CTSS
-
Official Full Name
cathepsin S
-
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene, a member of the peptidase C1 family, is a lysosomal cysteine proteinase that may participate in the degradation of antigenic proteins to peptides for presentation on MHC class II molecules. The encoded protein can function as an elastase over a broad pH range in alveolar macrophages. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010] -
Synonyms
CTSS; cathepsin S;
- Recombinant Proteins
- Cell & Tissue Lysates
- Native Proteins
- Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads
- Assay Kits
- Cattle
- Chicken
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Human Cell
- Human Spleen
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Insect Cell
- Mammalian Cell
- Mammalian cells
- NS0
- Wheat Germ
- C
- His
- Fc
- GST
- His (Fc)
- Avi
- His|T7
- N/A
- N
- Background
- Quality Guarantee
- Case Study
- Involved Pathway
- Protein Function
- Interacting Protein
- CTSS Related Articles
- CTSS Related Research Area
What is CTSS protein?
CTSS (cathepsin S) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1q21. The preproprotein encoded by this gene, a member of the peptidase C1 family, is a lysosomal cysteine proteinase that participates in the degradation of antigenic proteins to peptides for presentation on MHC class II molecules. The mature protein cleaves the invariant chain of MHC class II molecules in endolysosomal compartments and enables the formation of antigen-MHC class II complexes and the proper display of extracellular antigenic peptides by MHC-II. The CTSS protein is consisted of 331 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 37.5 kDa.
What is the function of CTSS protein?
CTSS play a key role in a variety of physiological processes, especially in protein degradation and antigen presentation. As an enzyme in the lysozyme, it is involved in degrading proteins within cells, thus helping to maintain cellular homeostasis. In addition, CTSS is involved in the MHC II molecule-mediated antigen presentation process, which is critical for immune surveillance and T cell activation.
CTSS Related Signaling Pathway
CTSS plays a key role in MHC Class II molecule-mediated antigen presentation. This protein is involved in the degradation of the ingestion protein, which in turn allows the generated peptide to bind to MHC II and be presented to CD4+ T cells for recognition, triggering a specific immune response. In addition, CTSS is involved in regulating the activity of a variety of cytokines and chemokines, affecting the inflammatory response.
CTSS Related Diseases
CTSS is associated with a variety of diseases. For example, it plays a role in tumor development, promoting tumor invasion and metastasis by influencing the degradation and remodeling of the extracellular matrix. In addition, CTSS is also associated with certain autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and atherosclerosis.
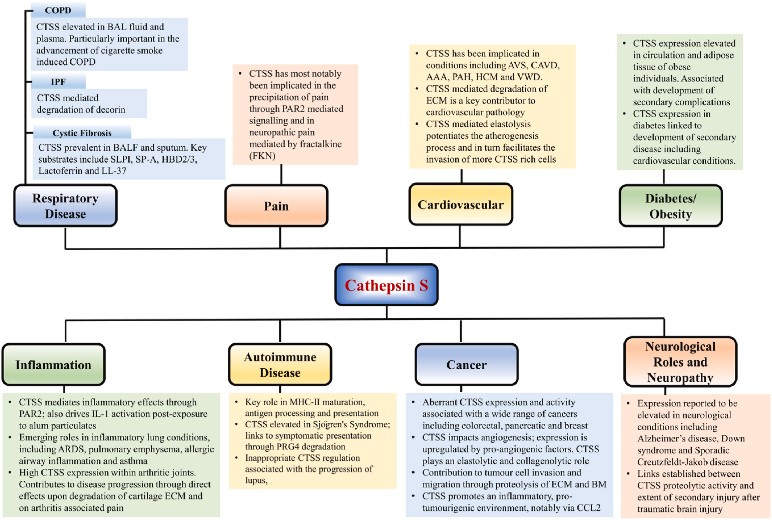
Fig1. CTSS–Activity and Pathological Implications. (Peter Smyth, 2022)
Bioapplications of CTSS
Small molecule inhibitors targeting CTSS are being investigated for the treatment of autoimmune diseases, chronic inflammatory diseases, and cardiovascular diseases. These inhibitors can reduce CTSS activity, reduce the destruction of diseased tissue, or slow the progression of atherosclerosis.
