PAK2
-
Official Full Name
p21 protein (Cdc42/Rac)-activated kinase 2
-
Overview
Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PAK2 gene. The p21 activated kinases (PAK) are critical effectors that link Rho GTPases to cytoskeleton reorganization and nuclear signaling. The PAK proteins are a family of serine/threonine kinases that serve as targets for the small GTP binding proteins, CDC42 and RAC1, and have been implicated in a wide range of biological activities. The protein encoded by this gene is activated by proteolytic cleavage during caspase-mediated apoptosis, and may play a role in regulating the apoptotic events in the dying cell. -
Synonyms
p21 protein (Cdc42/Rac)-activated kinase 2; PAK65; PAKgamma; PAK2; p21-activated kinase 2; S6/H4 kinase; p21 (CDKN1A)-activated kinase 2; EC 2.7.11.1; PAK-2; Gamma-PAK; p58;
- Recombinant Proteins
- Cell & Tissue Lysates
- Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads
- Human
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Rhesus Macaque
- E. coli
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Insect (sf21)
- Insect Cell
- Mammalian Cell
- Sf9 Insect Cell
- GST
- His
- His (Fc)
- Avi
- T7,His
- N/A
- Background
- Quality Guarantee
- Case Study
- Involved Pathway
- Protein Function
- Interacting Protein
- PAK2 Related Articles
- PAK2 Related Research Area
- PAK2 Related Signal Pathway
What is PAK2 protein?
PAK2 (p21 (RAC1) activated kinase 2) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 3 at locus 3q29. Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PAK2 gene. The p21 activated kinases (PAK) are critical effectors that link Rho GTPases to cytoskeleton reorganization and nuclear signaling. The PAK proteins are a family of serine/threonine kinases that serve as targets for the small GTP binding proteins, CDC42 and RAC1, and have been implicated in a wide range of biological activities. The PAK2 protein is consisted of 524 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 58 kDa.
What is the function of PAK2 protein?
Full-length PAK2 stimulates cell survival and cell growth. It phosphorylates MAPK4 and MAPK6 and activates the downstream target MAPKAPK5, a regulator of F-actin polymerization and cell migration. PAK2 phosphorylates many other substrates including histone H4 and JUN. Additionally, it associates with ARHGEF7 and GIT1 to perform kinase-independent functions such as spindle orientation control during mitosis. On the other hand, apoptotic stimuli such as DNA damage lead to caspase-mediated cleavage of PAK2, generating PAK-2p34, an active p34 fragment that translocates to the nucleus and promotes cellular apoptosis involving the JNK signaling pathway.
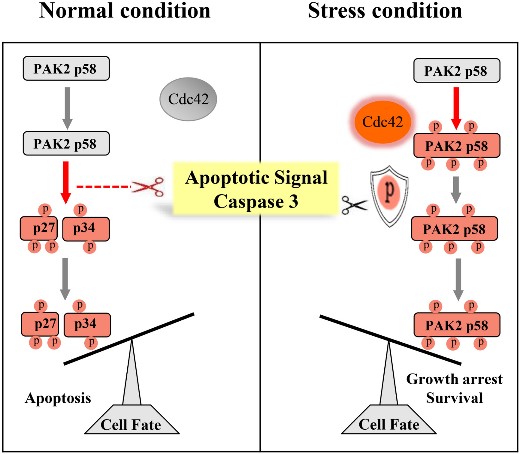
Fig1. Proposed working model for the differential activation of PAK2 by Cdc42 and caspase 3. (John Huang, 2020)
PAK2 Related Signaling Pathway
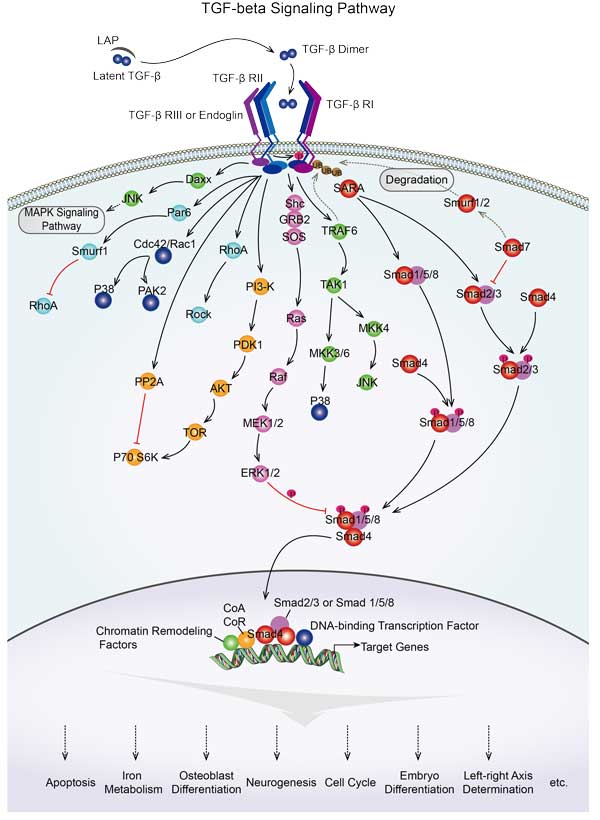
The RAC1 signaling pathway is an important signaling pathway involved in a variety of cellular functions and biological processes. PAK2 phosphorylation activates RAC1, thereby regulating cell morphology, migration, proliferation and other physiological processes. In addition, PAK2 can also interact with other signaling pathways, such as Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, ERK/MAPK signaling pathway, TGF-β signaling pathway, etc.
