Alzheimer’s Treatment with Stem Cells
Since the successful acquisition of human embryonic stem cells in 1998, scientists have begun to study the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) with stem cells. The possible mechanisms of stem cell therapy for AD include repairing and replacing damaged neurons, reconstructing neural circuits and functions, secreting trophic factors, and inhibiting amyloid protein formation. Using stem cells to treat AD is rapidly gaining momentum and considered to be the most potential treatment option for radical curing of this disease, as animal model-based researches indicate optimistic results, in addition, the world’s first stem cell drug derived from mesenchymal stem cells has been approved for the treatment of AD. Nonetheless, it is necessary to study the safety and efficacy of stem cell therapy prior to human clinical trials.
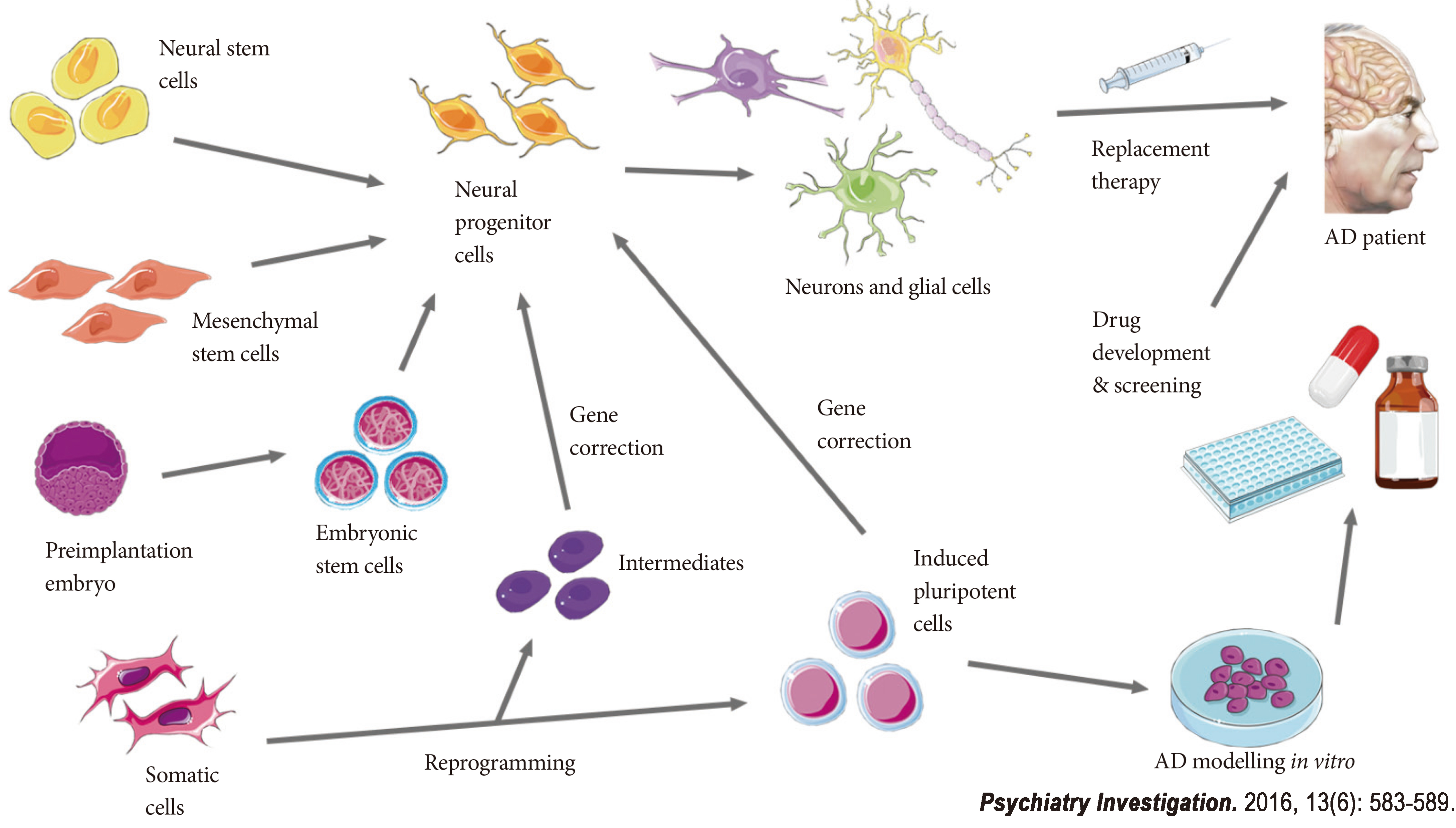
The stem cells currently utilized for the research and development of stem cell therapy in AD mainly include neural stem cells (NSCs), mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), embryonic stem cells (ESCs), as well as induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs).
About Alzheimacy
Although there are above-mentioned types of stem cells available for the development of stem cell therapy in AD, stem cells from each source have their own shortcomings. For example, NSCs are highly immunogenic and may produce strong immune rejection; ESCs may bring the risk of uncontrolled cell growth and tumor formation, therefore, the development of specific therapies must be comprehensively evaluated for effectiveness and safety, and then the prospect of clinical application can be predicted. Alzheimacy can fully support the development and treatment of stem cell therapy in AD, from basic research to pre-clinical studies.
Finding a suitable stem cell model or animal model for AD research can be challenging. At Alzheimacy, through long-term model creation and assessment, there are various stem cell models (including human stem cell models) and animal models (mice, rats, and non-human primates) available for researches in this field.
Additionally, we are also actively exploring the underlying mechanisms of stem cells transplantation for AD, understanding the regulation of migration rate and differentiation direction of stem cells after transplantation. Alzheimacy is confident to achieve this research goal by molecular biology, immunohistochemistry, imaging technology and other techniques. Moreover, genetic modification of stem cells as an effective delivery vector is one of our research directions.
Our scientists are well versed in the FDA requirements for stem cell therapy, such as recommendations on species selection, proof of concept researches, and duration of researches. Pivotal issues in stem cell research design include clinical relevance, appropriate comparative anatomy and physiology, relevant clinical routes of administration, and immune tolerance. Stem cell research toxicity studies are often performed in the related disease models. Crucial comprehensive assessments include disposition and tolerability of the stem cells following injection, the possible formation of ectopic tissues and tumor, site reactions, and functional impact. Our molecular imaging technology can successfully monitor the therapeutic effects.
Not only are we interested in cell-replacement therapy in AD, but we also hope that through the human stem cell model to predict the efficacy and safety of experimental Alzheimer’s drugs. Our industry-leading technology platform coupled with our complete pre-clinical capabilities allows us to optimize the time and effort spent to promote each pre-clinical project. At Alzheimacy, we make sure that each project is run as efficiently as possible by offering unique consultations with our scientists and business development teams.
As the AD drug research Technology Division of Creative BioMart, whose breadth of experience gained from being in the industry for over 10 years, Alzheimacy is an expert partner. We support pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies and leading academic institutions worldwide to develop stem cell therapy in AD.