High Purity
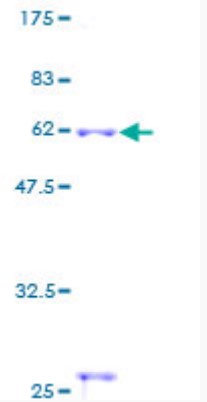
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CTSS-2118H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
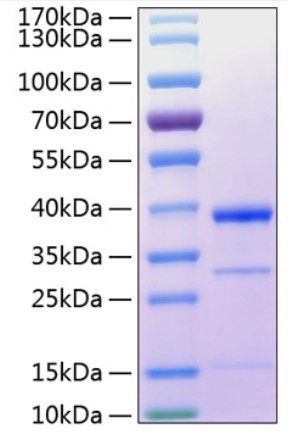
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CTSS-2695H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
Case study 1: Svenja Memmert, 2018
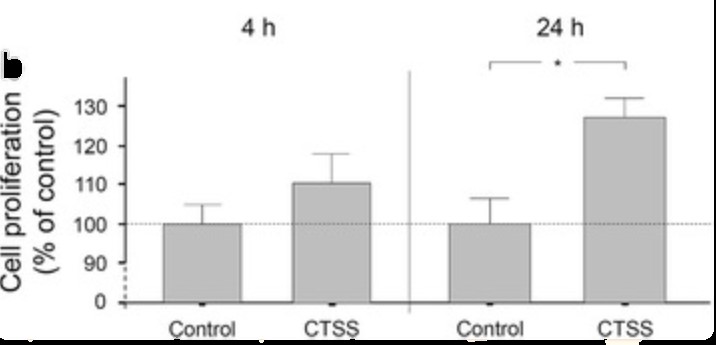
Cathepsin S is a cysteine protease, which is expressed in human periodontal ligament (PDL) cells under inflammatory and infectious conditions. This in vitro study was established to investigate the effect of cathepsin S on PDL cell wound closure. An in vitro wound healing assay was used to monitor wound closure in wounded PDL cell monolayers for 72 h in the presence and absence of cathepsin S. In addition, the effects of cathepsin S on specific markers for apoptosis and proliferation were studied at transcriptional level. Changes in the proliferation rate due to cathepsin S stimulation were analyzed by an XTT assay, and the actions of cathepsin S on cell migration were investigated via live cell tracking. Additionally, PDL cell monolayers were treated with a toll-like receptor 2 agonist in the presence and absence of a cathepsin inhibitor to examine if periodontal bacteria can alter wound closure via cathepsins. Cathepsin S enhanced significantly the in vitro wound healing rate by inducing proliferation and by increasing the speed of cell migration, but had no effect on apoptosis. Moreover, the toll-like receptor 2 agonist enhanced significantly the wound closure and this stimulatory effect was dependent on cathepsins.
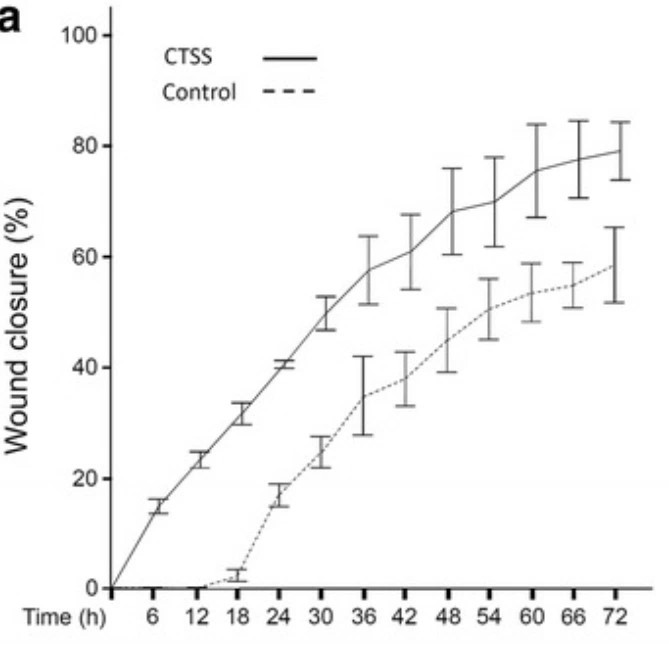
Fig1. Wound closure of PDL cell monolayers in the presence or absence of CTSS (1 ng/μl) over 72 h.
