NFKBIA
-
Official Full Name
nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cell extracts inhibitor, alpha
-
Overview
IκBα (Inhibitor of Nuclear Factor (NF)-κB α isoform) is a member of the IκB protein family with a MW of 40 kDa. IκBα is ubiquitously expressed among mammals. Located at IκBα's N-terminus is a signal response domain which contains serine residues that can be phosphorylated, while the C-terminus contains a PEST domain, a common feature among proteins with high turnover rates. As with all members of the IκB family, IκBα possesses ankyrin repeats approximately 33 amino acids in length, which mediate binding to the Rel homology region of NF-κB. The interaction of IκBα with NF-κB masks the nuclear localization sequence of NF-κB, preventing NF-κB translocation to the nucleus. A variety of stimuli can activate gene expression by liberating NF-κB through the degradation of IκBα. These stimuli include the proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-1β, chemokines, PMA, growth factors, LPS, UV irradiation, and viral infection, as well as various chemical and physical stresses. The series of events leading to this liberation is well-defined. In response to stimulus, Ser32/36 of IκBα are phosphorylated, which provides a signal for IκBα E3 ligase, a protein complex composed of SKP-1, Cul-1, Roc1, and Fbw1. IκBα E3 ligase polyubiquitinates IκBα at lysine residues 21 and 22, and the polyubiquitinated IκBα is then targeted to the 26S proteasome for degradation. Liberated NF-κB is transported across the nuclear membrane, where it activates transcription by binding to the consensus sequence GGRNNYYCC, which is found in the promoter regions of a large number of genes including IL-6, VEGF, VCAM-1, ICAM-1, HIV long terminal repeat, and many others. The initial event which targets IκBα for degradation is phosphorylation of Ser32/36. This phosphorylation is catalyzed by a protein complex known as IKK (IκB kinase). IKK contains two kinase subunits designated IKKα (MW=85 kDa) and IKKβ (MW=87 kDa), and scaffold protein designated IKKγ/NEMO (MW=48 kDa). The kinetic properties of IKK are regulated by complex formation as well as by phosphorylation events catalyzed by upstream kinases including members of the MAPK cascade, the SAPK/JNK cascade and NIK. Through its regulation of NF-κB, IκBα controls immune and inflammatory responses, cell division, and apoptosis. Numerous disease states including arthritis, asthma, and inflammatory bowel disease are associated with loss of IκBα regulation. The importance of regulation of IκBα in cancer is underscored by the observation that multiple myelomas often possess polymorphisms at IκBα regulatory sites, and certain symptoms can be ameliorated using the proteasome inhibitor PS-341 which favors the sequestration of NF-κB in the cytoplasm. -
Synonyms
IKBA; MAD-3; NFKBI; I-kappa-B-alpha; IkappaBalpha; NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha; ikB-alpha; major histocompatibility complex enhancer-binding protein MAD3; nuclear factor of kappa light chain gene enhancer in B-cells;
- Recombinant Proteins
- Cell & Tissue Lysates
- Antibody
- Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads
- Chicken
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Rhesus Macaque
- E. coli
- E.coli
- HEK293
- HEK293T
- Mammalian Cell
- Rabbit
- GST
- His
- His (Fc)
- Avi
- His|MBP
- Myc
- DDK
- Myc|DDK
- N/A
- N
- Background
- Quality Guarantee
- Case Study
- Involved Pathway
- Protein Function
- Interacting Protein
- NFKBIA Related Articles
- NFKBIA Related Research Area
What is NFKBIA protein?
NFKBIA (NFKB inhibitor alpha) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 14 at locus 14q13. This gene encodes a member of the NF-kappa-B inhibitor family, which contain multiple ankrin repeat domains. The encoded protein interacts with REL dimers to inhibit NF-kappa-B/REL complexes which are involved in inflammatory responses. The encoded protein moves between the cytoplasm and the nucleus via a nuclear localization signal and CRM1-mediated nuclear export. The NFKBIA protein is consisted of 317 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 35.6 kDa.
