Recently, in a study published in Nature, researchers from the University of Pennsylvania have found that the main features of different Parkinson‘s-related brain disorders may be intracellular misfolded proteins; the authors found that the pathological form of α-synuclein is the culprit in the induction of many diseases. Dr. Chao Peng said that the influence of cell types on different α-synuclein variants may be able to solve the most important…
Hotspot
The Latest Research Progress in Cancer Resistance (II)

(Continued) Scientific Reports: New Computational Approach to Identify Chemotherapy Targets (DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-19284-3) One of the most important features of tumors is the methylation of deoxycytidine to form 5-methylcytosine (5mC). DNA methylation is the process by which a methyl group is added to a DNA molecule. It has been found that the occurrence and distribution of 5mC are important for gene regulation, and it can also serve…
The Latest Research Progress in Cancer Resistance (I)

Drug resistance is one of the main reasons leading to the failure of cancer treatment, which greatly limits the choice and use of cancer drugs, and breaking the hopes of the cancer patients again and again. The study of drug resistance in cancer is of utmost importance. It is imminent to explore the mechanism of cancer resistance and new methods to combat drug resistance. Insulin pathways can lead to…
Cell: Special Cancer Protein Brings Hope for New Targeted Cancer Therapies

Highlights The oncogenic Gαs mutation R201C allows GDP-bound Gαs to activate adenylyl cyclase GDP-bound Gαs(R201C/C237S) adopts an active state in its crystal structure The R201C mutation activates Gαs by stabilizing an intramolecular H-bond network Loss-of-function mutations R228C and R265H destabilize the GTP active state of Gαs A few days ago, researchers from Howard Houston Medical School discovered a novel protein mutation in pituitary tumors, which may subvert the traditional concept,…
JEM: Prevent Exhaustion in Immune Cells Boosts Immunotherapy
If you are an immune cell ready to fight cancer, you’d better eat some breakfast. Because the tumor microenvironment is a harsh place, and tumor cells are always ready to make you exhausted. Improvement of highly specific immune fighter in vivo: The ability of T cells to attack tumors has achieved clinically significant advances in tumor immunotherapy. However, this method is only effective in 10-30% of patients. One reason…
Nature Communication: Proteins that Make Difference between Cancerous and Healthy Cells Found

A recent study published in Nature Communication reveals how cancerous cells differ from healthy ones, which paves way for the development of novel strategies for the therapeutic intervention for difficult-to-treat cancers in the future. An international research team discovered a “stop sign”- a mutated protein called PIP-stop, which is overused by tumor cells and can effectively prevent healthy cells from classifying in the way they are designed to. …
Recent Research Progress in Heart Disease (II)
(Continued) 4. Nat Commun: Latest research finds the key protein mechanism, which regulates heart and muscle David Giganti et al, Disulfide isomerization reactions in titin immunoglobulin domains enable a mode of protein elasticity, Nature Communications (2018). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-02528-7 Scientists from CNIC and Columbia University have identified a key protein regulatory mechanism that regulates skeletal muscle and heart muscle function. Research results have recently been published in…
Recent Research Progress in Heart Disease (I)
What we are bringing to you this time is recent advances in heart disease research and we hope it will be useful to you. 1. NEJM: Influenza increases the probability of heart attack by 6 times! Jeffrey C. Kwong et al.Acute myocardial infarction after laboratory-confirmed influenza.N Engl J Med 2018; 378:345-353 DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1702090 infection According to a recent study completed by ICRS and PHO researchers, the…
Cell: TBK1 Is the Blockage to Weight Loss

Highlights TBK1 operates at the intersection of energy expenditure and inflammation TBK1 deficiency attenuates HFD-induced obesity but exaggerates inflammation TBK1 represses energy expenditure by phosphorylating and inhibiting AMPK TBK1 attenuates NF-κB activation and mediates the anti-inflammatory effect of AMPK Do you ever wonder why fat body burns even fewer calories, or why dieting for weight loss always has bottlenecks? That’s because in both cases, our body tries to defend…
Breakthrough! Scientists Decipher The Fifteen Years’ Unresolved Secrets of IL-23, Revealed The Key Mechanism of Autoimmune Disease!
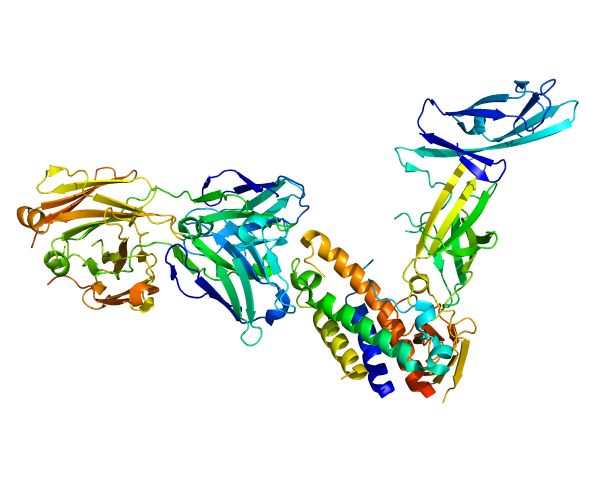
Recently an international team led by Professor Savvas Savvides at the VIB-UGent Inflammatory Research Center revealed the key molecular mechanisms of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases including psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and Crohn’s disease. By focusing on the immunomodulatory factor IL-23, they found that its proinflammatory activity is strongly dependent on its receptor IL-23R for its structural activation. The research was published in Immunity recently. Psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease…