Case study 2: Min-Chieh Hsin, 2017
Hispolon, a phenolic compound isolated from Phellinus igniarius, induces apoptosis and anti-tumor effects in cancers. However, the molecular mechanism involved in hispolon-mediated tumor-suppressing activities observed in cervical cancer is poorly characterized. Here, the researchers demonstrated that treatment with hispolon inhibited cell metastasis in two cervical cancer cell lines. In addition, the downregulation of the lysosomal protease Cathepsin S (CTSS) was critical for hispolon-mediated suppression of tumor cell metastasis in both in vitro and in vivo models. Moreover, hispolon induced autophagy, which increased LC3 conversion and acidic vesicular organelle formation. Mechanistically, hispolon inhibited the cell motility of cervical cells through the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway, and blocking of the ERK pathway reversed autophagy-mediated cell motility and CTSS inhibition. The results indicate that autophagy is essential for decreasing CTSS activity to inhibit tumor metastasis by hispolon treatment in cervical cancer; this finding provides a new perspective on molecular regulation.
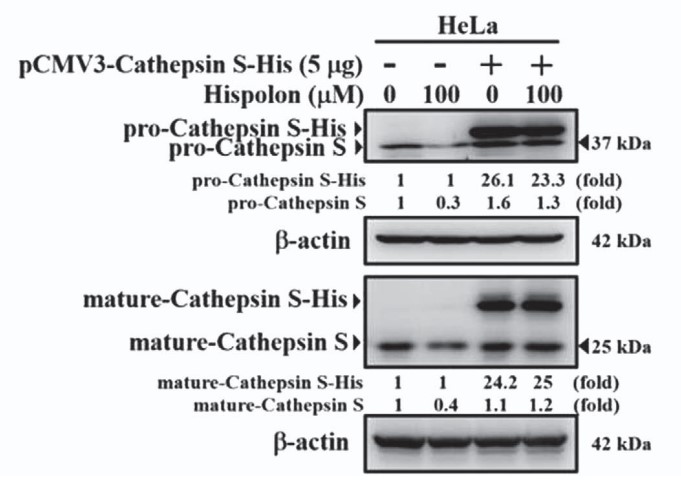
Fig3. HeLa cells transfected with pCMV3-CTSS-His plasmid 5 μg for 6 h and treated with hispolon for 24 h, then analyzed by Western blot and migration assay.
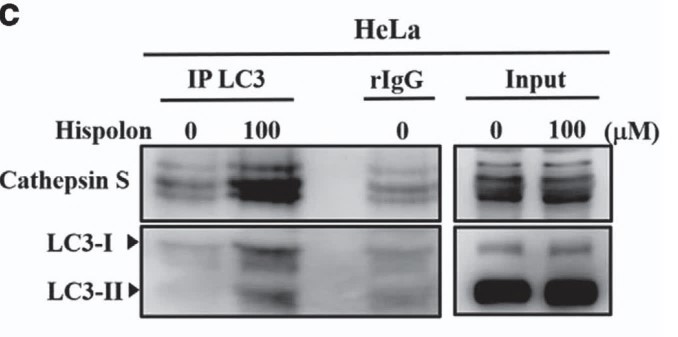
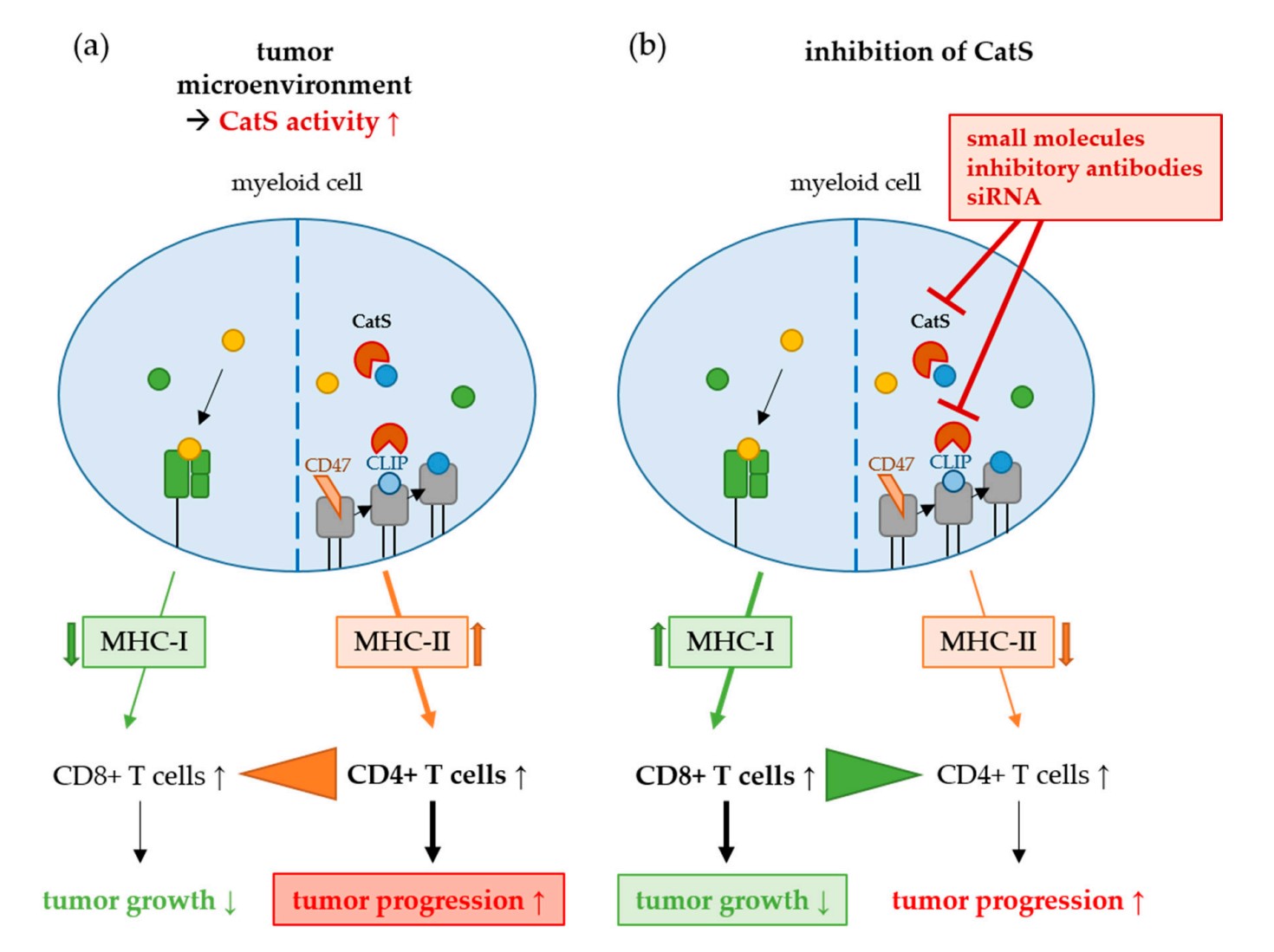
Fig1. Role of cathepsin S (CatS) in the immune-suppressive milieu of the tumor microenvironment (TME). (Natalie Fuchs, 2020)
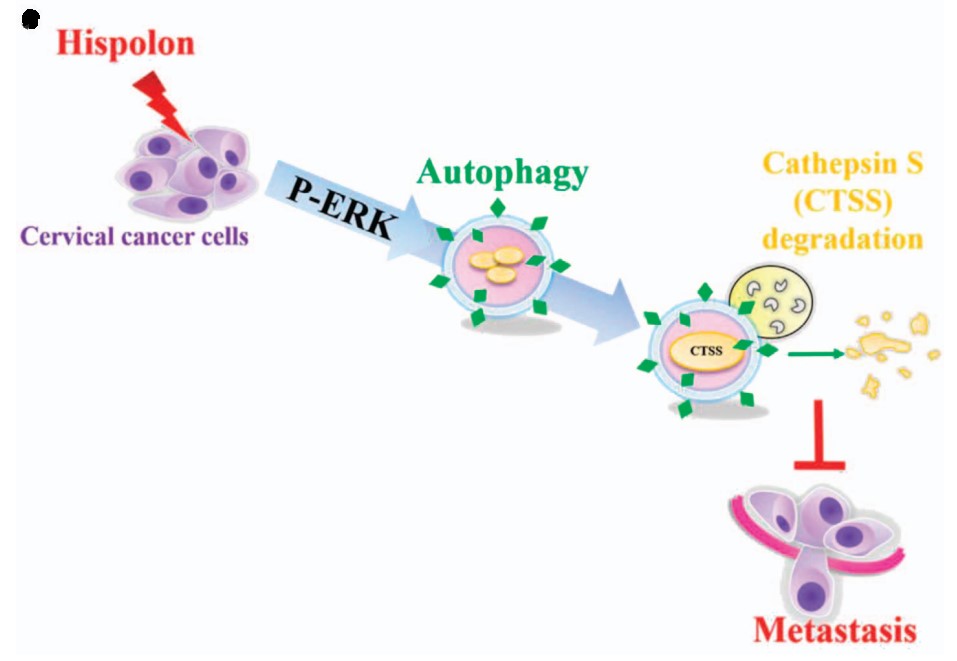
Fig2. The schematic representation of anti-metastasis effects of hispolon in human cervical cancer cell. (Min-Chieh Hsin, 2017)