What is the function of NFKBIA protein?
NFKBIA protein is an important cytokine that regulates the activity of nuclear factor κB (NF-κB). NF-κB is a transcription factor that plays a key role in immune and inflammatory responses. NFKBIA protein inhibits NF-κB activity by binding to NF-κB, preventing its entry into the nucleus and activating gene transcription. In this way, NFKBIA protein can regulate a variety of biological processes, including immune response, inflammatory response, cell proliferation, and apoptosis.
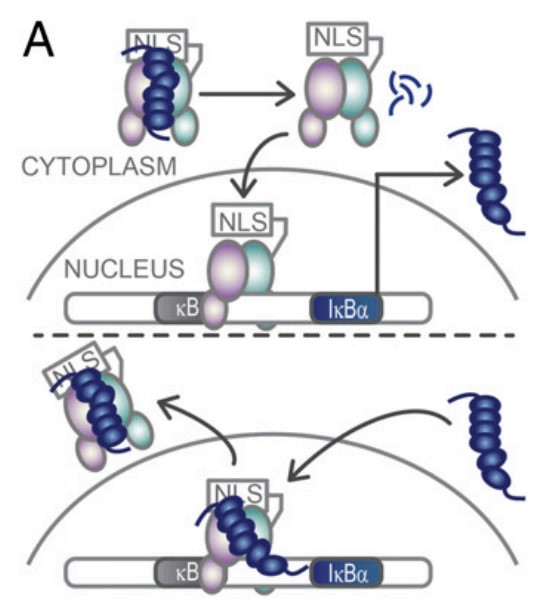
Fig1. IκBα sequesters NFκB in the cytoplasm. (Holly E Dembinski, 2017)
NFKBIA Related Signaling Pathway
NFKBIA protein is an important signaling pathway regulator, mainly involved in the nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway. NF-κB is a transcription factor widely found in cells and is involved in regulating many physiological and pathological processes, such as immune response, inflammation, cell growth, and apoptosis. NFKBIA proteins regulate intracellular signaling by binding to the NF-κB subunit and inhibiting its activity. In addition, NFKBIA is involved in other signaling pathways, such as tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) and interleukin receptor (IL-1R), which play important roles in cellular stress, inflammation, and immune responses.
NFKBIA Related Diseases
Abnormal expression or mutation of NFKBIA has been observed in many types of cancer because NF-kB plays a key role in cell proliferation, anti-apoptosis, and inflammation. For example, breast cancer, lung cancer, colon cancer, etc. In addition, abnormal NFKBIA may also be associated with immune diseases, inflammatory diseases, and neurodegenerative diseases.
Bioapplications of NFKBIA
The application of NFKBIA protein is mainly focused on the research and treatment of diseases related to dysregulation of NF-κB activity, such as cancer, autoimmune diseases, inflammatory diseases, and neurodegenerative diseases. In addition, due to its important role in cellular stress response, NFKBIA may also have potential applications in areas such as anti-aging and tissue repair.