PAK2 Related Diseases
PAK2 is abnormally expressed in a variety of cancers, including breast, lung, colon, and stomach cancers. Mutations in the PAK2 gene can lead to the onset and development of brain aneurysms or heart valve disease. At the same time, PAK2 deficiency can lead to abnormal function of the immune system, resulting in susceptibility to infection, and then the development of immunodeficiency syndrome.
Bioapplications of PAK2
The study of the PAK2 protein has enabled drug developers to develop novel drugs for diseases such as cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. These drugs can regulate the relevant signaling pathways by inhibiting or activating the action of the PAK2 protein, thereby enabling the treatment and prevention of the disease.
High Purity
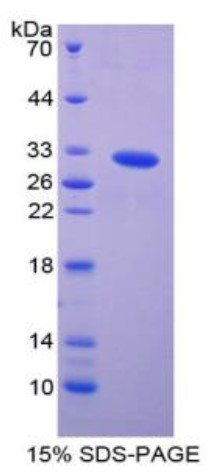
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PAK2-767H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
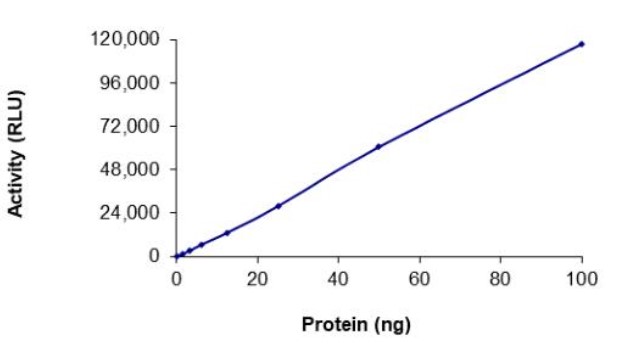
Fig2. Activity Data. (PAK2-6276H)
Case study 1: Lisbeth L V Møller, 2020
Muscle contraction is an important alternative pathway to increase glucose transport in insulin-resistant states, but the intracellular signaling mechanisms are not fully understood. PAK1 and PAK2 could be downstream effectors of Rac1 in contraction-stimulated glucose transport. The current study aimed to test the hypothesis that PAK1 and/or PAK2 regulate contraction-induced glucose transport.
