SYT1
-
Official Full Name
synaptotagmin I
-
Overview
The synaptotagmins are integral membrane proteins of synaptic vesicles thought to serve as Ca(2+) sensors in the;process of vesicular trafficking and exocytosis. Calcium binding to synaptotagmin-1 participates in triggering;neurotransmitter release at the synapse (Fernandez-Chacon et al., 2001 (PubMed 11242035)). -
Synonyms
SYT1; synaptotagmin I; SVP65, SYT; synaptotagmin-1; P65; sytI; synaptotagmin 1; SYT; SVP65; DKFZp781D2042;
- Recombinant Proteins
- Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads
- Aplysia californica (California sea hare)
- Chicken
- Cynomolgus Monkey
- Gallus gallus (Chicken)
- Homo sapiens (Human)
- Human
- Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque)
- Mouse
- Mus musculus (Mouse)
- Rat
- Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
- Rhesus Macaque
- E.coli
- E.coli expression system
- HEK293
- HEK293T
- Human
- In vitro E. coli expression system
- Mammalian Cell
- Mammalian cells
- C
- His
- Myc
- DDK
- Flag
- GST
- His (Fc)
- Avi
- Myc|DDK
- N/A
- N
- Background
- Quality Guarantee
- Case Study
- Involved Pathway
- Protein Function
- Interacting Protein
- SYT1 Related Articles
- SYT1 Related Research Area
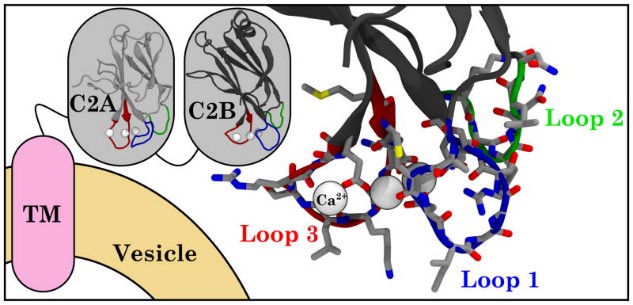
Fig1. Schematic of Synaptotagmin structure. (Josh V Vermaas, 2017)
What is SYT1 protein?
SYT1 (synaptotagmin 1) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 12 at locus 12q21. This gene encodes a member of the synaptotagmin protein family. The synaptotagmins are integral membrane proteins of synaptic vesicles that serve as calcium sensors in the process of vesicular trafficking and exocytosis. The encoded protein participates in triggering neurotransmitter release at the synapse in response to calcium binding. The SYT1 protein is consisted of 422 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 47.6 kDa.
What is the function of SYT1 protein?
SYT1 is a membrane protein found primarily on the synaptic vesicles of neurons and is essential for regulating the release of neurotransmitters. It is a member of the calcium-sensitive protein family that responds to changes in calcium ion concentration within cells. When the action potential reaches the nerve endings, the intracellular calcium concentration increases, and SYT1 binds to calcium ions through its C2 domain, thus promoting the fusion of synaptic vesicles with the presynaptic membrane, triggering the quantized release of neurotransmitters. This process is the basis for rapid synaptic transmission and is essential for the function of the nervous system. In addition to its role in synaptic transmission, SYT1 is also involved in regulating the endocytosis and recycling of synaptic vesicles, ensuring that the effective release of neurotransmitters can be sustained.
SYT1 Related Signaling Pathway
SYT1 binds to calcium ions through its C2 domain, thereby sensing changes in intracellular calcium concentration. When the action potential reaches the nerve endings, the voltage-gated calcium channel opens and the local calcium ion concentration increases. SYT1 senses this change and causes the vesicles to fuse with the cell membrane, triggering the release of neurotransmitters. Therefore, the signaling pathway involved in SYT1 is mainly the signaling pathway of neurotransmitter release, including classical synaptic transmission processes and some mechanisms related to synaptic plasticity, such as short-term and long-term potentiation (STP and LTP).