CTSS involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CTSS participated on our site, such as Adaptive Immune System, Antigen processing and presentation, Antigen processing-Cross presentation, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CTSS were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Adaptive Immune System | ASB18;CD200R2;UBE2V1;NRG3;NCR3LG1;ASB6;FGFR1B;TRIM11;AP2M1 |
| Antigen processing and presentation | HLA-DMA;KIR2DL1;HLA-DRA;IFNG;CD8A;HLA-DPB1;HLA-G;HLA-DRB3;HSPA5 |
| Antigen processing-Cross presentation | CTSS;CTSL2;CD207;FCGR1B;CYBB;SEC61B;CTSL1;CYBA |
| Assembly of collagen fibrils and other multimeric structures | LOXL4;BMP1A;CTSS;TLL1;LOXL1;COL8A1A;CTSB;BMP1;MMP13 |
| Class I MHC mediated antigen processing & | TPP2;RNF34;RNF25;ERAP2;TRIM39;BLMH;UBE2V2;ASB13;LRSAM1 |
| presentation | NPEPPS;FBXO17;RBCK1;UBE2L6;CTSS;TRIM50;RNF14;ASB3;WWP1 |
| Collagen formation | COL6A2;COL1A2;COL17A1A;COL5A3B;COL9A1B;COL4A4;BMP1;COL28A1D;LOX |
| Degradation of the extracellular matrix | LOC100686744;COL19A1;MGC174857;CTSG;MMP13;ADAM15;FURINB;MMP11;ADAMTS1 |
| Endosomal/Vacuolar pathway |
CTSS has several biochemical functions, for example, collagen binding, cysteine-type endopeptidase activity, fibronectin binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CTSS itself. We selected most functions CTSS had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CTSS. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| collagen binding | ITGA9;Itga10&Itgb1;SMAD3;PCOLCE2;PDGFA;GPR56;ITGA3;CD44;HSD17B12 |
| cysteine-type endopeptidase activity | CTSW;CTSJ;CTSL2;SFRP1;CFLARA;USP15;CASPB;USP40;CTSM |
| fibronectin binding | LPA;ITGB3;SDC4;CTSL1;FBLN1;MYOC;CTSK;IGFBP5B;IGFBP5 |
| laminin binding | RPSA;ITGA7;LYPD5;NID1;ACHE;CTSS;ECM1;ITGA9;LGALS1 |
