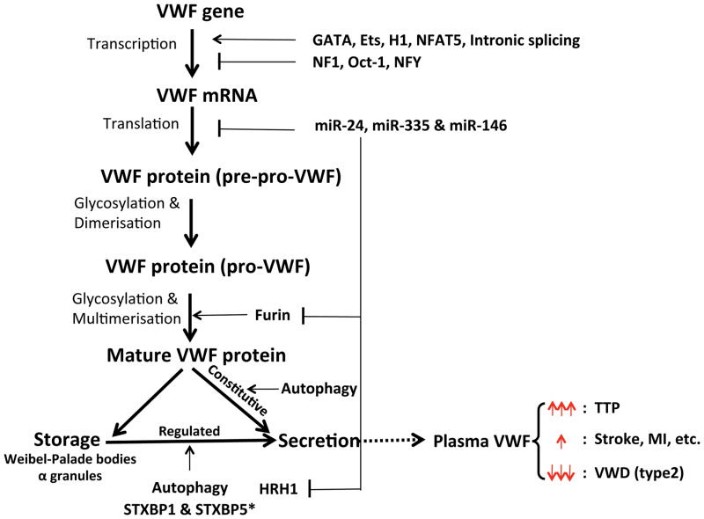
Fig2. Regulation of VWF expression & secretion and diseases. (Yaozu Xiang, 2016)
Bioapplications of VWF
In patients with von Willebrand disease, supplementation of exogenous VWF proteins or coagulation factors may be required to maintain normal clotting function. Because VWD is a genetic disorder, VWF genetic testing and counseling are important for genetic risk assessment and family planning in patients with familial VWD. Intraoperative or daily monitoring of the protein level to avoid the risk of bleeding.
High Purity
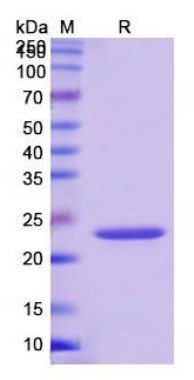
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (VWF-6569H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
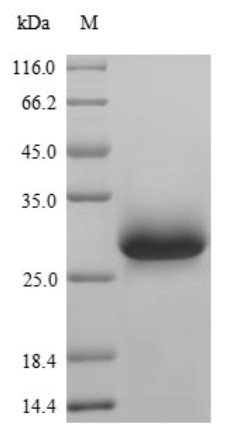
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (VWF-2463M) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
Case study 1: Jirawat Khanongnoi, 2018
Snake venom-metalloproteinases (SVMPs) are the primary factors that disturb hemostasis and cause hemorrhage in the venomous snake bitten subjects. Kaouthiagin is a unique SVMP that binds and cleaves von Willebrand factor (vWF) at a specific peptide bond leading to inhibition of platelet aggregation, which enhances the hemorrhage. Kaouthiagin is a low abundant venom component of Thai cobra (Naja kaouthia); thus, most horse-derived antivenins used for cobra bite treatment do not contain adequate anti-kaouthiagin. This study aimed to produce human single-chain antibody variable fragments (HuscFvs) that bind to and interfere with kaouthiagin activity for further clinical use.
Kaouthiagin was purified from N. kaouthia-holovenom by a single-step gel-filtration chromatography. The selected phages were used to infect Escherichia coli bacteria. Soluble HuscFvs expressed by three phage-transformed-E. coli clones interfered with cobra kaouthiagin binding to human vWF. omputerized simulation indicated that HuscFv of two phage-transformed E. coli clones formed contact interface with kaouthiagin residues at or near catalytic site and effectively inhibited fibrinogenolytic activity of the kaouthiagin.

Fig1. Western blotting patterns of the SDS-PAGE-separated fractions 44–56 probed with 1 μg/mL of recombinant human von Willebrand factor (vWF).
