Earlier this month, multiple health departments confirmed that BA.2.86- a highly mutated SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19- poses a risk of rapid transmission in countries around the world. This week, the latest vaccination plan will be launched across the United States, but it remains to be seen whether this latest vaccination plan will effectively slow down the spread of BA.2.86 or other new virus variants. However, vaccines remain the…
Nature
Discovering New Protein Families and Folds Using Artificial Intelligence Tools

In a new study, researchers from the Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics and the University of Basel have discovered a treasure trove of uncharacterized proteins. In the recent deep learning revolution, they have discovered hundreds of new protein families and even a new predictive protein fold. The relevant research results were published online in the journal Nature, with the title “Uncovering new families and folds in the natural protein universe”. …
The Three-Dimensional Structure of Type A GABA Receptors in Natural State
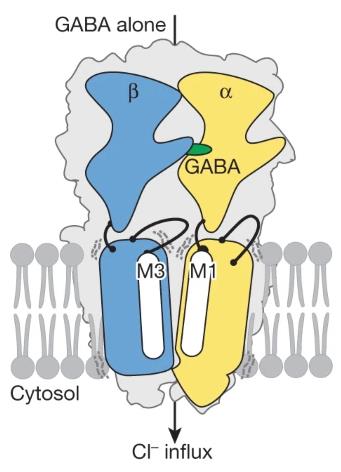
In a new study, researchers from the University of Health and Science of Oregon in the United States revealed the molecular structure of a receptor crucial for brain development and function – the Type A GABA receptor. The relevant research results were published online in Nature titled “Cryo-EM structures reveal native GABAA receptor assemblies and pharmacology”. The A-type GABA receptor has become a target for drug anesthetics, sedatives, and antidepressants…
Virus ADP Ribotransferase Couples RNA with Host Protein
Prior to this, people had always believed that RNA and protein only interacted briefly during cellular processes. In a new study, researchers from the Max Planck Institute of Land Microbiology in Germany found that this is not the case: bacterial viruses, also known as bacteriophages, “bind” specific RNA to host proteins during the developmental cycle. This chemical modification, called RNAylation, may open up new avenues for phage therapy or drug…
PPARΑ Pretreatment of Agonist WY14643 Reduced Cardiomyopathy Caused By Mitochondrial Dysfunction in the Hearts of Lipopolysaccharide Treated Mice
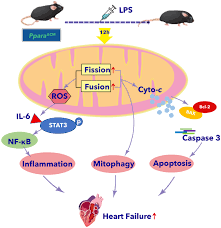
Sepsis is defined as Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), which is the most common cause of death in ICU. The main reason for the increased mortality rate of sepsis is septic shock. Septicemia continuously damages the cardiovascular system, and cardiac dysfunction is the main cause of septic shock. Therefore, there is an urgent need for new mechanisms and effective treatment methods to treat cardiac dysfunction caused by sepsis. Recently,…
Structure and Function of the RAD51B-RAD51C-RAD51D-XRCC2 Protein Complex
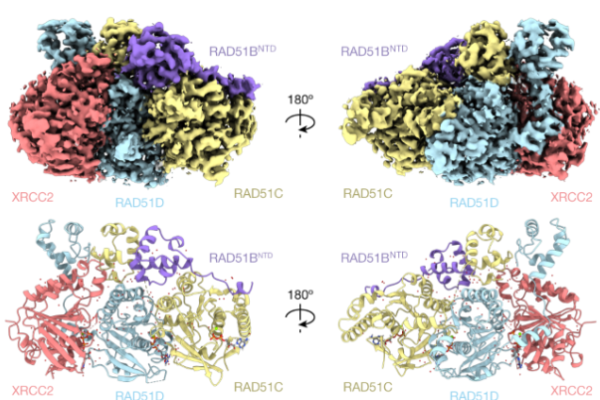
Homologous recombination is a basic process of life, which is necessary to protect and restart broken replication forks, repair chromosome breaks and exchange genetic material during meiosis. Recently, in a research report titled “Structure and function of the RAD51B-RAD51C-RAD51D-XRCC2 tumor suppressor complex” published in the journal Nature, scientists from institutions such as the Francis Crick Institute summarized the structure and function of a special protein complex, which is crucial for…
Mutated TG2 Enzyme Promotes the Progression and Diffusion Mechanism of Prostate Cancer
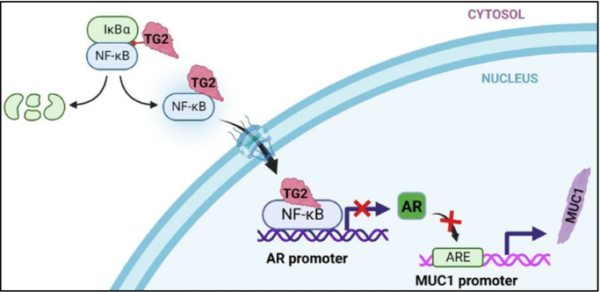
In a new study, researchers from Nottingham Trent University in the UK identified how a specific enzyme plays a key role in making prostate cancer more invasive and difficult to treat. They found that this enzyme, called transglutaminase 2 (TG2), which is abundant in many cells of the body, is responsible for driving the process leading to the progression and spread of prostate cancer. The relevant research results have recently…
Three Dimensional Structure of the Smallest Programmable Nuclease Tnpb
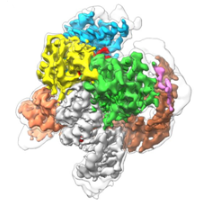
In a new study, professor Virginijus Šikšnys from the Life Sciences Center (VU-LSC) of Vilnius University in Lithuania and his research team cooperated with Professor Guillermo Montoya of the Novo Nordisk Foundation Protein Research Center (CPR) of the University of Copenhagen in Denmark and his research team to determine the structure of TnpB using Cryo-EM. The relevant research results were published in Nature on April 13, 2023, with the title…
Discovering an Autoimmune Inflammatory Disease Induced by LYN Gene Mutation
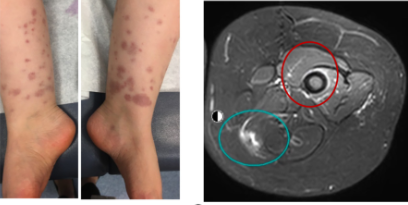
Scientists from institutions such as the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases in the United States have identified an autoimmune disease induced by mutations in the LYN gene, which is an important regulator of the body’s immune response in both healthy and diseased states. Neutrophilic inflammation is a hallmark of the occurrence of many monogenic autoimmune diseases. Currently, researchers are not very clear about the pathological mechanisms that…
The Role of the Third Intracellular Ring of GPCR in GPCR Signal Conduction Mechanism
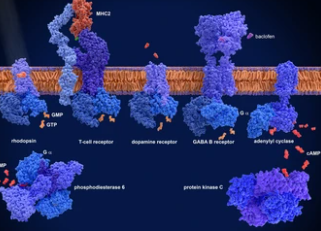
In a new study, American researchers have discovered the role of the third intracellular loop of GPCR in the GPCR signal transduction mechanism, indicating the possibility of adopting more targeted drug discovery methods and developing new drugs. More than one-third of the drugs approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) function by targeting G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). The human body has over 800 types of GPCRs,…