| proteoglycan binding | CECR1A;NID1;COL5A1;CECR1;CTSB;CTSL1;THBS1;CTSS;FCN2 |
CTSS has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CTSS here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CTSS.
tktA; q9rid8_yerpe
- Q&As
- Reviews
Q&As (6)
Ask a questionThe function of CTSS proteins can be studied through gene knockout or knockdown techniques, such as using techniques such as CRISPR-Cas9 or RNAi. These techniques can create cellular models of missing or reduced CTSS proteins to observe their effects on cell death, among other things.
Expression level of CTSS protein can be detected by immunohistochemistry, western blotting, and real-time quantitative PCR.
CTSS proteins promote cell death by degrading proteins inside cells. During apoptosis, CTSS proteins degrade key proteins within cells, leading to cell death.
The interaction between CTSS proteins and other proteins is regulated by the formation of complexes or the regulation of signal transduction pathways. These interactions can be influenced by a variety of factors, such as ion concentrations, neurotransmitters, and growth factors.
Some studies have shown that the expression level of CTSS protein may be associated with the onset and progression of certain diseases. For example, in some cancers, the expression level of the CTSS protein may change.
It is mainly expressed in lysosomes, which is one of the major proteases in lysosomes.
Customer Reviews (3)
Write a reviewHigh catalytic efficiency, short time, saving time.
The solubility is very good and can be easily dissolved in various buffers.
Anti-pollution ability is very strong, not easy to be polluted.
Ask a Question for All CTSS Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All CTSS Products
Required fields are marked with *


