RAB7A
-
Official Full Name
RAB7A, member RAS oncogene family
-
Overview
RAB family members are small, RAS-related GTP-binding proteins that are important regulators of vesicular transport.;Each RAB protein targets multiple proteins that act in exocytic / endocytic pathways. This gene encodes a RAB family;member that regulates vesicle traffic in the late endosomes and also from late endosomes to lysosomes. This encoded;protein is also involved in the cellular vacuolation of the VacA cytotoxin of Helicobacter pylori. Mutations at highly;conserved amino acid residues in this gene have caused some forms of Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) type 2 neuropathies. -
Synonyms
RAB7A; RAB7A, member RAS oncogene family; RAB7, RAB7, member RAS oncogene family; ras-related protein Rab-7a; Ras-associated protein RAB7; RAB7, member RAS oncogene family; RAB7; PRO2706; FLJ20819;
- Recombinant Proteins
- Cell & Tissue Lysates
- Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads
- Dog
- Human
- Rat
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cell
- Mammalian cells
- Flag
- His
- His (Fc)
- Avi
- His|GST
- N/A
- N
- Background
- Quality Guarantee
- Case Study
- Involved Pathway
- Protein Function
- Interacting Protein
- RAB7A Related Articles
- RAB7A Related Research Area
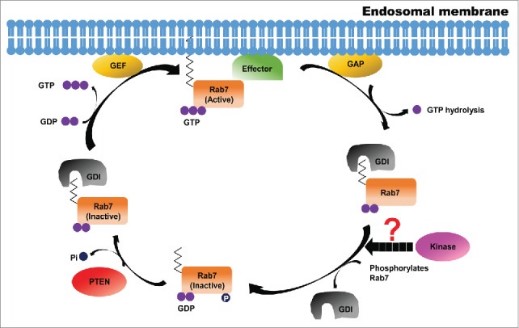
Fig1. A schematic to present probable regulatory role of phosphorylation in Rab GTPase activity cycle. (Swapnil Rohidas Shinde, 2016)
What is RAB7A protein?
RAB7A (RAB7A, member RAS oncogene family) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 3 at locus 3q21. RAB family members are small, RAS-related GTP-binding proteins that are important regulators of vesicular transport. Each RAB protein targets multiple proteins that act in exocytic/endocytic pathways. This gene encodes a RAB family member that regulates vesicle traffic in the late endosomes and also from late endosomes to lysosomes. This encoded protein is also involved in the cellular vacuolation of the VacA cytotoxin of Helicobacter pylori. The RAB7A protein is consisted of 207 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 23.5 kDa.
What is the function of RAB7A protein?
RAB7A is a small GTPase which cycles between active GTP-bound and inactive GDP-bound states. In its active state, it binds to a variety of effector proteins playing a key role in the regulation of endo-lysosomal trafficking. RAB7A governs early-to-late endosomal maturation, microtubule minus-end as well as plus-end directed endosomal migration and positioning, and endosome-lysosome transport through different protein-protein interaction cascades. It plays a central role, not only in endosomal traffic, but also in many other cellular and physiological events, such as growth-factor-mediated cell signaling, nutrient-transportor mediated nutrient uptake, neurotrophin transport in the axons of neurons and lipid metabolism. RAB7A also involved in regulation of some specialized endosomal membrane trafficking, such as maturation of melanosomes, pathogen-induced phagosomes (or vacuoles) and autophagosomes.
RAB7A Related Signaling Pathway
The RAB7A protein is involved in several signaling pathways, the most important of which plays a key role in the endocytosomal lysosomal pathway. This protein regulates the maturation of endocytosomes and the incorporation of lysosomes, and promotes the activity of lysosomal enzymes, thus achieving intracellular waste degradation, phagocytosis of foreign substances and anti-microbial function. In addition, RAB7A is involved in the regulation of the autophagy process by regulating early and late steps in the autophagy pathway to promote self-recovery and clearance of damaged parts of the cell. In addition, there are cell cycle and proliferation, apoptosis, cell migration and invasion and other pathways.