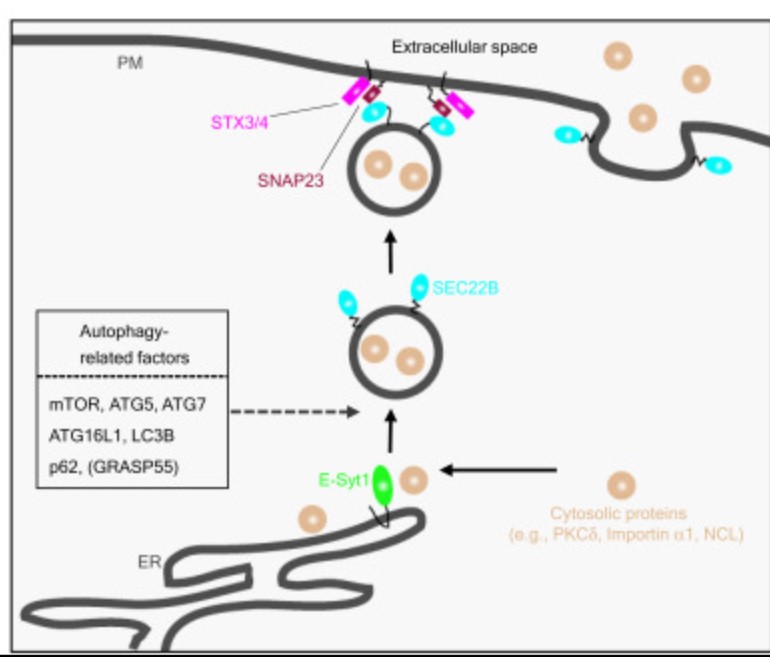
Fig2. A model for the role of E-SYT1 as a link between the ER and vesicle-mediated secretion of cytosolic proteins. (Kohji Yamada, 2022)
SYT1 Related Diseases
Diseases associated with this protein include: neuropsychiatric disorders such as Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, autism spectrum disorder, and schizophrenia. In Parkinson's disease, mutations in SYT1 are associated with neuronal dysfunction and cell death. Huntington's disease is associated with abnormal aggregation of SYT1 and neuronal death. The occurrence of disorders such as autism spectrum disorder and schizophrenia may be related to the role of SYT1 in neuronal signaling.
Bioapplications of SYT1
SYT1 is widely used as a marker to study synaptic transmission mechanisms, especially in exploring the molecular mechanisms of anchoring and fusion of synaptic vesicles and neurotransmitter release. In addition, manipulating SYT1 expression or function by means of genetic engineering is used to develop neuroscience models to better understand the function and disease of the nervous system.
High Purity
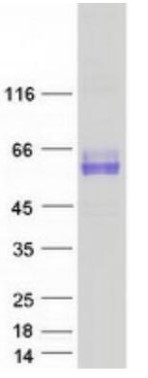
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (SYT1-426HFL) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
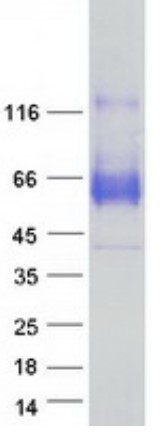
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (SYT1-6479H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
Case study 1: Mazdak M Bradberry, 2020
At neuronal synapses, synaptotagmin-1 (SYT1) acts as a Ca2+ sensor that synchronizes neurotransmitter release with Ca2+ influx during action potential firing. Heterozygous missense mutations in SYT1 have recently been associated with a severe but heterogeneous developmental syndrome, termed SYT1-associated neurodevelopmental disorder. Well-defined pathogenic mechanisms, and the basis for phenotypic heterogeneity in this disorder, remain unknown. Here, the researchers report the clinical, physiological, and biophysical characterization of three SYT1 mutations from human patients. Synaptic transmission was impaired in neurons expressing mutant variants, which demonstrated potent, graded dominant-negative effects. Biophysical interrogation of the mutant variants revealed novel mechanistic features concerning the cooperative action, and functional specialization, of the tandem Ca2+-sensing domains of SYT1. These mechanistic studies led to the discovery that a clinically approved K+ channel antagonist is able to rescue the dominant-negative heterozygous phenotype. The results establish a molecular cause, basis for phenotypic heterogeneity, and potential treatment approach for SYT1-associated neurodevelopmental disorder.