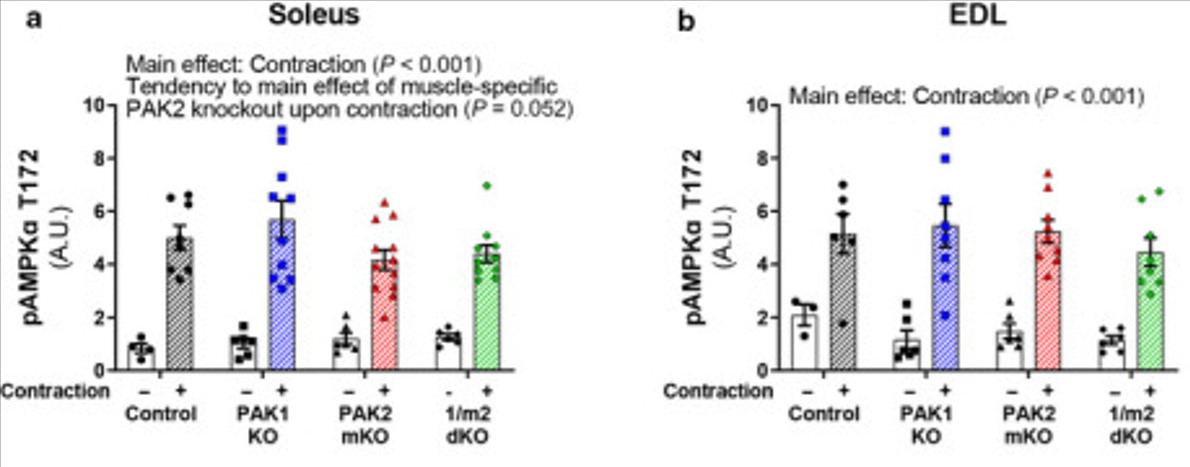
Glucose transport was measured in isolated soleus and extensor digitorum longus (EDL) mouse skeletal muscle incubated either in the presence or absence of a pharmacological inhibitor (IPA-3) of group I PAKs or originating from whole-body PAK1 knockout, muscle-specific PAK2 knockout or double whole-body PAK1 and muscle-specific PAK2 knockout mice. Lack of PAK2, either alone (-13%) or in combination with PAK1 (-14%), partly reduced contraction-stimulated glucose transport compared to control littermates in EDL, but not soleus muscle. Contraction-stimulated glucose transport in isolated glycolytic mouse EDL muscle is partly dependent on PAK2, but not PAK1.
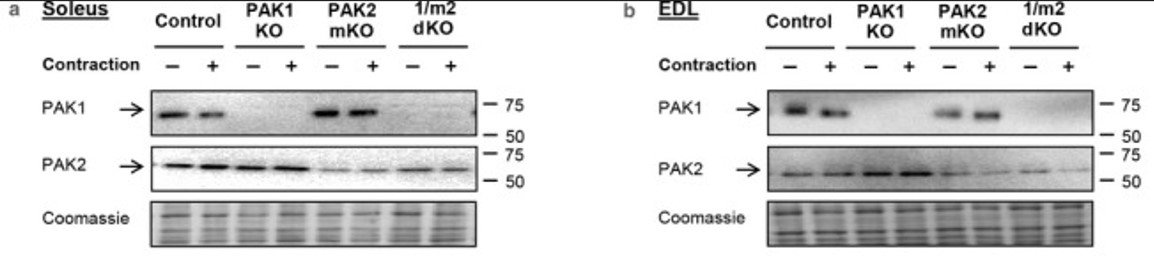
Fig1. Representative blots showing PAK1 and PAK2 protein expression in soleus (a) and extensor digitorum longus (EDL; b) muscles from whole-body PAK1 knockout (KO), muscle-specific PAK2 (m)KO, PAK1/2 double KO (1/m2 dKO) mice, or control littermates.
Case study 2: John Huang, 2020
Cdc42-activated PAK2 mediates cytostasis, whereas caspase 3-cleaved PAK2 contributes to apoptosis. However, the relationship between these two states of PAK2 activation remains elusive. In this study, through protein biochemical analyses and various cell-based assays, the researchers demonstrated that full-length PAK2 activated by Cdc42 was resistant to the cleavage by caspase 3 in vitro and within cells.
This study identified two states of PAK2 activation, wherein Cdc42- and autophosphorylation-dependent activation inhibited the constitutive activation of PAK2 by caspase cleavage. The regulation between these two states of PAK2 activation provides a new molecular mechanism to support PAK2 as a molecular switch for controlling cytostasis and apoptosis in response to different types and levels of stress with broad physiological and pathological relevance.
