In a recent study published in The Journal of Neuroscience, scientists from Mount Sinai Hospital have discovered that a specific protein called RGS4 (Regulator of G protein signaling 4) may play an important role in maintaining the body’s long-term chronic pain state, which may serve as a novel potential target to help develop new therapies for human chronic pain and other diseases. The study findings or can help clinicians…
New Research
E-cadherin Found to Be an Essential Protein for Metastasis of Various Breast Cancers
Metastasis is a major cause of death in cancer patients. According to the inverse relationship between migration and E-cadherin levels in vitro, it has been proposed that invasion and metastasis of the surrounding tissues begin after the loss of the intercellular adhesion protein E-cadherin. However, this hypothesis is inconsistent with the observation that the majority of breast cancers are invasive ductal carcinomas and express E-cadherin in the primary tumor and…
TDP-43 and Paraspeckle: Key Factor to Determine Stem Cells Differentiated or Remain Pluripotent
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells) can be transformed into any cells in the body or maintain their original form. In a new study, researchers from research institutions such as the Helmholtz Center in Germany described how cells decide which of these two directions to choose. In their research, they identified a protein and a ribonucleic acid (RNA) that played a very important role in this process. Their findings also…
New Research Reveals How Light-sensitive Proteins Regulate Skin Tone

A team at Brown University found that Opsin3 is a protein closely related to rhodopsin, a protein that enables low-light vision. It regulates the amount of pigment produced in human skin, which is a determining factor in skin color. When humans spend their time in the sun without proper skin protection, the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) radiation sends a signal to the skin that produces more melanin – which prevents…
New Study Reveals That Protein TRAIP is The Major Regulator of DNA Cross-linking Repair
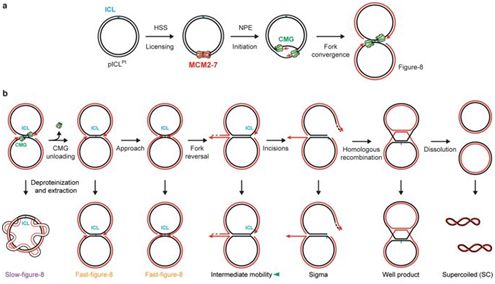
In general, there are multiple pathways taken by cells to repair the same DNA damage, and the choice of repair pathway is important for maintaining genomic fidelity. Cross-linking between DNA strands covalently links two DNA strands together, thereby blocking DNA replication and transcription, chemotherapy takes effect by utilizing the cytotoxicity of these crosslinks. In Xenopus laevis egg extracts, the collision of the replication fork with the interstrand crosslinker initiated two…
Summary on The Status Quo and Future Development of Protein Modification Research
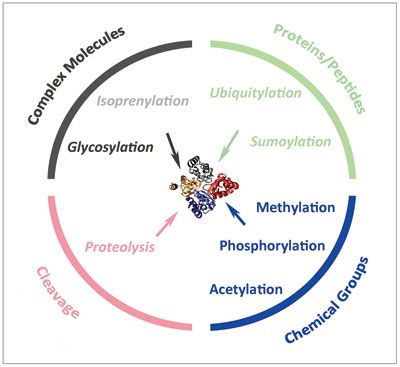
Protein post-translational modifications (PTM) include phosphorylation, methylation, acetylation etc. Protein expression is regulated by genomics and epigenetics, and after expression, it needs to be modified to different degrees to perform the required functions. PTM research is crucial. Here, let’s review the significant research in the field of protein modification in 2018. PNAS: Ubiquitin-like protein ubiquilin 2 (UBQLN2) regulates ALS/FTD-linked FUS-RNA complex kinetics and stress granule formation The ubiquitin-like protein…
The Rhomboid Protease Breaks the “Cell Speed Limit” When Through the Cell Membrane
In a new study, researchers from Johns Hopkins University in the United States found that as a special protein that cleaves other proteins, rhomboid proteases can break the “cell speed limit” as they pass through the cell membrane. Rhomboid protease does this by distorting their surroundings, allowing them to slide quickly from one end of the cell membrane to the other. The results of the study were published in the…
New Breakthrough Developed A Technology that can Detect Hundreds of Proteins in A Single Blood Sample
Recently, in a research report published in the international journal Nature Nanotechnology, scientists from McGill University have developed a new technology that can detect hundreds of proteins in a single sample which is expected to be used as a fast, high-capacity and cost-effective tool for hospitals and research laboratories. Proteins in the blood provide researchers and clinicians with vital information that indicates the health of the body. Meanwhile, these…
New Study Published on J Virol Reveals The Molecular Mechanism of Human T Cell Leukemia Virus Infection and Spread

Recently, research published in the Journal of Virology, scientists from the University of Minnesota developed a new strategy that is expected to block the spread of a highly infectious virus in remote areas of central Australia. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) infected more than 40% adults in the community, as the first human-type cancer virus discovered by scientists, HTLV-1 induces leukemia and lymphoma. “Currently, we have…
J Cell Biol: How Does a Genetic Mutation Induce a Neurological Disease Such as Parkinson’s?
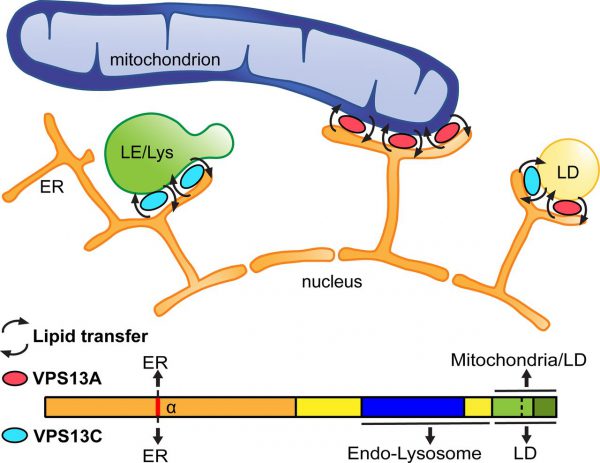
Mutations in multiple genes are directly related to Parkinson’s disease, but researchers are not sure how these mutations affect individuals with Parkinson’s disease. A recent study published in The Journal of Cell Biology, in the study, scientists from Yale University focused on a genetic mutation that induced familial Parkinson’s disease. They found that the gene encodes a specific protein that controls lipids transfer between organelle membranes. In the…