RAB7A Related Diseases
Diseases associated with RAB7A include Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, neurogranulocytosis, and congenital immune deficiency. These diseases are associated with abnormal or defective function of RAB7A protein, resulting in a lack of accurate endocytosis and lysosomal function within cells, affecting the normal function of several tissues and organs, including the nervous system and immune system. They also include cancer, neurodegenerative diseases and certain infectious diseases. For example, RAB7A is overexpressed in certain types of cancer, such as breast, prostate, and stomach cancers, and is associated with poorer prognosis. RAB7A is also involved in the endocytosis pathway of pathogens such as bacteria and viruses and may play a role in the host immune response.
Bioapplications of RAB7A
Because RAB7A has been linked to the onset and development of multiple diseases, particularly cancer, it is considered a potential drug target. Therefore, in the field of drug development, small molecule inhibitors or activators of RAB7A are being investigated to evaluate their potential value for disease treatment.
High Purity
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (RAB7A-6589H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (RAB7A-2649H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
Case study 1: Huiyong Liu, 2020
Rab7 belongs to the Ras oncogene family. Many studies have shown that its dysfunction is associated with many types of malignant tumors, but its effect on the pathogenesis of gastric cancer (GC) is still unknown. Therefore, the researchers investigated the effect and mechanism of Rab7 in GC.
The expression of Rab7 in GC and adjacent tissues was detected by immunohistochemistry, Western blot analysis, and qRT-PCR. The relationship of Rab7 with clinicopathological parameters and prognosis was analyzed. The expressions of Rab7, PI3K, and AKT in GC cells were assessed by Western blot. Overexpressed and silenced GC cell lines were constructed and AGS cells were treated with LY294002. The expression of Rab7 was upregulated in the samples and cells, and was positively correlated with lymph node metastasis but negatively correlated with histological differentiation and clinical prognosis. In cell function experiments, overexpression of Rab7 induced the transition from S phase to G2 phase and promoted the proliferation, invasion, and migration of GC cells. These results show that the Rab7 affects GC cell progression by modulating the PI3K/AKT pathway.
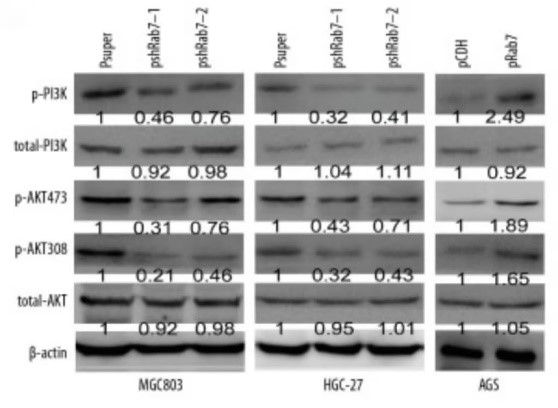
Fig1. Rab7 promotes the proliferation, invasion and migration of GC cells through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
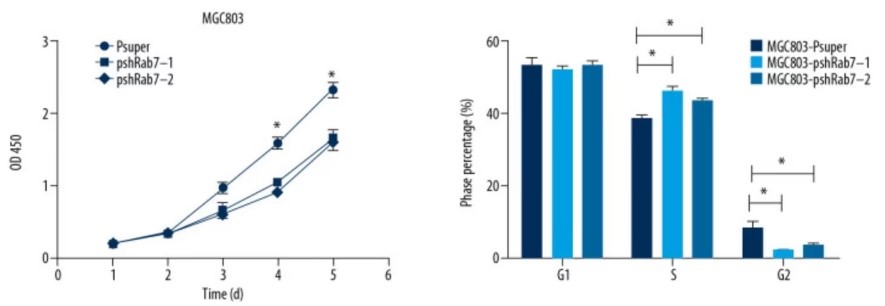
Case study 2: Guang Wang, 2019
The primary cilium is a sensory organelle that protrudes from the cell surface. Primary cilia undergo dynamic transitions between assembly and disassembly to exert their function in cell signaling. In this study, the researchers aimed to identify the function of small GTPase Rab7 in cilia disassembly.