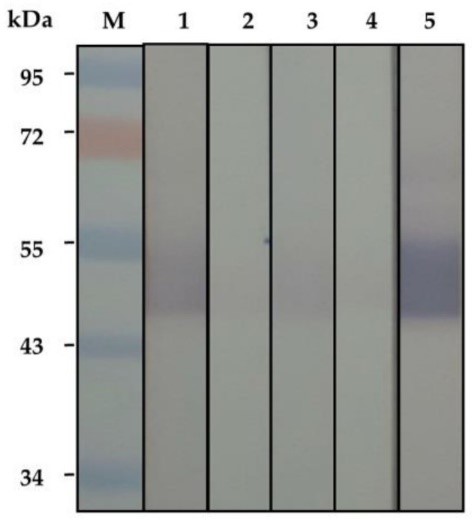
Case study 2: Yingxue Qi, 2018
Platelet glycoprotein Ibα (GPIbα) extracellular domain, which is part of the receptor complex GPIb-IX-V, plays an important role in tumor metastasis. However, the mechanism through which GPIbα participates in the metastatic process remains unclear. The researchers established a series of screening models and obtained rat anti-mouse GPIbα monoclonal antibodies (mAb) 1D12 and 2B4 that demonstrated potential value in suppressing cancer metastasis. 1D12 and 2B4 affected the von Willebrand factor (vWF)-GPIbα interaction via binding to GPIbα aa 41-50 and aa 277-290 respectively, which markedly inhibited the interaction among platelets, tumor cells, and endothelial cells in vitro, and reduced the mean number of surface nodules in the experimental and spontaneous metastasis models in vivo.
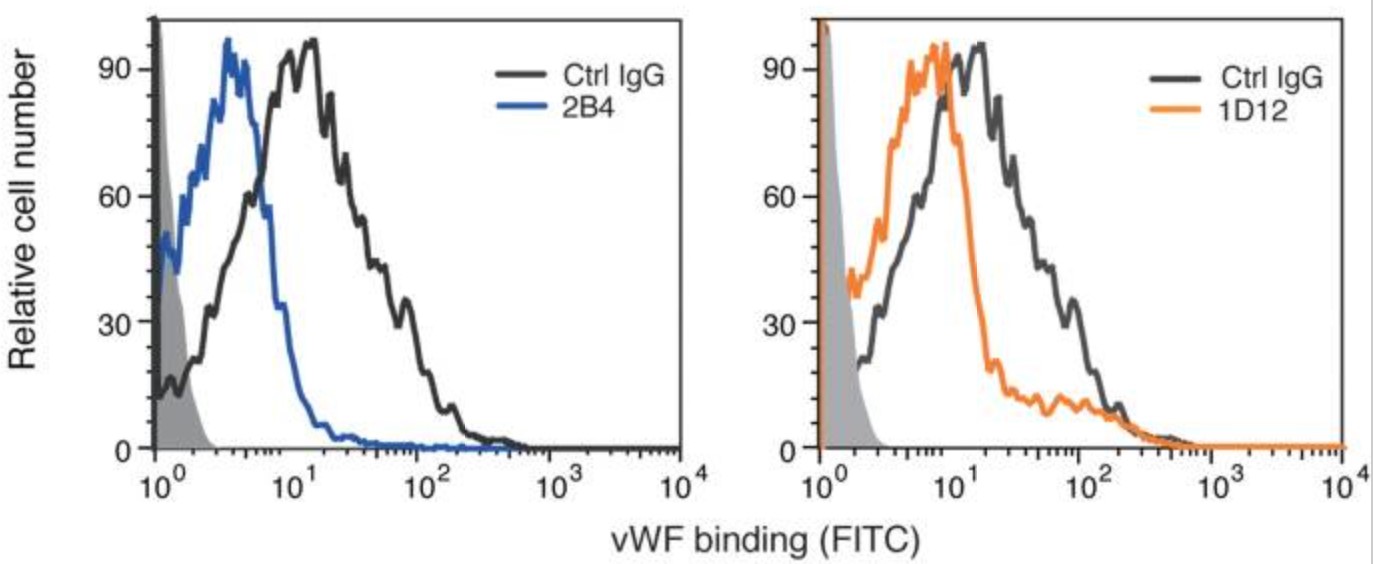
Fig3. The vWF binding was inhibited by 2B4 and 1D12 and detected by flow cytometry. Binding of vWF was detected with FITC-conjugated mouse vWF IgG by flow cytometry and quantitated by mean fluorescence intensity.
