Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) is a central regulatory factor of innate immunity in the body, mainly able to recognize the lipopolysaccharide cell wall components of bacteria and induce cytokine release. Recently, a research report titled “RHBDL4-triggered downregulation of COPII adaptor protein TMED7 suppresses TLR4-mediated inflammatory signaling” was published in Nature Communications. Scientists from institutions such as the University of Cologne found through their research that the membrane protease RHBDL4…
Nature
The Release of Special Inhibitory Pathways May Promote the Body’s Immune Response against HIV Infection
During antiretroviral therapy, the persistent presence of HIV-1 may be due to its establishment of a long-lived virus library in quiescent immune cells. Recently, an article titled “TGF-β blockade drives a transitional effector phenotype in T cells reversing SIV latency and decreasing SIV reservoirs in vivo” was published in the international journal Nature Communications. In the research report, scientists from institutions such as Northwestern University in the United States used…
Regulatory Mechanism of RAS Palmitoyltransferase
RAS participates in multiple signaling pathways, and post-translational modifications regulate the subcellular localization of RAS to regulate downstream signal transduction. Among them, palmitoylation is a necessary modification of HRAS and NRAS signal transduction. The acyltransferase DHHC9 binds to the helper protein GCP16 to catalyze palmitoylation of HRAS and NRAS, but the interaction between GCP16 and DHHC9, as well as the molecular mechanism by which GCP16 regulates the palmitoylation activity of…
How HIV Capsid Enters the Nuclear Pore Barrier Pathway
In a new study, Dr. David Jacques, a medical researcher at the University of New South Wales in Australia, and his team discovered how the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) breaks through the nucleus to establish infection, a discovery that goes beyond the scope of HIV biology. The relevant research results were published online in the journal Nature, with the title “The HIV capsid mimics karyopherin engagement of FG-nucleoporins”. To…
The Mechanism by Which Leukemia Stem Cells Promote Their Own Growth after Chemotherapy
The mystery of why myeloid leukemia begins to grow again after chemotherapy kills most malignant cells and how to prevent growth through reused drugs may be solved through new research. The bone marrow of patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) contains a rare group of leukemia stem cells (LSCs) that do not grow and therefore are not killed by chemotherapy. However, after treatment, these cells began to grow and…
The New Role of STING in the Human Innate Immune System
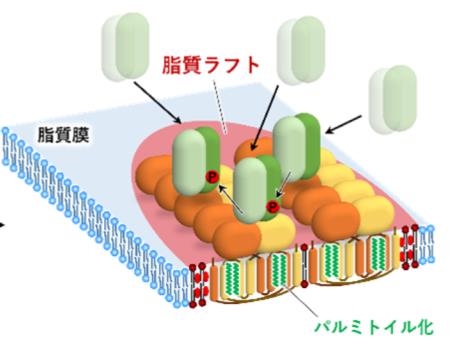
When pathogens invade the body, the innate immune system will play a role in resisting the invading pathogens. The innate immune system is the first line of defense. It can accurately detect viruses or bacteria, and then activate proteins to fight against pathogens. In order to better understand the working principle of the innate immune system in the body, researchers from research institutions such as the National Cancer Center Research…
MSL2 Ensures the Expression Mechanism of Mammalian Biallelic Genes
Have you ever thought about why every chromosome in our cells has two copies? During the breeding process, we obtain a copy from each of our parents. This means that we also obtained two copies or alleles of each gene from each chromosome or pair of parents. Both alleles can produce messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA), which is the formula required for mRNA to manufacture proteins and maintain cell operation….
PLSCR1 Is a Cellular Autonomous Defense Factor That Resists SARS-Cov-2 Infection
Earlier this month, multiple health departments confirmed that BA.2.86- a highly mutated SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19- poses a risk of rapid transmission in countries around the world. This week, the latest vaccination plan will be launched across the United States, but it remains to be seen whether this latest vaccination plan will effectively slow down the spread of BA.2.86 or other new virus variants. However, vaccines remain the…
Discovering New Protein Families and Folds Using Artificial Intelligence Tools

In a new study, researchers from the Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics and the University of Basel have discovered a treasure trove of uncharacterized proteins. In the recent deep learning revolution, they have discovered hundreds of new protein families and even a new predictive protein fold. The relevant research results were published online in the journal Nature, with the title “Uncovering new families and folds in the natural protein universe”. …
The Three-Dimensional Structure of Type A GABA Receptors in Natural State
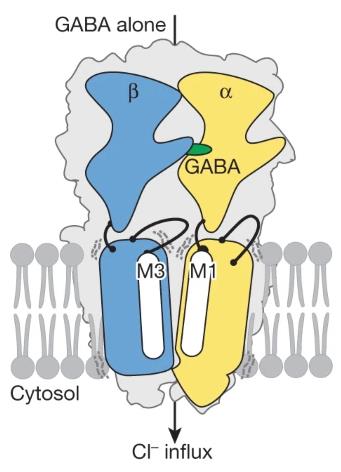
In a new study, researchers from the University of Health and Science of Oregon in the United States revealed the molecular structure of a receptor crucial for brain development and function – the Type A GABA receptor. The relevant research results were published online in Nature titled “Cryo-EM structures reveal native GABAA receptor assemblies and pharmacology”. The A-type GABA receptor has become a target for drug anesthetics, sedatives, and antidepressants…