High Purity
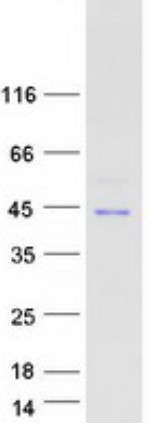
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (NFKBIA-3784H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
High Bioactivity
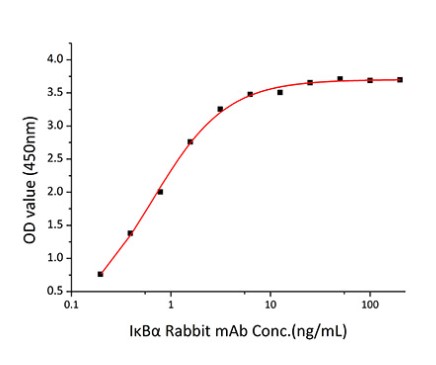
Fig2. Activity Data. (NFKBIA-2581H)
Case study 1: Yanquan Li, 2023
The nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway regulates specific immunological responses and controls a wide range of physiological processes. NF-κB inhibitor alpha (IKBA) is an NF-κB inhibitory mediator in the cytoplasm that modulates the nuclear translocation and DNA binding activities of NF-κB proteins. However, whether the upstream cascade of the canonical NF-κB signaling pathway has physiological roles independent of IKBA-mediated transcriptional activation remains unclear. Herein the researchers investigated the function of IKBA in mature sperm in which transcriptional and translational events do not occur. IKBA was highly expressed in human sperm. The repression of IKBA phosphorylation by its inhibitor Bay117082 markedly enhanced sperm motility. On the contrary, lipopolysaccharide-stimulated IKBA phosphorylation significantly decreased sperm motility. Nevertheless, Bay117082 treatment did not affect the motility of IKBA-knockout sperm. Further, untargeted metabolomic analysis and pharmacological blocking assays revealed that the Bay117082-induced increase in sperm motility was attributable to fatty acid β-oxidation (FAO) enhancement.
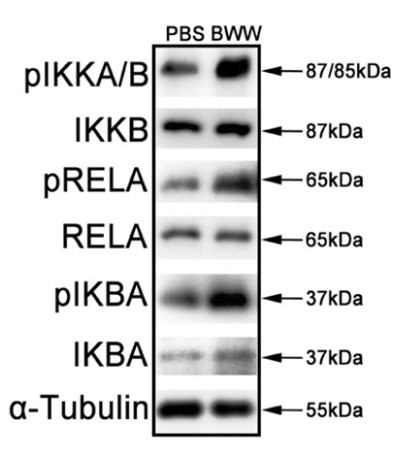
Fig1. Phosphorylation states of IKKA/B, RELA and IKBA proteins in human sperm in PBS and BWW media. α-Tubulin served as the loading control.
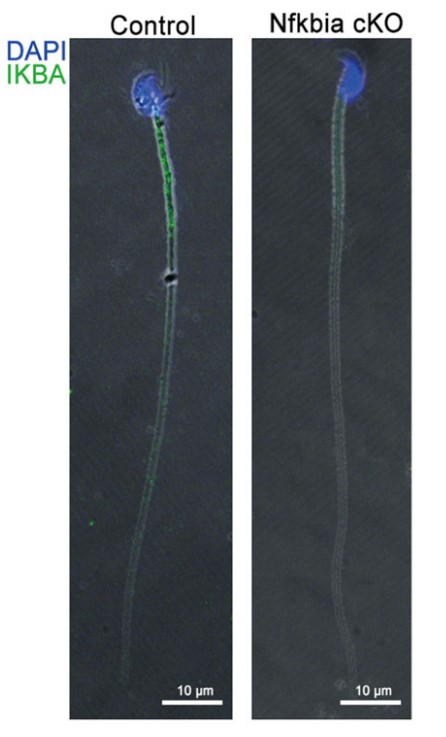
Case study 2: Holly E Dembinski, 2017
Stress-response transcription factors such as NFκB turn on hundreds of genes and must have a mechanism for rapid cessation of transcriptional activation. The researchers recently showed that the inhibitor of NFκB signaling, IκBα, dramatically accelerates the dissociation of NFκB from transcription sites, a process they have called "stripping." To test the role of the IκBα C-terminal PEST (rich in proline, glutamic acid, serine, and threonine residues) sequence in NFκB stripping, a mutant IκBα was generated in which five acidic PEST residues were mutated to their neutral analogs. This IκBα(5xPEST) mutant was impaired in stripping NFκB from DNA and formed a more stable intermediate ternary complex than that formed from IκBα(WT) because DNA dissociated more slowly. NMR and amide hydrogen-deuterium exchange mass spectrometry showed that the IκBα(5xPEST) appears to be "caught in the act of stripping" because it is not yet completely in the folded and NFκB-bound state. When the mutant was introduced into cells, the rate of postinduction IκBα-mediated export of NFκB from the nucleus decreased markedly.
