Recently, Professor Cao Wei’s team from the School of Chemistry and Pharmacy of Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University published a paper entitled “TRPC channels blockade organisms endotoxic cardiac dysfunction by hamming intelligent inflammation and Ca2+ leakage” in Nature Communications.
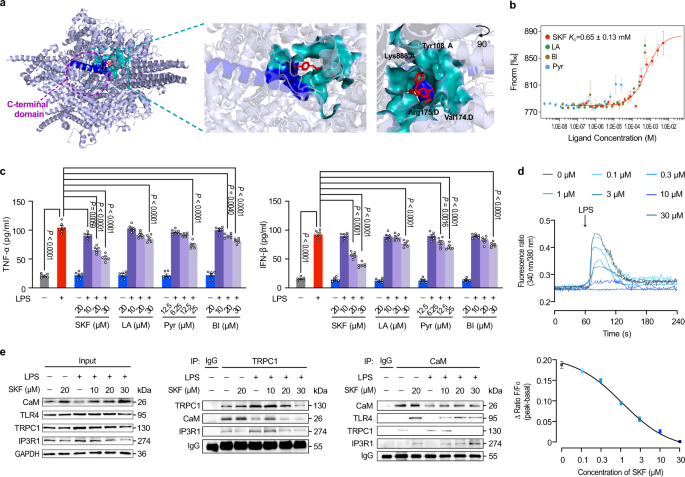
This study revealed that the classical transient receptor potential channel (TRPC) subtypes 1 and 6 can significantly regulate the cardiac inflammatory cascade reaction induced by endotoxin, thus playing a key role in endotoxemia (ETM). This study laid a theoretical foundation for the pathogenesis of endotoxin-related cardiomyopathy, and also provided a new idea for drug treatment. ETM is a thorny problem in modern severe medicine, which can lead to multiple organ failures and death. Cardiac dysfunction is considered to be one of the most serious syndromes of ETM. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is an endotoxin released by gram-negative bacteria, which plays a key role in the occurrence and development of ETM as a strong inflammatory response stimulus. Although antibiotics are the basis for the current treatment of ETM, there is no effective treatment for ETM so far.
The study found that the knockout of Trpc1 or Trpc6 in mice could significantly improve LPS-induced cardiac dysfunction and prolong the survival time. Trpc1 or Trpc6 knockout can inhibit MyD88 and TRIF-dependent inflammatory pathways by uncoupling them with molecular chaperone calmodulin (CaM), blocking the activation of macrophage and TLR4 receptor of cardiomyocytes, and blocking LPS-induced Ca2+leakage of endoplasmic reticulum, thus producing a significant protective effect on LPS induced cardiac dysfunction. It is worth mentioning that the TRPC inhibitor SKF96365 can identify the binding domain of TRPC and CaM/IP3R, showing a strong cardioprotective effect in LPS induced ETM model and mouse caecal puncture abdominal infection model, and significantly reducing mortality.
This topic clarified the key pathological mechanism of ETM cardiac dysfunction caused by TRPC, confirmed that TRPCs are potential new targets for ETM treatment, and provided a potentially efficient and specific new method for ETM treatment.
Reference
Tang N, Tian W, Ma GY, Xiao X, Zhou L, Li ZZ, Liu XX, Li CY, Wu KH, Liu W, Wang XY, Gao YY, Yang X, Qi J, Li D, Liu Y, Chen WS, Gao J, Li XQ, Cao W. TRPC channels blockade abolishes endotoxemic cardiac dysfunction by hampering intracellular inflammation and Ca2+ leakage. Nat Commun. 2022 Dec 2;13(1):7455. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-35242-0. PMID: 36460692; PMCID: PMC9718841.