GABA Receptors
About GABA Receptors
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) receptors are a type of neurotransmitter receptor found in the central nervous system (CNS). They play a critical role in regulating neuronal activity and inhibiting the transmission of signals between neurons.
There are two main types of GABA receptors: GABA-A and GABA-B. These receptors differ in their structure, mechanisms of action, and physiological effects.
GABA-A receptors are ligand-gated ion channels located on the cell membrane of neurons. When GABA, the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the CNS, binds to the GABA-A receptor, it opens the ion channel, allowing negatively charged chloride ions to enter the neuron. This influx of chloride ions results in hyperpolarization of the neuron, making it less likely to fire an action potential. GABA-A receptors are associated with fast inhibitory neurotransmission and play a significant role in regulating brain activity and controlling anxiety, sedation, and muscle relaxation.
GABA-B receptors, on the other hand, are metabotropic receptors that are coupled to intracellular signaling pathways via G-proteins. When GABA binds to the GABA-B receptor, it activates a cascade of intracellular events, ultimately leading to the inhibition of neuronal activity. GABA-B receptors are involved in slower inhibitory processes, such as long-term regulation of synaptic transmission, pain modulation, and the control of neurotransmitter release.
Both GABA-A and GABA-B receptors are widely distributed throughout the CNS and have diverse effects on brain function. They are the target of several drugs, including benzodiazepines, barbiturates, and alcohol, which enhance GABAergic inhibition and produce sedative, anxiolytic, and anticonvulsant effects.
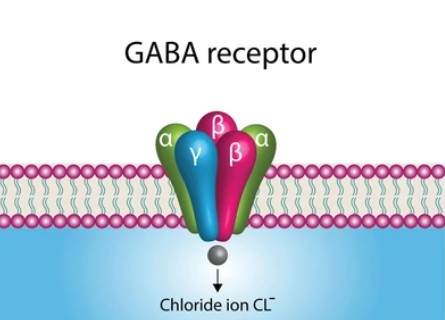
Biological Functions of GABA Receptors
Inhibition of Neuronal Activity: GABA receptors are responsible for inhibiting the firing of neurons in the CNS by allowing negatively charged chloride ions to enter the neuron. This inhibitory effect helps in preventing excessive excitation and maintaining a balance between inhibitory and excitatory neuronal activity.
Regulation of Anxiety and Stress: GABA receptors play a significant role in regulating anxiety and stress responses. Activation of these receptors leads to a decrease in neuronal activity, leading to a calming effect on the brain. An imbalance in GABAergic neurotransmission is associated with anxiety disorders and increased stress response.
Sleep Regulation: GABA receptors are involved in the regulation of sleep. Activation of GABA receptors promotes sleep by inhibiting wake-promoting neurons and promoting deep sleep states. Medications that enhance GABAergic neurotransmission, such as benzodiazepines, are used as sedatives and sleep aids.
Motor Control: GABA receptors in the spinal cord and cerebellum regulate motor control by inhibiting certain motor pathways. Activation of GABA receptors inhibits the activity of motor neurons, preventing unwanted muscle contractions and ensuring smooth movement.
Seizure Control: GABA receptors play a crucial role in preventing seizures and controlling epileptic activity. Dysfunction of GABAergic neurotransmission can lead to hyperexcitability of neurons and an increased risk of seizures. Medications that enhance GABAergic neurotransmission, such as benzodiazepines and barbiturates, are commonly used as antiepileptic drugs.
Modulation of Pain Perception: GABA receptors are involved in modulating pain perception. Activation of GABA receptors in certain areas of the brain can reduce the transmission of pain signals and modify the perception of pain. This is why drugs that enhance GABAergic activity, such as benzodiazepines, can be used as analgesics in the treatment of acute and chronic pain.
Application of GABA Receptors
GABA receptors play a crucial role in the nervous system and are involved in various physiological and pathological processes. These receptors are widely distributed in the central nervous system and are the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter receptors, modulating neuronal excitability. Here are some application areas where GABA receptors are significant:
Anxiety and Mood Disorders: GABA receptors, particularly GABA-A receptors, are the primary targets for anxiolytic drugs like benzodiazepines. Modulating these receptors can help in managing anxiety disorders and certain mood disorders.
Epilepsy: GABA receptors are involved in the regulation of neuronal excitability, and their dysfunction can lead to conditions like epilepsy. Medications targeting GABA receptors, such as benzodiazepines and barbiturates, are used as antiepileptic drugs.
Sedation and Anesthesia: GABA receptors play a central role in mediating the effects of sedative and anesthetic drugs. Understanding and targeting these receptors are crucial for developing anesthetics and sedatives that work effectively and safely.
Neurological Disorders: GABA receptors are implicated in various neurological disorders, including schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Research into these receptors may lead to a better understanding and management of these conditions.
Neurodegenerative Diseases: GABA receptors have been linked to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. Understanding their role in these conditions could pave the way for potential therapeutic interventions.
Drug Addiction: GABA receptors and the neurotransmitter GABA are involved in the reward system of the brain. Understanding how these receptors function in addiction could lead to the development of treatments for substance abuse disorders.
Sleep Disorders: GABA receptors play a role in the regulation of sleep, and medications targeting these receptors, such as benzodiazepines, are sometimes used to manage sleep disorders.
Spinal Cord Injury and Pain Management: GABA receptors are involved in modulating pain signals in the spinal cord. Research into these receptors may lead to advancements in pain management and in understanding the mechanisms of neuropathic pain.
Gastrointestinal Disorders: GABA receptors are found in the enteric nervous system, which regulates gastrointestinal function. They are potential targets for drugs aimed at treating conditions like irritable bowel syndrome.
Understanding the roles and functions of GABA receptors is critical in the development of therapeutic agents for a wide range of neurological, psychiatric, and systemic disorders. Ongoing research into GABA receptors continues to unveil their potential applications across various areas of medicine and neuroscience.
Available Resources for GABA Receptors
Creative BioMart is a biotechnology company dedicated to the field of life sciences, providing a variety of high-quality research tools and services to global scientific research institutions and biopharmaceutical companies. Including providing products covering GABA receptor-related recombinant proteins, cell and tissue lysates, protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, etc., which can be used to analyze the structure and function of GABA receptors, thus helping to in-depth study of related biological processes and disease mechanisms.
In addition, Creative BioMart also provides customization services to produce customized GABA receptor-related products according to customers' specific needs. Customers can choose the appropriate protein or cell tissue lysate according to their experimental design to obtain the best experimental results. At the same time, Creative BioMart also has extensive technical resources, including rich experimental plans, technical guidance, and data analysis support, which can help customers solve problems that may be encountered in various experiments.
The following are GABA receptor-related molecules. Click on the molecule/target to view the research resources.