By deleting the Rab7, they found it potently induced spontaneous ciliogenesis in proliferating cells and promoted cilia elongation during quiescence, knockdown of Rab7 blocked serum-induced ciliary resorption, and active Rab7 was required for this process. Mechanically, the failure of F-actin polymerization at the site of excision of cilia tips caused suppression of cilia ectocytosis on Rab7 depletion. Overall, the results suggest a novel function for Rab7 in regulating cilia ectocytosis and cilia disassembly via control of intraciliary F-actin polymerization.
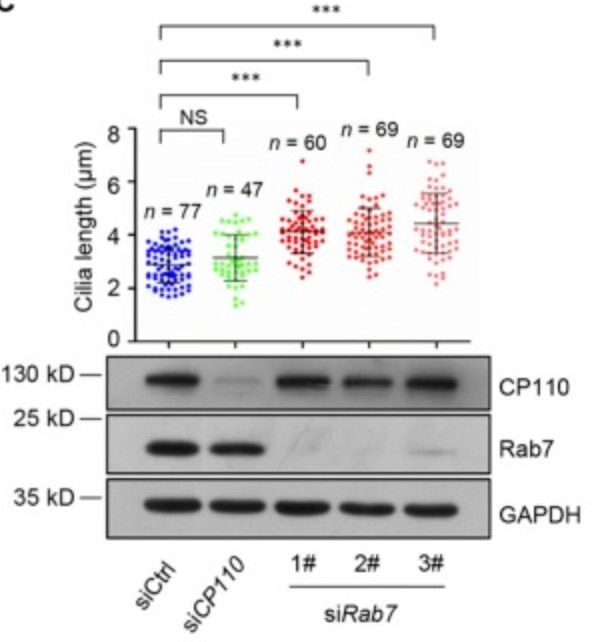
Fig3. Rab7 knockdown promoted cilia elongation in quiescent (-serum) RPE-1 cells.
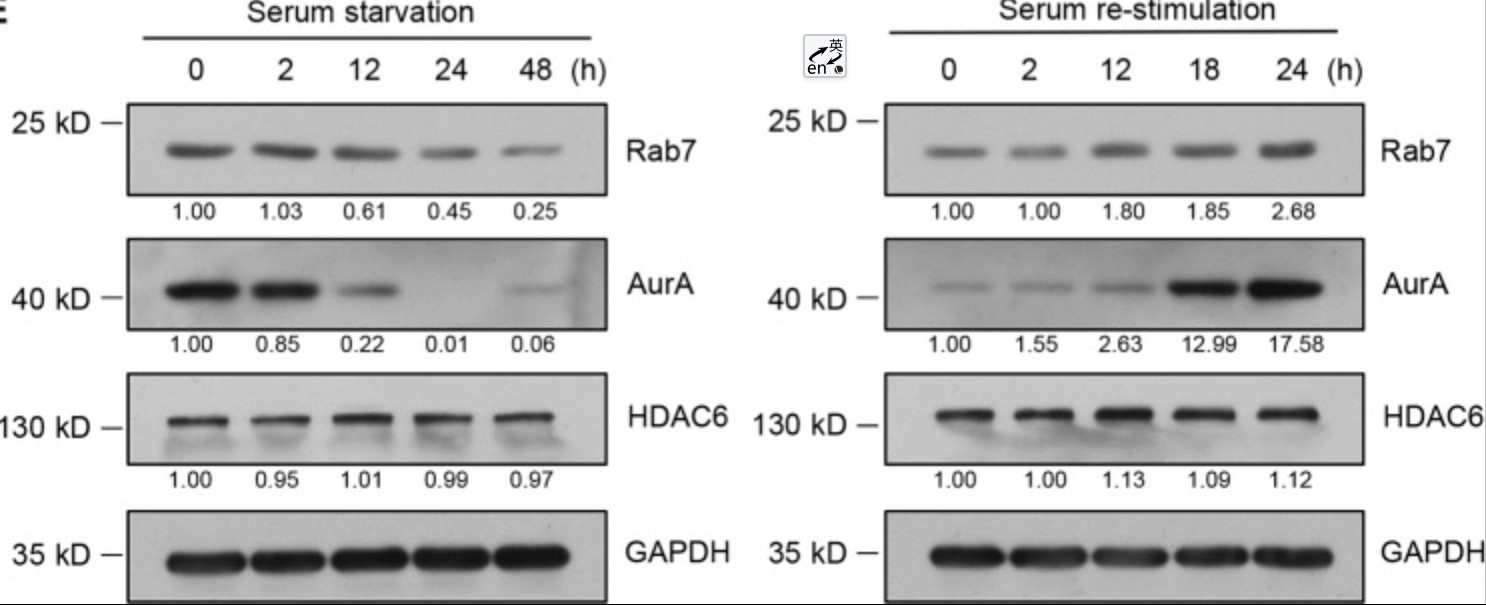
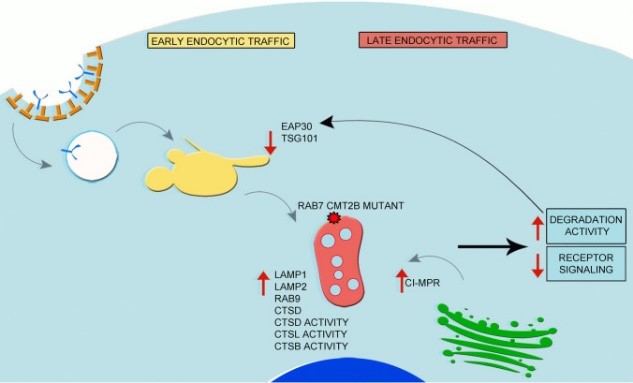
Fig1. Model of the Impact of the CMT2B-causing RAB7 mutant protein on the endocytic pathway. (Roberta Romano, 2021)
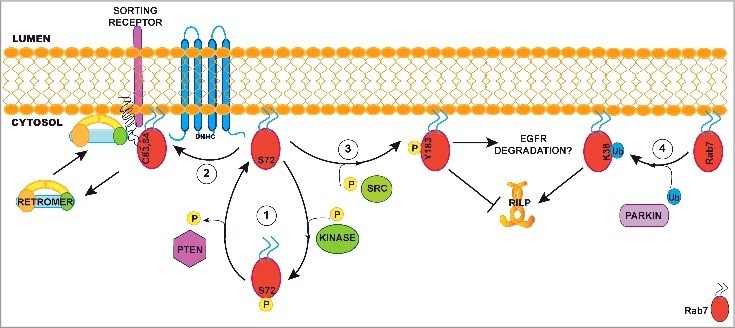
Fig2. Role of post-translational modifications in modulating Rab7 functions. (Graziana Modica, 2020)
RAB7A involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways RAB7A participated on our site, such as Endocytosis, Phagosome, Salmonella infection, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with RAB7A were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Endocytosis | WASL;ARF5;ZFYVE16;RAB11FIP2;SNX1A;TFRC;SMAD2;PIP5K1C;CHMP4A |