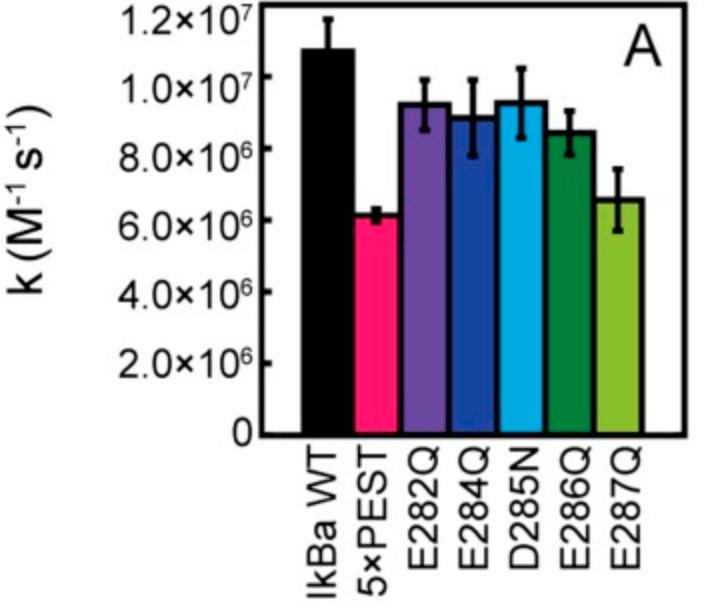
Fig3. Rates of IκBα PEST mutants associating with NFκB by stopped-flow fluorescence following the native IκBα Trp258.
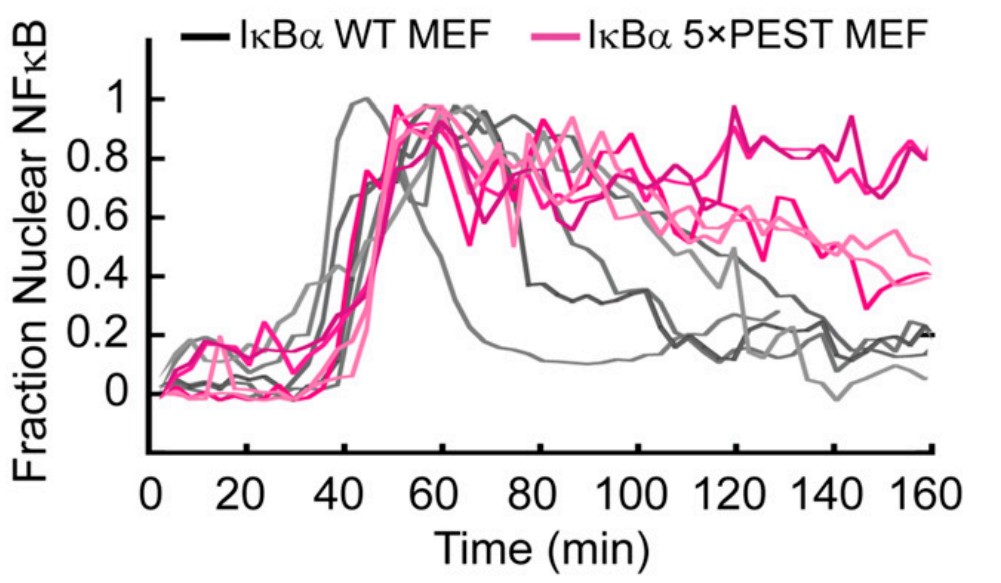
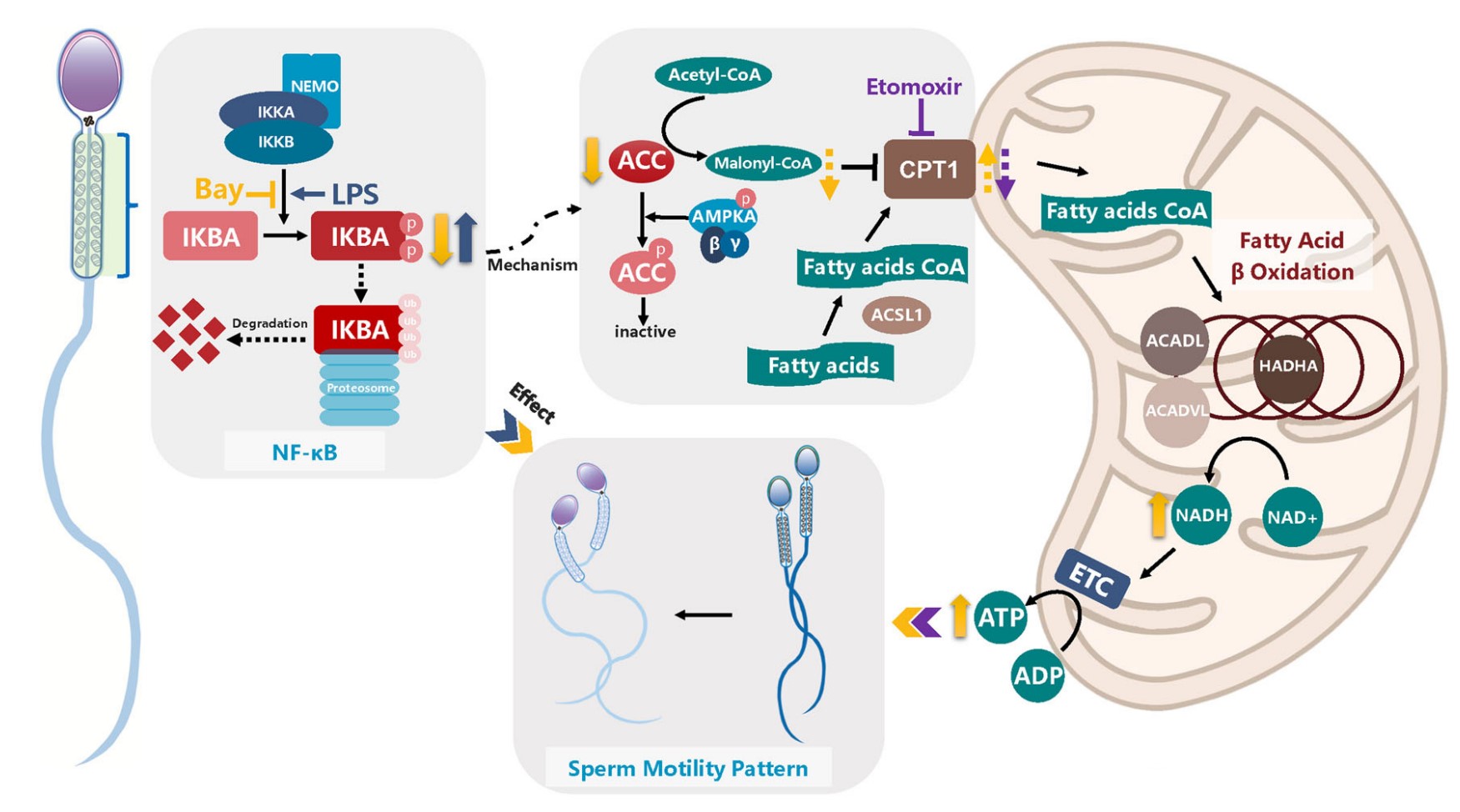
Fig1. Diagram depicting the regulation mechanism of IKBA phosphorylation in sperm motility. (Yanquan Li, 2023)
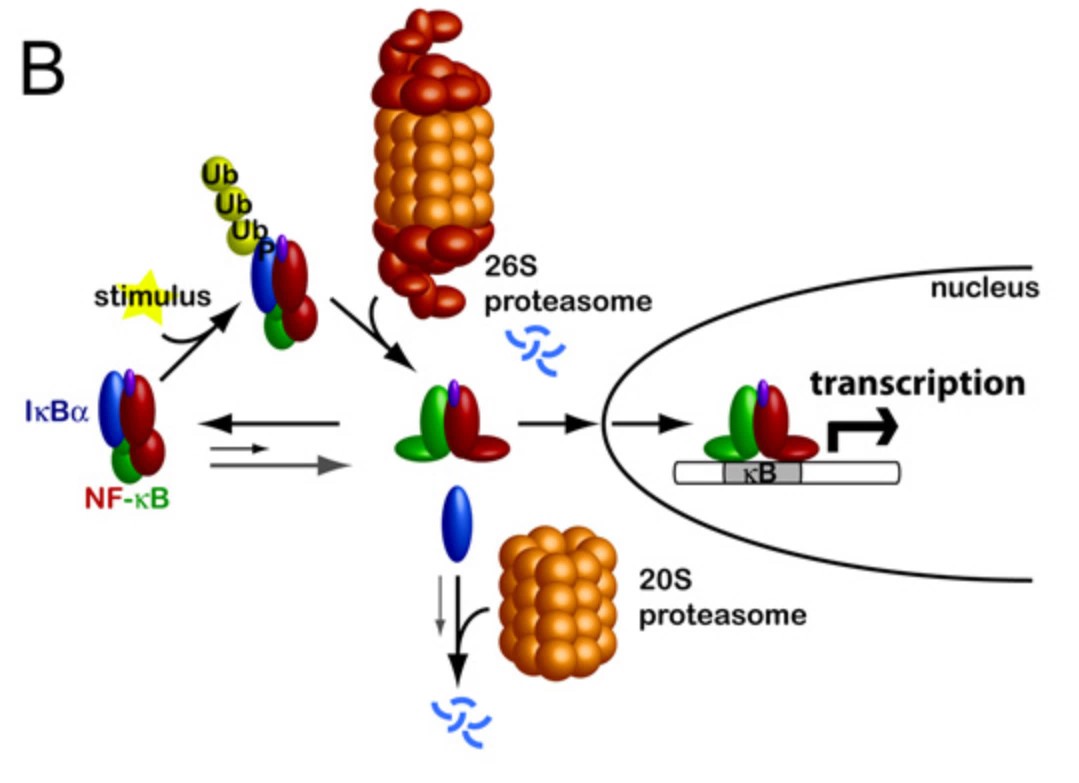
Fig2. Schematic outlining stimulus-induced activation of NF-κB. (Stephanie M E Truhlar, 2008)
NFKBIA involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways NFKBIA participated on our site, such as cAMP signaling pathway, Chemokine signaling pathway, NF-kappa B signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with NFKBIA were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| cAMP signaling pathway | GABBR2;CREB3L1;PDE4A;PLN;HTR1F;MAPK10;GNAI1;GLP1R;FXYD1 |
| Chemokine signaling pathway | GNG3;CCR9;VAV1;GNAI1;LYN;NRAS;PRKCB;CCL11;IKBKB |
| NF-kappa B signaling pathway | LTB;PLCG2;VCAM1;TNFAIP3;RIPK1;TNFRSF1A;LTBR;MYD88;TRAF1 |
| Apoptosis | HRK;DBNLB;CASP7;PRKAR2AB;BCAP31;PIK3R3A;CDK5RAP2;PPP3R1B;NTRK1 |
| Osteoclast differentiation | MAPK8;LILRA4;PLCG2;IKBKG;FCGR3A;MAP2K1;IFNAR2;CYBB;SIRPA |
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | RAC1;MYD88;CCL5;MAP2K6;CD80;IFNA8;IFNA10;IFNA2;AKT1 |
| NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | CASP8;NFKBIAA;ERBB2IP;RIPK2;CARD8;MAP3K7;TAB3;CXCL1;NFKB1 |
| RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | ATG12;IFNA17;IL8L2;NFKBIAB;RIPK1;IFNW1;OTUD5A;IFNA6;MAPK9 |
| Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway | DDX58;POLR3H;IKBKE;POLR3K;IFN-a;RIPK1L;TMEM173;IL1B;MAVS |
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | PIK3R3;NFKBIB;CD8A;CARD11;IL5;DEF6A;FOS;SHB;CD8B |
| B cell receptor signaling pathway | MAP2K1;IKBKG;HRAS;ITK;TTC6;RAC2;GRB2;LILRB3;CTNNB2 |
| TNF signaling pathway | RPS6KA5;RIPK1;TRADD;MAPK11;MAP2K4;FOS;CASP8;MMP3;MAP3K5 |
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | PIK3CA;SHC4;PIK3CB;RELA;MAP3K1;RPS6KA2;PSEN1;GAB1;NTRK3 |
| Adipocytokine signaling pathway | PRKAA1;SOCS3;NFKBIE;ACSL3B;PRKAB1B;LEP;PRKAG2A;POMC;PRKAG1 |
| Insulin resistance | CREB3L2;SLC27A2;PRKAG2;TBC1D4;PTEN;PPP1R3CA;PRKCBA;PTPRF;G6PCA.1 |
| Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection | IKBKG;TJP1;ATP6V1G3;LYN;ATP6V0B;ADAM17;CXCR1;ATP6V1H;ATP6V1E2 |
| Shigellosis | ITGA5;SRC;MAPK3;PFN4;MAPK10;NFKBIA;RIPK2;BTRC;HCLS1 |
| Legionellosis | CLK1;APAF1;SAR1B;HSPA6;NFKBIA;HSPD1;BCL2L13;HSPA1A;NAIP7 |
| Leishmaniasis | STAT1;TRAF6;HLA-DMB;HLA-DRB3;TLR2;MAPK1;NCF4;FCGR2A;HLA-DPB1 |
| Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis) | TGFBR2;PPP2R2D;MAPK12;PIK3R3;PIK3CB;C1QC;NOS2;GNAL;CD3E |
| Toxoplasmosis | LAMB3;MAPK12;HLA-DPA1;LAMB2;PDPK1;STAT1;LAMA5;XIAP;MAP2K6 |