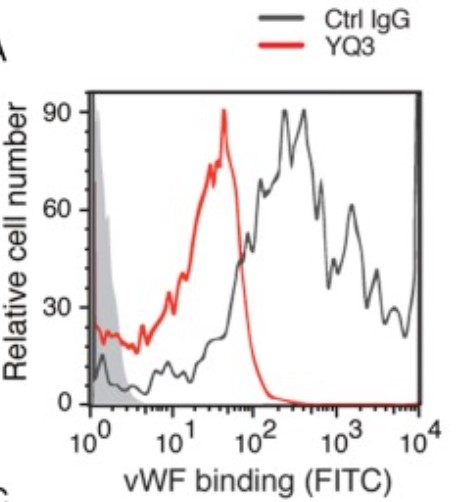
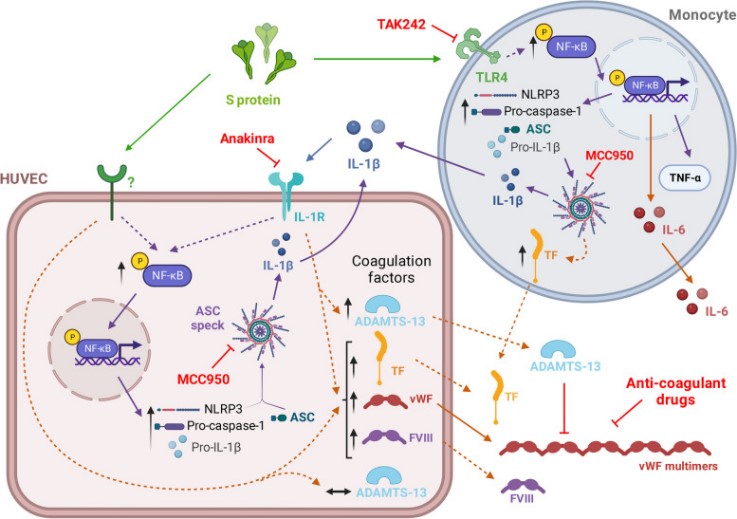
Fig1. Diagram of cellular pathways activated by SARS-CoV-2 S protein and the targets for pharmacological interference. (Alicia Villacampa, 2024)
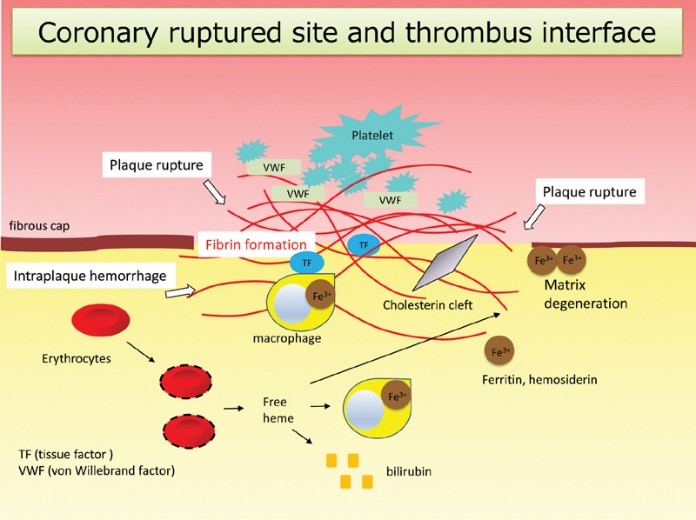
Fig2. Coronary ruptured site and thrombus interface. (Atsushi Yamashita, 2021)
vWF involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways vWF participated on our site, such as PIK-Akt signaling pathway, Focal adhesion, ECM-receptor interaction, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with vWF were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| PIK-Akt signaling pathway | KRAS;PIK3R1;FGF11;BCL2;PPP2R2A;LAMB2;ITGB3;LPAR5;ITGA9 |
| Focal adhesion | MYL7;BCAR1;COL27A1;GRB2A;SHC3;ACTN3;PIK3CA;SEPP1;LAMB1 |
| ECM-receptor interaction | DAG1;THBS3A;CHAD;ITGA2;CD44;COL6A4;HMMR;ITGA11A;VTNA |
| Complement and coagulation cascades | THBD;A2M;PLAT;F13B;VWF;MASP2;C6;F2;C5AR1 |
| Platelet activation | P2RY12;GP5;GNAI3;PIK3R2;STIM1;PIK3CA;F2RL3;ARHGEF1;PRKACB |
vWF has several biochemical functions, for example, chaperone binding, collagen binding, glycoprotein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by vWF itself. We selected most functions vWF had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with vWF. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| chaperone binding | AHSA1;TIMM10;BAG5;ERP29;DNAJA2;DNAJA3A;RNF207;CDC37;AHSA2 |
| collagen binding | VWF;TGFBI;CTSK;CHADL;SERPINH1A;SMAD7;PCOLCE;ITGA9;Itga10&Itgb1 |
| glycoprotein binding | HFE2;FBXO6;FYN;ERBB2;FGFR1;SHB;ACE2;SERPINA1A;PIP |
| identical protein binding | FKBP8;LEPR;CST3;C1S;HSPB8;ACY3;BCL2;DNMT3A;CEP57L1 |
| immunoglobulin binding | cgr2b;VWF;HRG |
| integrin binding | WISP2;COL4A3;SFRP2;CD226;WISP1B;CYR61;TLN1;ADAMTS5;LYN |
| protease binding | CCDC71L;TIMP3;SERPINE1;TIMP2;C10orf2;SELL;COMP;LDLR;SERPINB13 |
| protein N-terminus binding | ERCC4;ALOX5AP;ERCC6;NTSR1;ACTN4;FEZ1;RPA3;PHB2;SLA2 |
| protein binding | PHF7;COLGALT2;FLOT1;SHC4;STK25;FBXL5;ASL;LONRF3;VEPH1 |
| protein homodimerization activity | DRD2;SLC26A5;UBE4A;ENO3;FAM109A;TREX1;IMPA1;GOLGA5;GSTM4 |
vWF has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with vWF here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of vWF.
GP1BA; ADAMTS13
- Q&As
- Reviews
Q&As (6)
