A small study of 8 patients in Greece found that the clinically approved anti-inflammatory drug anakinra (anakinra, which is essentially an IL-1 inhibitor) for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis It can improve the respiratory function of severe COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019, 2019 coronavirus disease) patients. The eight patients also suffered from a disease called secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (sHLH), which was characterized by excessive immune system activation and organ failure. One…
Author: biomart
Smokers Express Higher ACE2 and Are Susceptible to Coronavirus Infection

Data from COVID-19 patients indicate that smokers are at higher risk of complications. The researchers published an article in the journal Developmental Cell that one of the possible reasons is that smoking increases the gene expression of ACE2 (a protein that binds to SARS-CoV-2), which may promote COVID- 19 infections. The study shows that long-term smoking will increase the ACE2 protein in the lungs, which may lead to a higher…
Tumor Cell–Derived IL1β Promotes Desmoplasia and Immune Suppression in Pancreatic Cancer
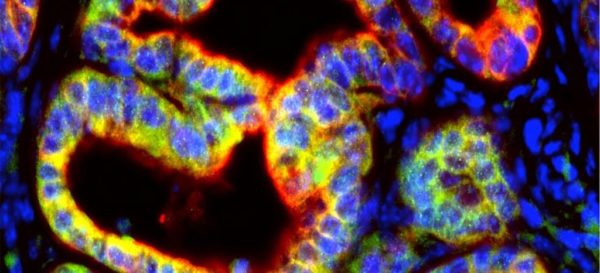
Recently, in a study published in Cancer Research, scientists from New York University and other institutions have found that a key immune signal may play a previously unknown role in turning off the immune system to attack pancreatic cancer. The researchers found that the immune signaling protein interleukin 1β (IL-1β) can be made and released by pancreatic tumor cells, while it reduces the body’s anti-cancer immune response, thereby promoting the…
Study Found the Global SARS-CoV-2 Is Composed of Six Main Subtypes

The World Health Organization announced the global pandemic of COVID-19 in March 2020, the second pandemic in the 21st century. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is an RNA beta coronavirus of the Coronaviridae family. The expansion of virus populations, such as SARS-CoV-2, has accumulated many shared polymorphisms, which has caused confusion in traditional clustering methods. In this case, a method to reduce the complexity of the sequence space…
Do You Know How Cells Recognize Uninvited Guests?
Recently, a team led by the University of Bonn discovered how TLR8 plays an important role in defending human cells against invaders. It was found that when RNaseT2 and RNase2 cut the ribonucleic acid (RNA) of bacteria into small fragments with fingerprint characteristics, they were able to be recognized by TLR8 and countermeasures were initiated. And the results are published in the recent issue of Immunity. When bacteria or…
Why SARS-CoV-2 Spread So Easily Among People?
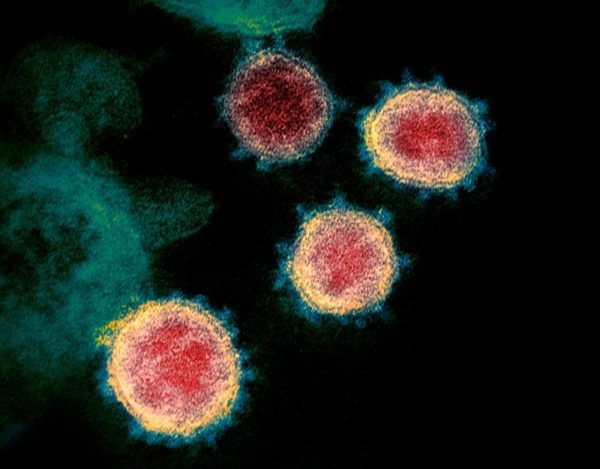
Researchers have identified microscopic features that may make this pathogen more infectious than the SARS virus and can serve as drug targets. With nearly 100,000 people infected with SARS-CoV-2 worldwide, researchers are racing to understand what makes it so easy to spread. Several genetic and structural analyses have identified a key feature of this virus—a protein on the surface—which may explain why it is so susceptible to infect…
Nature: Scientists are Developing Nanovaccines to Fight New Crown Viruses
As infections from SARS-CoV-2 spread from Wuhan, China, to all over the world, researchers are scrambling to develop a vaccine, and life science companies are providing help. On January 28, 2020, a few weeks after the first official report of the first case of coronavirus in 2019, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services held a press conference in Washington, D.C., saying that SARS-CoV-2 infected thousands of people…
Immunity: Activating Tumor-Associated Macrophages to Fight Cancer
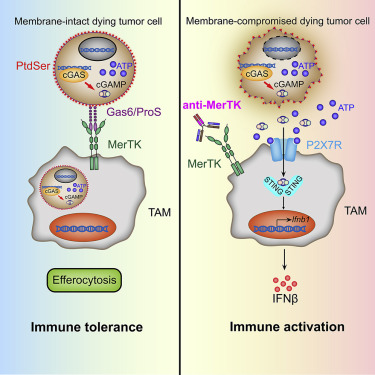
Cancer immunotherapy is continuing to revolutionize the means of patient care, bringing hope and good news to patients. However, only a minority of patients respond to treatment, which drives the development of strategies to further address the immunosuppressive tumor environment. In a recent report, Zhou et al developed a method to enhance the immune response to tumors by preventing tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) from removing dying tumor cells. In tumors…
Nat Immunol: Revealing New Mechanisms of Increased Immunity Following Lung Infection
According to a recent study by the Francis Crick Institute, the immune system response to respiratory infections is constantly changing, depending on the history of previous unrelated infections. The body has two kinds of immunity to infection. Adaptive immunity provides an immune “memory” that can respond rapidly and strongly when the same disease occurs more than once. In contrast, innate immunity provides a broad and less specific first line…
PNAS: New Study Shows that Remdesivir Prevents Coronavirus MERS-CoV Infection in Monkeys
In a new study, researchers from the National Institutes of Health reported that the experimental antiviral drug remdesivir (also known as GS-5734) successfully prevented rhesus monkeys infected with the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) coronavirus (MERS-CoV) from becoming ill from this virus infection. Giving remdesivir before infection can prevent them from getting sick, while giving this drug after they are infected can improve their condition. The results were published in…