| Hepatitis C | IRF1;TRAF2;PPP2R2B;TRADD;IFNAR2;CLDN11;GSK3B;PIK3R3;TBK1 |
| Hepatitis B | IKBKE;CXCL8;YWHAZ;IFNA14;MAP2K4;IRF3;PRKCB;CREB3L3;NFKBIA |
| Measles | IFNA14;STAT2;CCND1;CD209A;TACR1;PIK3CB;IFNA12;IFNA5;MAVS |
| Influenza A | HLA-DRB5;MAP2K4;BLB1;HLA-DRB3;PABPN1L;HLA-DQB1;MAPK9;IFNB;PIK3CA |
| HTLV-I infection | STAT5B;MAP2K4;AKT1;NFATC1;RANBP1;CCND1;MYB;HLA-DMB;KAT2A |
| Herpes simplex infection | PPP1CA;BLB2;SRSF2B;PVRL1;SRSF6;HLA-F;HLA-DRB3;EIF2AK3;RNASEL |
| Epstein-Barr virus infection | TNFAIP3;PLCG2;HLA-DRB3;PIK3CG;TP53;PSMD11;NCOR2;POLR2J2;PSMC1 |
| Pathways in cancer | FGF16;MMP1A;GNB2;PTCH1;TGFBR1;PPARD;GNB4;FZD6;BIRC3 |
| Viral carcinogenesis | TRAF5;HIST1H2BH;GTF2H4;RBPJL;NFKBIA;HRAS;GRB2;HIST1H2BM;CREB3L1 |
| Prostate cancer | CREB3L2;PIK3CB;RAF1;INSRR;SMARCD1;SPRY1;ARID1A;IGF1;GSTP1 |
| Chronic myeloid leukemia | CCND1;CDK6;MAPK3;BRAF;CBLC;NFKB1;RELA;BCL2L1;IKBKG |
| Small cell lung cancer | LAMA4;PIK3CD;PIK3CG;AKT1;IKBKG;NFKB1;LAMA3;TRAF6;PIK3CA |
NFKBIA has several biochemical functions, for example, NF-kappaB binding, enzyme binding, heat shock protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by NFKBIA itself. We selected most functions NFKBIA had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with NFKBIA. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| NF-kappaB binding | HDAC3;COMMD6;RNF25;NFKBIA;CDKN2A;HDAC2;COMMD7;BRMS1;FAF1 |