Ask a questionThere is currently no treatment that directly targets the VWF protein. However, some medications can improve the patient's clotting status and reduce the risk of bleeding. For example, the use of recombinant human coagulation factor VIII. can replace the deficient factor VIII and improve coagulation function. In addition, the use of antifibrinolytic drugs can inhibit the degradation of fibrin and maintain the stability of the coagulation process.
VWF protein is closely related to coagulation factor VIII. Coagulation factor VIII. is a serine protease that plays a key role in the coagulation process. VWF protein can act as a cofactor for coagulation factor VIII., accelerating the coagulation process. In addition, VWF protein can also inhibit the activity of plasminogen activators, thereby inhibiting the degradation of fibrin and maintaining the stability of the coagulation process.
In the process of hemostasis, the role of VWF protein is mainly to promote platelet adhesion and aggregation. When platelets bind to VWF protein, morphological changes occur and the phospholipid surface is exposed, which interacts with other platelets or endothelial cells to form platelet thrombosis and play a hemostatic role.
There is a complex interaction between VWF protein and other coagulation factors. For example, VWF proteins can bind to glycoprotein II.b/III.a receptors on the surface of platelets, promoting platelet adhesion and aggregation.
Genetic variations in the VWF protein can lead to coagulation disorders such as von Willebrand disease (VWD). Some variants can cause VWF protein deficiency or dysfunction, which can affect the ability of platelets to adhere and aggregate, increasing the risk of bleeding. Understanding these variants can help diagnose and classify different subtypes of VWD.
The main function of VWF protein in blood is to promote platelet adhesion and aggregation, thereby participating in the process of hemostasis and coagulation. In addition, VWF protein can also act as a regulator of endothelial cells and participate in the repair and remodeling of blood vessel walls.
Customer Reviews (3)
Write a reviewStrong activity, a small amount can play a role, save reagents.
It has been used in experiments, and the results are accurate and reliable.
No significant difference was found between different batches, and the repeatability between batches was good.
Ask a Question for All vWF Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All vWF Products
Required fields are marked with *