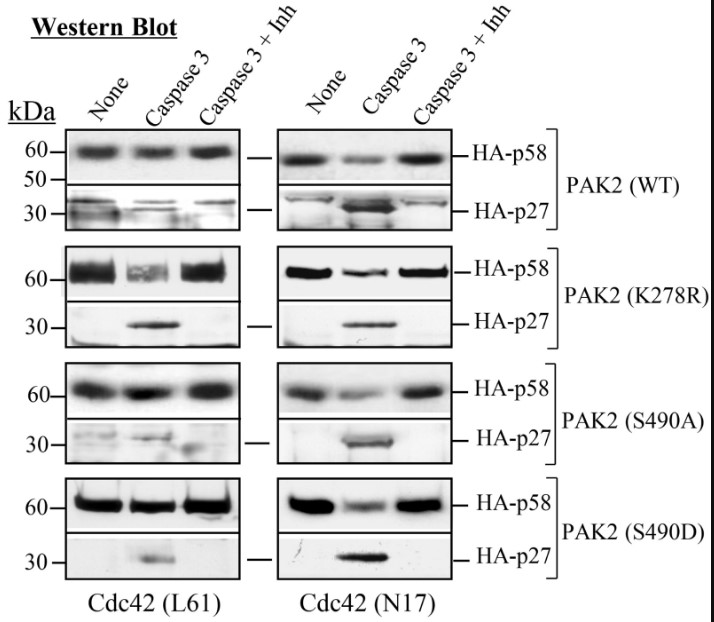
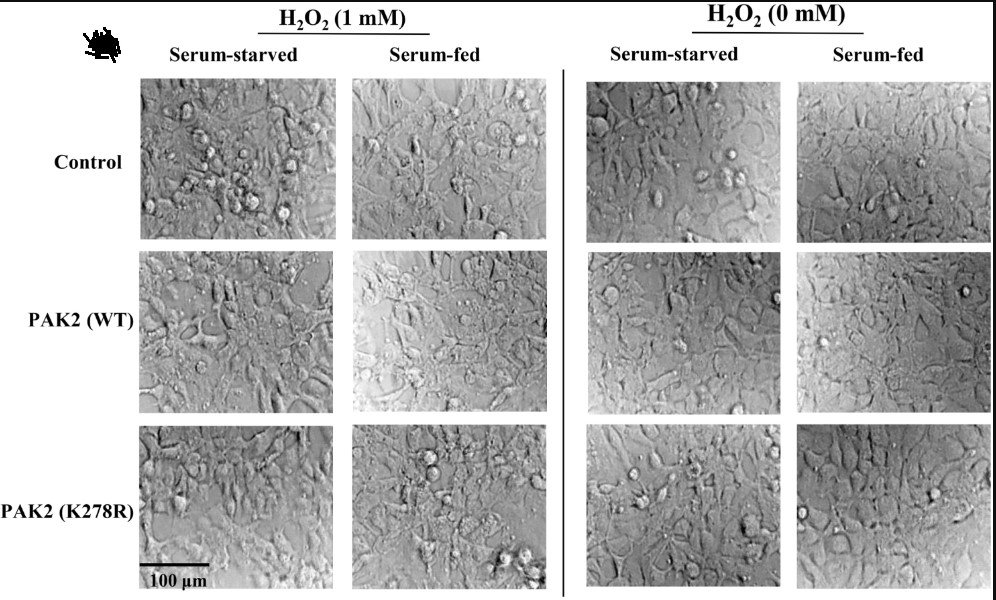
Fig3. HEK 293T cells were co-transfected with HA-tagged wild type or mutant forms of PAK2 and Cdc42-L61 (active) or Cdc42-N17 (inactive) as indicated.
PAK2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PAK2 participated on our site, such as MAPK signaling pathway, ErbB signaling pathway, Ras signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PAK2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | ECSIT;MAP2K7;CACNG6;CACNG2A;MAPK12B;GNG12;FAS;PPM1BB;FGF20B |
| ErbB signaling pathway | ERBB3B;CAMK2B;GRB2;AREG;ERBB4A;NRG1;PIK3R3B;CAMK2D2;ERBB2 |
| Ras signaling pathway | PRKCB;PGF;FGF9;VEGFC;Kitl;FGF1;SHC2;MAPK1;ETS2 |
| Axon guidance | NTNG1;RAC3;CNTN1;SEMA3AB;PPP3CC;ANK2B;CNTN6;SEMA3D;RAC2 |
| Focal adhesion | TNN;MYLPFA;PARVG;RHOAA;ITGB3B;MYL9A;TNW;ERBB2;MYLK4 |
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | Il2;ICOS;NFKBIB;CD3D;MAP2K2;BCL10;GSK3B;PIK3CD;CD3E |
| Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | PXNA;ITGB8;ABI2A;FGF10;ITGAV;MSNA;RHOAB;FGF6A;ACTN4 |
| Renal cell carcinoma | PIK3CG;VEGFA;MAP2K1;ETS1;TGFB3;RAC1;RAP1B;NRAS;MET |
PAK2 has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding, Rac GTPase binding, identical protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PAK2 itself. We selected most functions PAK2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PAK2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | TTLL11;MCM3;ATP8B3;PIP5K1B;MYH7B;cka1;ATP1A3B;KIF5A;CLP1 |
| Rac GTPase binding | PAK3;ARHGAP4A;SOD1;FLNA;CORO1C;PAK2B;MAP3K11;NOX1;ARHGEF2 |
| identical protein binding | TRIM55;ALDH4A1;COL18A1;COL1A2;CHMP4A;CLPP;TGFB3;ZBTB16;HAND2 |
| protein binding | EIF3I;ELF1;ZNF543;FCRL4;ZFP423;UBE2D3;HSPA9;EPB41L1;MTMR7 |
| protein kinase activity | MAP4K3;NAT1;MAPK12A;PIK3C3;TBRG4;LMTK2;NEK1;ADRBK2;CLK4B |
| protein kinase binding | KCNQ3;CASP9;FBXW5;LIMS1;PTK2;SPRED2;RPS6;CDC25B;TRPV4 |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | SGK2B;CDK14;MAPK12A;PRKD2;EIF2AK4;MAP3K11;ADCK1;PAK7;TSSK1 |
| protein tyrosine kinase activator activity | ERBB3;GAS6;ABI1A;ABI3A;ABI1;Cd24a;NRG1;PAK2;ERCC6 |
PAK2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PAK2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PAK2.