| Phagosome | TUBA1L2;C3A.2;C3A.1;ATP6V0A4;FCGR2B;ATP6V1B1;NOS1;RAB7A;ITGB2L |
| Salmonella infection | PFN1;CXCL2;MYD88;NOS2;TJP1;ARPC5LB;MYH9;CDC42L2;TLR5 |
| Amoebiasis | IL1R2;ACTN1;IL-8;PRKACB;PIK3R2;LAMA4;ITGB2;PIK3R1;COL4A3 |
| Tuberculosis | HLA-DOB;IFNA6;HLA-DRB1;FCGR1;RFXANK;FCGR2A;IRAK1;ITGAX;IL18 |
RAB7A has several biochemical functions, for example, GDP binding, GTP binding, GTPase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by RAB7A itself. We selected most functions RAB7A had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with RAB7A. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| GDP binding | RALB;PRPS2;RAB27B;RAB12;RAB5C;RAB7L1;RAB2A;RRAS;RAB9B |
| GTP binding | RHOUA;GIMAP7;RNGTT;TUBG1;RHOH;RRAGA;IRGC;ARL4CA;ATL3 |
| GTPase activity | MTG1;GNGT1;SAR1B;RHOQ;ARL1;GSPT2;DNM3A;DIRAS3;EEF1A2 |
| Rac GTPase binding | PAK2A;SOD1;SRGAP2;DOCK4;PAK2B;CDKL5;NCF2;RAB7;RALBP1 |
| protein binding | TWSG1;RGS8;IL15;NEK6;GLA;NCF1;PAK4;LGALSL;ZC4H2 |
RAB7A has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with RAB7A here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of RAB7A.
