Immune checkpoint inhibitors can stimulate the body’s anti-tumor immune system, but they can also have toxic effects called immune-related adverse events (irAEs). Colitis is a common and serious immune-related adverse event that can cause treatment interruption. As researchers did not observe a strong colitis response in laboratory mice treated with checkpoint inhibitors, Therefore, the understanding of the underlying mechanisms of intestinal immune-related adverse events is often hindered. Recently, an article…
Science
Host Limiting Factor ProtΑ can Inhibit HIV Infection in the Body
In a new study, researchers from research institutions such as the Walter Reed Army Research Institute in the United States confirmed previous research on host limiting factors for HIV-1. They detailed how omics reveal correlations when searching for treatment strategies. The relevant research results were published in the issue of the Science Translational Medicine journal, with the title “Single-cell transcriptomics identifies prothymosin α restriction of HIV-1 in vivo.” These…
Insufficient Sleep Can Lead to Dementia, Affecting the Clearance of Toxic Proteins in the Brain and Increasing the Risk of Dementia
This study reveals how sleep deprivation affects microglia, and finds that TREM2 mediates sleep deprivation-induced microglia overactivation, and β-Amyloid protein (Aβ) deposition increases. Long-term chronic sleep deprivation regulates inflammation and the metabolic reaction of microglia and Aβ in the brain. With the accelerating pace of society and increasing work pressure, it is sometimes particularly luxurious for modern people to have a good sleep. However, a large number of studies…
Molecular Mechanism of Melanoma Induced by CDK13 Mutant Protein
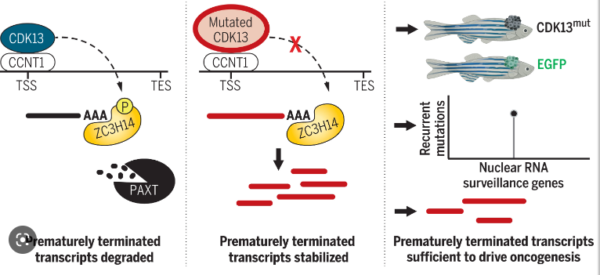
The RNA surveillance pathway can detect and interpret defective transcripts to ensure the fidelity of RNA. Recently, in a research report entitled “Oncogenic CDK13 mutations infinite nuclear RNA surveillance” published on the international journal Science, scientists from Howard Hughes Medical Research Institute and other institutions found a new mechanism that affects the occurrence of melanoma through research, which has a very broad and important significance for the treatment of multiple…
CAR-T cell therapy is expected to eliminate residual tumor cells after solid tumor surgery
In a new preclinical study, researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania found that as a method of reprogramming patients’ autoimmune cells to attack their blood cancer, CAR-T cell therapy may improve the effectiveness of surgical treatment of solid tumors. The relevant research results were published in the journal Science Advances, and the title of the paper was “Chiric antigen receiver T cells as adjuvant-therapy…
A New Method of Rewriting the Genetic Code of Bacterial Genome Can Add Many Unnatural Amino Acids to the Protein At One Time

Almost all organisms build their proteins by combining 20 different amino acids. In order to add new amino acids to this combination, scientists have redesigned genes and other protein-building tools to produce proteins with unique chemical properties that are very helpful for the manufacture of drugs. However, this kind of research is time-consuming and laborious, and usually, only one new amino acid can be added at a time. Now,…
Targeted Nucleotide Rescue Factor DNPH1 Can Improve the Sensitivity of Cancer Cells to PARP Inhibitors

Mutations in BRCA1 or BRCA2 tumor suppressor genes increase the risk of breast and ovarian cancer. In clinical practice, these cancer patients often receive targeted poly ADP ribose polymerase (PARP) inhibitors treatment. According to a recent study published in the journal Science, Stephen C. West from the Francis Crick Institute in the UK showed that inhibition of DNPH1, a protein that eliminates the cytotoxic nucleotide 5-hydroxymethyl-deoxyuridine (hmdU) monophosphate, enhances the…
The Use of Activin/GDF Fusion Protein Is Expected to Treat Pulmonary Hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension (PAH) is an insidious disease. Its symptoms may start slowly, and even before the symptoms appear, extensive damage has caused the blockage of small arteries, resulting in increased blood pressure in the lungs. When the symptoms—the most obvious being shortness of breath—are severe enough for PAH patients to seek treatment and obtain a definite diagnosis, based on currently available treatments, the patient’s chance of survival within five years…
Inhibition of the STING Protein Pathway Can Prevent Patients from Developing Graft-versus-host Disease

In a new study, researchers found that inhibiting the STING protein pathway can protect some patients from graft versus host disease (GVHD), among which, GVHD is the most serious complication of bone marrow (stem cell) transplantation. The relevant research results were published in the journal Science Translational Medicine. The title of the paper is “STING differentially regulates experimental GVHD mediated by CD8 versus CD4 T cell subsets”. Dr. Levy…
VDAC Oligomers Found to Promote Mitochondrial DNA Release and Autoimmune Responses

The immune system uses its mitochondria to self-stimulate innate and adaptive responses against infection. Reactive oxygen species (ROS), immunogenic mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) and even whole mitochondria are mobilized locally in a delicate balance, generating hotspots of inflammatory action. When the normally limiting feedback of these processes is disrupted, detrimental autoimmune responses often arise. A common sign of an abnormal immune system is the presence of antimitochondrial antibodies (AMA) in…