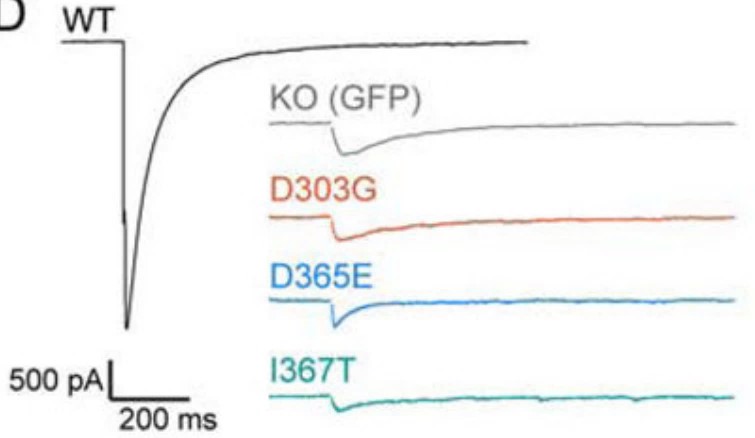
Fig1. Average traces of evoked IPSCs from neurons expressing no SYT1 (KO), WT, or mutant SYT1 variants.
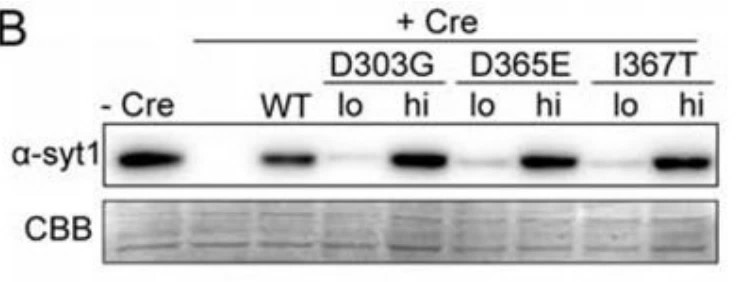
Case study 2: Joao Miguel Cordeiro, 2013
A low-affinity Ca²⁺/H⁺-antiport was described in the membrane of mammalian brain synaptic vesicles. Electrophysiological studies showed that this antiport contributes to the extreme brevity of excitation-release coupling in rapid synapses. Synaptotagmin-1, a vesicular protein interacting with membranes upon low-affinity Ca²⁺-binding, plays a major role in excitation-release coupling, by synchronizing calcium entry with fast neurotransmitter release. Here, the researchers report that synaptotagmin-1 is necessary for expression of the vesicular Ca²⁺/H⁺-antiport. They measured Ca²⁺/H⁺-antiport activity in vesicles and granules of pheochromocytoma PC12 cells by three methods: (i) Ca²⁺-induced dissipation of the vesicular H⁺-gradient; (ii) bafilomycin-sensitive calcium accumulation and (iii) pH-jump-induced calcium accumulation. The results were congruent and highly significant: Ca²⁺/H⁺-antiport activity is detectable only in acidic organelles expressing functional synaptotagmin-1. In contrast, synaptotagmin-1-deficient cells--and cells where transgenically encoded synaptotagmin-1 was acutely photo-inactivated--were devoid of any Ca²⁺/H⁺-antiport activity. Therefore, in addition to its previously described functions, synaptotagmin-1 is involved in a rapid vesicular Ca²⁺ sequestration through a Ca²⁺/H⁺ antiport.
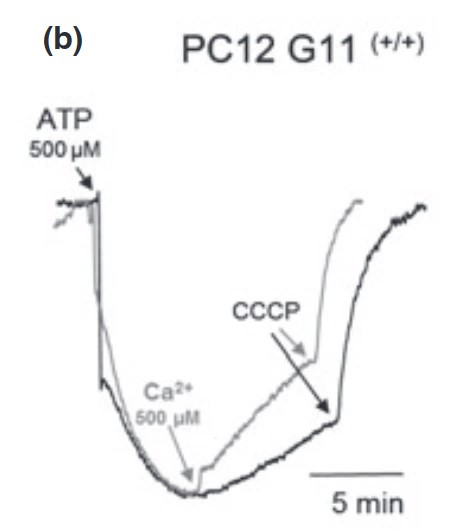
Fig3. Experiment carried out on post-nuclear supernatant (PNS) from PC12 G11(+/+) cells, which spontaneously express SYT1.