| enzyme binding | DNM2;UBE2L3;CTNNBL1;BRCA1;PLSCR4;PPP1R3B;PRKCH;KDM1A;MARCH6 |
| heat shock protein binding | CDC37L1;PPID;PACRG;HSPA9;HSPA1L;TFAM;TPR;GPR37;GRXCR2 |
| identical protein binding | TRP63;SMN2;TPRG1L;TTN;TYSND1;HAND1;NUDT16;CLDN4;PLN |
| nuclear localization sequence binding | TNPO3;KPNA5;TNPO2;KPNB3;KPNB1;IPO5;KPNA3;BRAP;NFKBIA |
| protein binding | ZFPL1;NR0B2;PSMB10;ULK3;PRKCB;ASB13;CDC25C;MUC7;FAIM |
| protein complex binding | PDCL;PPP1R9B;NCK2;MTAP1B;ATM;STRN;RELA;EPCAM;RPH3A |
| transcription factor binding | TRIB1;TFDP1;SIX2;SRY;CHCHD2;RARA;NIF3L1;HEYL;ATOH8 |
| ubiquitin protein ligase binding | DTX1;CUL3A;ATP6V0C;AKTIP;UBE2G1B;WFS1;SNX9;SMAD2;RAD18 |
NFKBIA has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with NFKBIA here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of NFKBIA.
RELA
- Q&As
- Reviews
Q&As (6)
Ask a questionThe interaction between NFKBIA protein and NF-κB can be identified by co-immunoprecipitation, bimolecular fluorescence complementation, etc. In addition, these methods can also be used to study the interaction sites and mechanisms of action between them.
Knockdown of the NFKBIA gene leads to increased cell growth arrest and apoptosis, which may be related to the aberrant activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway.
The effect on the expression level and activity of molecules related to the NF-κB signaling pathway can be observed by overexpressing or knocking down NFKBIA protein. In addition, studies can also be performed with specific knockout or mutant cell lines.
Its role in physiological and pathological processes can be studied by specifically knocking out the NFKBIA gene using specific short hairpin RNA or zinc finger nuclease technology.
Studies have shown that the expression level of NFKBIA protein is associated with the occurrence and progression of a variety of diseases. For example, in some cancers, the expression levels of the NFKBIA protein are reduced or missing, leading to aberrant activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway.
When cells are stimulated by inflammation, the NFKBIA protein is phosphorylated, causing its dissociation from NF-κB. After dissociation, NF-κB is transferred to the nucleus and activates the transcription of specific genes. In addition, NFKBIA protein can further regulate the activity of NF-κB by interacting with other proteins.
Customer Reviews (3)
Write a reviewI am very happy with the results, they performed very well in my experiments.
It has high sensitivity and strong specificity.
It is easy to use and requires little preparation before the experiment.
Ask a Question for All NFKBIA Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All NFKBIA Products
Required fields are marked with *