RILP; 1-phosphatidyl-1d-myo-inositol 3,5-bisphosphate; 1-phosphatidyl-1d-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate; DNM2; SH3KBP1; EIF1B; MCC; MPG; HLA-B; VHL; GABARAPL2; IKBKE; ATG5; PRKAB1; TRAF6
- Q&As
- Reviews
Q&As (7)
Ask a questionRAB7A activity is regulated by several signaling pathways. One important pathway involves the phosphorylation of RAB7A by protein kinases, such as LRRK2 and CDK1, which modulate its GTPase activity and subcellular localization. Additionally, RAB7A can be regulated by post-translational modifications, including ubiquitination and acetylation. These modifications can affect its interaction with effector proteins and its ability to regulate vesicle trafficking and autophagy.
Targeting RAB7A for therapeutic purposes faces several challenges. One challenge is the need for selective modulation of RAB7A activity without affecting other closely related RAB GTPases. Additionally, the development of efficient delivery systems to specifically target RAB7A in affected cells or tissues is essential. Furthermore, understanding the precise spatiotemporal regulation of RAB7A and its interactions with effector proteins is crucial for designing effective therapeutic interventions. Overcoming these challenges will be instrumental in harnessing the therapeutic potential of targeting RAB7A in neurodegenerative diseases.
argeting RAB7A could be a promising therapeutic strategy for neurodegenerative diseases. One approach is to modulate RAB7A activity using small molecules or gene therapy to restore its normal function in vesicle trafficking and autophagy. Another strategy is to identify compounds that enhance the clearance of aggregated proteins through the autophagy-lysosome pathway, where RAB7A plays a crucial role. Further research is needed to develop and optimize these therapeutic interventions.
RAB7A interacts with various effector proteins to exert its functions in intracellular trafficking. For example, it binds to RILP (RAB7A-interacting lysosomal protein) to recruit dynein-dynactin motor complexes, facilitating the movement of late endosomes towards microtubule minus ends. RAB7A also interacts with FYCO1 and PLEKHM1, which are involved in autophagosomal maturation and fusion with lysosomes. These interactions enable RAB7A to coordinate and regulate vesicle trafficking processes.
RAB7A dysfunction has been implicated in various neurodegenerative diseases. For example, mutations in the RAB7A gene have been associated with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2B and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. In these diseases, impaired RAB7A function disrupts the transport of essential cargoes, such as neurotrophic factors and lysosomal enzymes, leading to neuronal degeneration and dysfunction. Understanding the precise mechanisms by which RAB7A contributes to these diseases is an active area of research.
RAB7A is a small GTPase protein that plays a crucial role in regulating late endocytic trafficking. It controls the maturation of late endosomes to lysosomes by mediating the fusion of these compartments. Additionally, RAB7A is involved in autophagy, a process that degrades damaged organelles and protein aggregates. It promotes the formation of autophagosomes and their fusion with lysosomes. RAB7A also regulates the transport of cargo along the endocytic pathway.
RAB7A is involved in the regulation of lysosomal biogenesis. It promotes the transport of lysosomal enzymes from the trans-Golgi network to late endosomes/lysosomes. RAB7A also regulates the fusion of late endosomes with lysosomes, allowing the delivery of newly synthesized lysosomal proteins. Moreover, RAB7A interacts with transcription factors, such as TFEB and MITF, to regulate the expression of lysosomal genes, thereby influencing lysosomal biogenesis and function.
Customer Reviews (3)
Write a reviewAfter using this protein reagent, my protein gel electrophoresis results are notably clear, aiding in analysis and interpretation.
Using this reagent, my experimental results are more consistent and reliable.
Combining the instructions provided with this protein reagent, I am able to easily accomplish experimental design and execution.
Ask a Question for All RAB7A Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All RAB7A Products
Required fields are marked with *