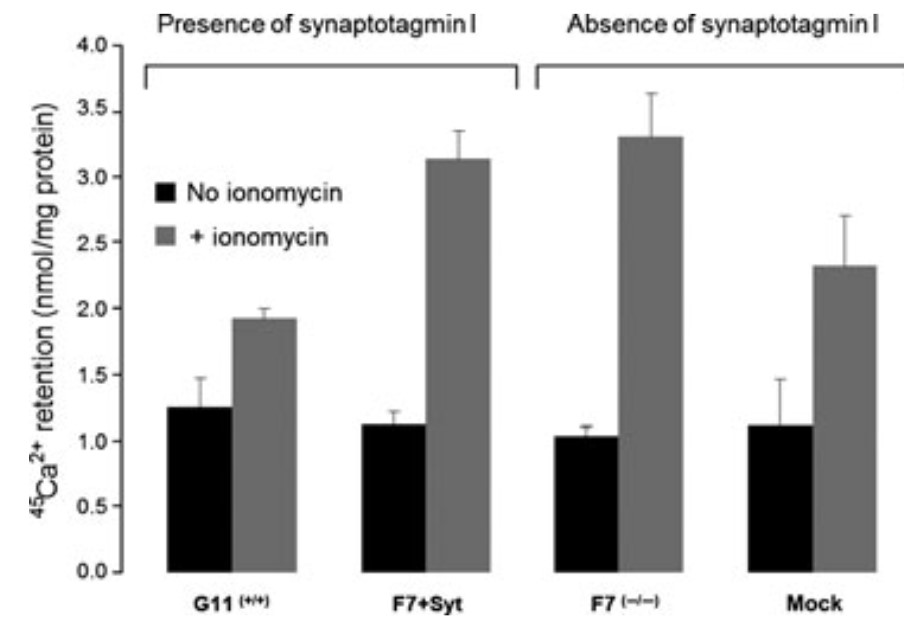
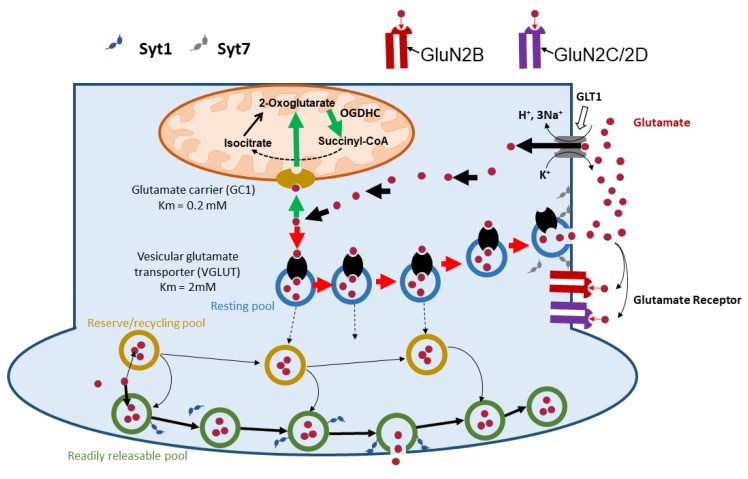
Fig1. Evoked and spontaneous glutamate release, resulting in a balance between extracellular and intracellular glutamate pools. (Annette Vaglio-Garro, 2024)
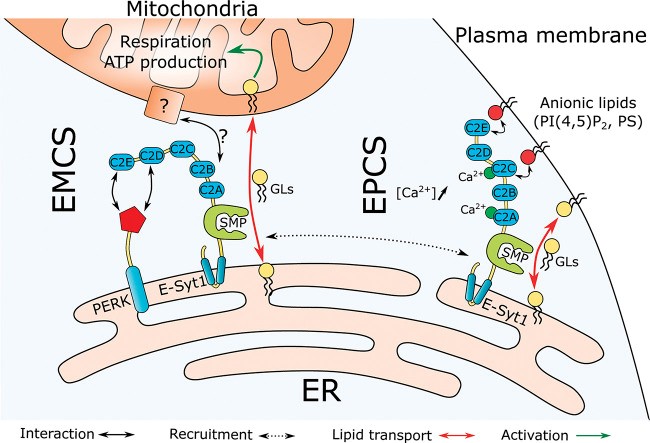
Fig2. The PERK/E-SYT1 complex promotes lipid transport to mitochondria and the maintenance of mitochondrial functions in human cells. (Sébastien Leterme, 2023)
SYT1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways SYT1 participated on our site, such as Synaptic vesicle cycle, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with SYT1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Synaptic vesicle cycle | RAB3A;STXBP1;ATP6V1B1;SYT1;ATP6V0E1;STX1B;RIMS1;ATP6V0E2;ATP6V1F |
SYT1 has several biochemical functions, for example, 1-phosphatidylinositol binding, SNARE binding, calcium ion binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by SYT1 itself. We selected most functions SYT1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with SYT1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| 1-phosphatidylinositol binding | WDFY3;PLEKHA2;FRMPD2;SYT1;CCDC167;SCIN;ZFYVE9;SNAP91;EEA1 |
| SNARE binding | VAMP7;UNC13A;VTI1A;SYBL1;VAMP4;TRIM9;GOSR2;SYT1;STX11B.1 |
| calcium ion binding | EFCAB1;CASQ2;Shh;PCDHA8;VCAN;EFHB;FAT4;ANKRD5;PCDHB14 |
| calcium-dependent phospholipid binding | SYTL1;ANXA4;ANXA9;ANXA1A;CCDC167;SYT1;ANXA3;SYT17;AP1S2 |
| calcium-dependent protein binding | NELF;RAC3;S100B;SNAP25;SEC31A;MASP2;ANXA7;ALG2;MYO1D |
| clathrin binding | SCLT1;CLINT1;LRRK2;SNAP91;SYTL4;LDLRAP1;AP2B1;TOM1;SYTL1 |
| low-density lipoprotein particle receptor binding | LDLRAP1;SACS;APOE;ARRB2;AP2M1;PCSK9;APOB;SYT1;SNX17 |
| phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding | RAB35;ADAP2;ACTN2;KCNQ1;STXBP6;FCHO2;VIL1;PARD3;PLCB1 |
| protein binding | OPRM1;HMGB3;PSMD10;TRDN;ZNF550;SCP2;CSRP2BP;TXNIP;PLK1 |
| syntaxin-1 binding | SNPH;GOLSYN;LRRK2;SNAP25A;SNAP25;VAMP2;SLC6A4;STXBP3A;CCDC167 |
SYT1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with SYT1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of SYT1.
IKBKG; CACNB4; IKBKG; Syt1; ZDHHC17; PCBD1; TFCP2; CBFB; SMAD2; CACNB3; GOLM1; Caskin1; SNAPIN; Slc14a2; EPS15; STON2; COPS4
- Q&As
- Reviews
Q&As (6)
Ask a questionIn clinical practice, the expression level of SYT1 can be detected to predict the progression and prognosis of the disease, and to guide the choice of treatment regimen. For example, in the diagnosis and treatment of neurological diseases, the expression level of SYT1 can help doctors determine the type, stage and prognosis of the disease, and guide the choice of treatment regimen.
Studies have shown that SYT1 protein can participate in the regulation of antiviral immune response and affect the course of viral infection.
SYT1 protein plays an important role in the pathogenesis of certain autoimmune diseases.
Studies have shown that SYT1 protein may be associated with the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction.
There is no conclusive evidence that diet can improve the nutritional status of SYT1 protein, but maintaining a balanced diet and moderate protein intake can help maintain good health.
Drug development for SYT1 is currently in clinical trials, including small molecule inhibitors against SYT1 and inhibitors against the SYT1 signaling pathway.
Ask a Question for All SYT1 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All SYT1 Products
Required fields are marked with *