RAC1; SORBS3; CDC42; N/A; ARHGEF7
- Q&As
- Reviews
Q&As (7)
Ask a questionPAK2 signaling can be regulated by various upstream signaling molecules. Small GTPases, including Rac and Cdc42, are key activators of PAK2. Their activation leads to the recruitment and activation of PAK2 at specific cellular locations. Additionally, growth factors, such as EGF and PDGF, and cytokines can also activate PAK2 through receptor-mediated signaling pathways.
PAK2 phosphorylates and regulates the activity of various downstream targets, affecting multiple cellular processes. Notably, PAK2 can phosphorylate components of the actin cytoskeleton, including LIM kinase and myosin light chain kinase, leading to actin cytoskeleton reorganization and cell motility. PAK2 also phosphorylates transcription factors, such as c-Jun and Elk-1, impacting gene expression and cell proliferation. Moreover, PAK2 can influence cell survival through the regulation of apoptotic factors, such as Bad and Bcl-2 family members. Overall, the downstream targets of PAK2 activation are diverse and depend on the specific cellular context and upstream signals.
PAK2 (p21-activated kinase 2) is a serine/threonine kinase that plays a crucial role in cellular signaling pathways. It is involved in regulating cytoskeletal dynamics, cell migration, cell proliferation, and cell survival. PAK2 is activated by binding to small GTPases, such as Rac and Cdc42, which leads to downstream phosphorylation and activation of various substrates involved in these cellular processes.
PAK2 is regulated by multiple mechanisms. Its activation is primarily regulated by GTPases, which promote conformational changes and autophosphorylation of PAK2. Additionally, PAK2 activity can be modulated by post-translational modifications, including phosphorylation and ubiquitination. Moreover, PAK2 activity can be influenced by its interaction with scaffolding proteins and other signaling molecules in specific cellular contexts.
PAK2 phosphorylates a wide range of substrates involved in various cellular processes. Some well-known substrates of PAK2 include LIM kinase, myosin light chain, paxillin, and Bad. These substrates are involved in cytoskeletal dynamics, cell adhesion, cell motility, and apoptosis regulation, highlighting the diverse functional roles of PAK2 in cellular signaling networks.
PAK2 has been implicated in cancer progression and metastasis. It promotes tumor cell migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by modulating cytoskeletal dynamics and focal adhesion turnover. PAK2 also influences cancer cell survival and proliferation through its interactions with various oncogenic signaling pathways, such as MAPK and PI3K/Akt. Inhibition of PAK2 has shown potential as a therapeutic strategy to suppress tumor growth and metastasis.
Targeting PAK2 holds therapeutic potential in various diseases, including cancer and neurological disorders. In cancer, inhibition of PAK2 has shown promise in suppressing tumor growth, metastasis, and overcoming drug resistance. Furthermore, PAK2 inhibitors have been explored for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, due to their involvement in synaptic plasticity and neuronal survival. However, further research is required to optimize the efficacy and safety of PAK2-targeted therapies in clinical settings.
Customer Reviews (3)
Write a reviewWith this reagent, I can perform a large number of sample determinations in a short period of time.
Suited for proteomics research, this protein reagent enables efficient screening of large sample volumes.
Using this reagent, I can complete experiments in a shorter time.
Ask a Question for All PAK2 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All PAK2 Products
Required fields are marked with *