The correct positioning of membrane proteins on the corresponding organelles is important for maintaining the specific “identity” and physiological functions of the organelles. The correct positioning of membrane proteins relies on precise protein sorting pathways and requires corresponding mechanisms on organelles to eliminate mislocated proteins. For example, the AAA-ATPase Msp1 of the outer mitochondrial membrane can remove the protein that is incorrectly located on the outer mitochondrial membrane. However, what…
New Research
Research Reveals Cross-species Transmission of Primate Lentivirus

Humans continue to be threatened by viral diseases such as Ebola, Zika, and Coronavirus. Such emerging/re-emerging virus outbreaks may be caused by cross-species viruses transmitted from wild animals to humans. In order to achieve cross-species transmission, the new host must be exposed to the virus in the old host. Next, the virus acquires certain mutations that may be beneficial for replication in the new host. Finally, by continuing to…
New Regulation Mechanism of Interferon Signaling Pathway

The interferon (IFN) signaling pathway is the main component of innate immunity and plays an important role in the host’s resistance to pathogens; the production of IFN and the activation of downstream pathways are precisely regulated. The transcription factor STAT1 is a key effector of the IFN pathway. When the IFN signaling pathway is activated, the STAT1 protein is phosphorylated and modified by its kinase JAK1 to form heterologous or…
Identify a Key Protein that Can Regulate the Female Body’s Estrogen Cycle – RSK2
Recently, in a research report titled “RSK2 Maintains Adult Estrogen Homeostasis by Inhibiting ERK1/2-Mediated Degradation of Estrogen Receptor Alpha” published in the Cell Reports, scientists from Vanderbilt University and other institutions found a key regulatory protein through research that can regulate the body’s estrogen cycle. Oral contraceptives will moderately increase the risk of breast cancer in women, and birth control methods will use estrogen, a hormone that binds to…
The Use of Activin/GDF Fusion Protein Is Expected to Treat Pulmonary Hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension (PAH) is an insidious disease. Its symptoms may start slowly, and even before the symptoms appear, extensive damage has caused the blockage of small arteries, resulting in increased blood pressure in the lungs. When the symptoms—the most obvious being shortness of breath—are severe enough for PAH patients to seek treatment and obtain a definite diagnosis, based on currently available treatments, the patient’s chance of survival within five years…
PNAS: Obese Hormones Increase the Risk of Sepsis
Scientists from the Gulbenkian de Ciência Institute (IGC) led by Luís Moita have discovered that a hormone believed to treat obesity reduces the body’s resistance to bacterial infections and increases the risk of sepsis. The research results were recently published in PNAS. Sepsis is a potentially fatal disease that stems from the dysregulation of the organism’s response to infection, leading to organ failure. A recent study published in the…
PNAS: New Study Shows that Remdesivir Prevents Coronavirus MERS-CoV Infection in Monkeys
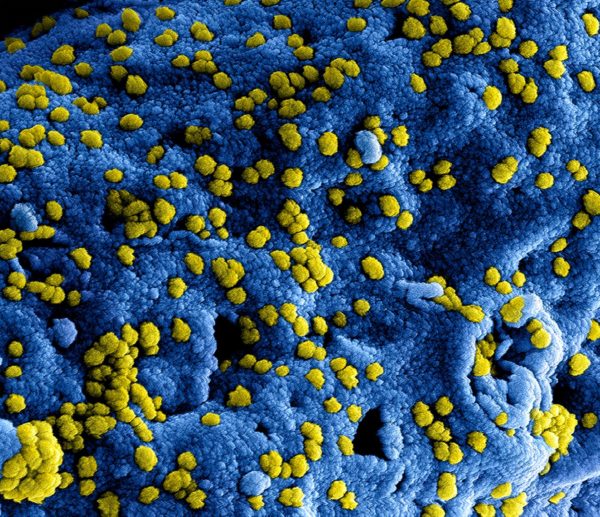
In a new study, researchers from the National Institutes of Health reported that the experimental antiviral drug remdesivir (also known as GS-5734) successfully prevented rhesus monkeys infected with the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) coronavirus (MERS-CoV) from becoming ill from this virus infection. Giving remdesivir before infection can prevent them from getting sick, while giving this drug after they are infected can improve their condition. The results were published in…
New Method to Predict Protein-Environment Interactions

It is well-known that proteins are the cornerstone of life and play a key role in all biological processes. Therefore, understanding how they interact with the environment is critical to developing effective treatments and designing the basis for artificial cells. Recently, the Protein Design and Immune Engineering Laboratory (LPDI) of the Institute of Bioengineering at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (EPFL), in collaboration with the Institute of Computational Science…
Mechanism of Human Immune Dysregulation Induced by Roquin-1 Protein Mutation Unveiled
Recently, researchers from Ghent University Hospital in Belgium published an article entitled “A human immune dysfunction syndrome characterized by severe hyperinflammation with a homozygous nonsense roquin-1 mutation” in Nature Communications. By studying a case of the hyperinflammatory syndrome with a homozygous nonsense mutation in Roquin-1, they discovered the mechanism of human immune dysregulation triggered by mutations in Roquin-1 protein, which may provide a new approach for the diagnosis and treatment…
Key Protective Proteins Affect the Prognosis of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Isolated Recently
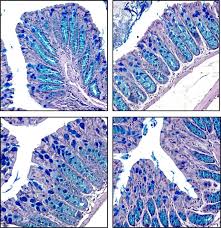
Recently, scientists at Trinity College Dublin have identified for the first time a family of proteins that may be directly linked to lower blood sugar levels in obese patients with type 2 diabetes. The results of this study show that patients with type 2 diabetes who have higher levels of IL-36 cytokines tend to have lower blood glucose levels, suggesting that these proteins (IL-36) may better control blood glucose levels…