Intestinal inflammation can trigger a vicious cycle that disrupts the sensitive relationships between food, digestive acids, microorganisms, and the immune system, further promoting inflammation and sometimes even leading to tumor growth; Recently, a research report published in the journal JCI Insight titled “Farnesoid X receptor mediates macrophage-intrinsic responses to suppress colitis-induced colon cancer progression,” scientists from institutions such as the University of Wisconsin Madison identified a promising new target for…
New Research
TRIB3-TRIM8 Complex Regulates HNF4Α Stability to Promote the Progression of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
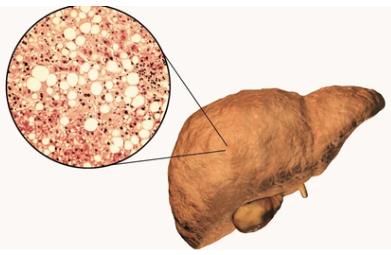
Hepatocellular endoplasmic reticulum stress plays an important role in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Hepatonuclear factor 4 α (HNF4α) reduced expression is an important event in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver and other liver diseases. Does endoplasmic reticulum stress regulate the expression of HNF4α is not clear yet. The purpose of this study is to elucidate the mechanism of HNF4 α protein degradation and exploration of…
Acinar-Ductal Cell Rearrangement Drives Branching Morphogenesis of the Murine Pancreas in an IGF/PI3K Dependent Manner
Many epithelial organs undergo branching morphogenesis during development, resulting in the construction of complex dendritic networks and the acquisition of specialized tissue structures. Understanding the establishment and maintenance of organizational structure is a core issue in developmental biology, which directly impacts organ physiology and diseases. In adult life, the loss of organizational structure may occur in the early stages and various human cancers. However how these processes are coordinated and…
SARS-Cov-2 Can Infect Dopaminergic Neurons
In a new study, researchers from the Will Cornell Medical Center, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, and Columbia University’s Wagros School of Internal and External Medicine pointed out that the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, which causes COVID-19, can infect dopaminergic neurons in the brain and cause aging, meaning they lose their ability to grow and divide. They believe that further research on this discovery may reveal neurological symptoms related to long-term COVID-19,…
New Research Has Found Biomarkers for Predicting the Risk of Human Cell Aging and Death

As cells age, they experience aging, a state where they stop growing but continue to release inflammatory and tissue-degrading molecules. When a person is young, the immune system will respond by eliminating aging cells, commonly known as “zombie cells”. However, zombie cells will continue to exist and lead to a series of age-related health problems and diseases. In a new study, researchers from the Mayo Clinic in the United…
CDK4 Is Expected To Be Used In the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
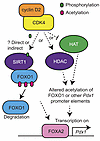
Type 2 diabetes affects more than 500 million people worldwide. In a new study, researchers from Weill Cornell Medical College in the United States found a new pathway that stimulates insulin production in the preclinical diabetes model for healthy pancreas β cell growth. This discovery brings hope for future treatment, which will improve the life of patients with type 2 diabetes. The relevant research results have recently been published in…
The Three-Dimensional Structure of Type A GABA Receptors in Natural State
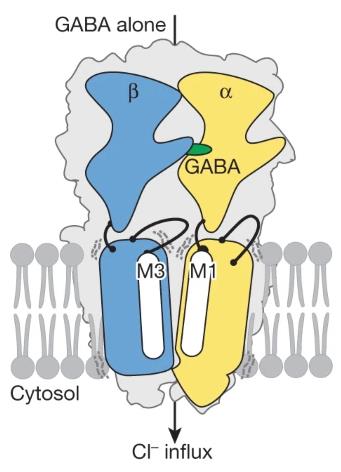
In a new study, researchers from the University of Health and Science of Oregon in the United States revealed the molecular structure of a receptor crucial for brain development and function – the Type A GABA receptor. The relevant research results were published online in Nature titled “Cryo-EM structures reveal native GABAA receptor assemblies and pharmacology”. The A-type GABA receptor has become a target for drug anesthetics, sedatives, and antidepressants…
Virus ADP Ribotransferase Couples RNA with Host Protein
Prior to this, people had always believed that RNA and protein only interacted briefly during cellular processes. In a new study, researchers from the Max Planck Institute of Land Microbiology in Germany found that this is not the case: bacterial viruses, also known as bacteriophages, “bind” specific RNA to host proteins during the developmental cycle. This chemical modification, called RNAylation, may open up new avenues for phage therapy or drug…
Intranasal injection of human mitochondrial protein alleviates the progression of Parkinson’s disease
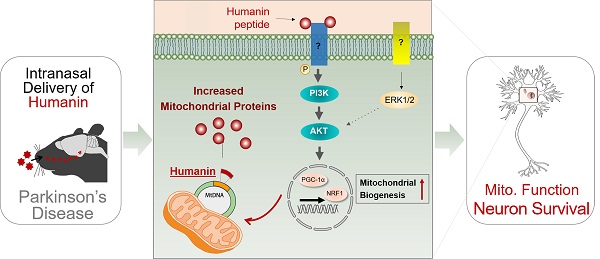
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a common neurodegenerative disease, which has become a serious problem worldwide. The typical clinical features of Parkinson’s disease include motor manifestations such as bradykinesia, static tremors, and postural instability. Although several physiological processes are related to the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease, some studies have reported the central role of mitochondrial dysfunction in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Recently, researchers from the Department of Health Sciences…
PROTAC R&D to Achieve the Latest Progress
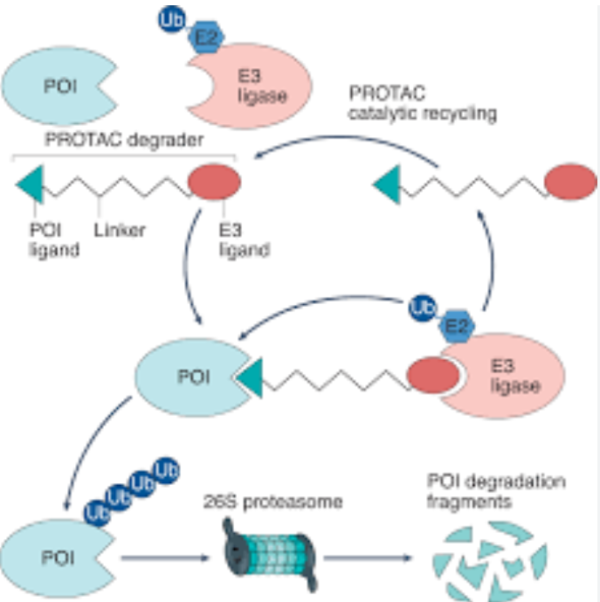
Recently, the Li Zigang/Yin Feng research group at the Shenzhen Graduate School of Peking University published a research paper titled “Targeted biomolecule regulation platform: a Split and Mix PROTAC approach” in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, reporting peptide self-assembly formed Split and Mix PROTAC (SM PROTAC), which achieved significant degradation effects on multiple targets, such as ERα, EGFR, MEK1/2, BRD2/4, CDK4/6, AR, BCR-ABL, etc. Targeted protein degradation…