Hepatocellular endoplasmic reticulum stress plays an important role in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Hepatonuclear factor 4 α (HNF4α) reduced expression is an important event in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver and other liver diseases. Does endoplasmic reticulum stress regulate the expression of HNF4α is not clear yet. The purpose of this study is to elucidate the mechanism of HNF4 α protein degradation and exploration of treatment strategies protecting HNF4α stability during the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Recently, researchers from Tongji University published an article titled “TRIB3-TRIM8 complex drives NAFLD progression by regulating HNF4Αα stability” in J Hepatol Journal. The study revealed that the TRIB3-TRIM8 complex promotes non-alcoholic fatty liver progression by regulating HNF4Α stability.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Source | Species | Tag |
| TRIB3-3073H | Recombinant Human TRIB3 protein(Met1-Gly358), GST-tagged | Insect Cells | Human | N-GST |
| TRIB3-3114H | Recombinant Human TRIB3 protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His |
| TRIB3-25H | Recombinant Human TRIB3, GST-tagged | Sf9 Insect Cell | Human | GST |
| HNF4A-2893H | Recombinant Human HNF4A protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His |
| HNF4A-9719Z | Recombinant Zebrafish HNF4A | Mammalian Cell | Zebrafish | His |
| HNF4A-7752M | Recombinant Mouse HNF4A Protein | Mammalian Cell | Mouse | His |
| HNF4A-630H | Recombinant Human HNF4A Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His |
| HNF4A-4895H | Recombinant Human HNF4A Protein, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST |
| HNF4A-2550C | Recombinant Chicken HNF4A | Mammalian Cell | Chicken | His |
| HNF4A-28507TH | Recombinant Human HNF4A | Wheat Germ | Human | N/A |
The correlation between HNF4Α and endoplasmic reticulum stress sensor TRIB3 was studied in non-alcoholic fatty liver tissue of humans and mice. The mechanism of TRIB3-mediated degradation of HNF4Α was studied using methods such as ribonucleic acid sequencing, mass spectrometry analysis, co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP), in vivo and in vitro ubiquitination analysis. A cell-penetrating peptide that can inhibit TRIB3-HNF4Α interaction was identified through molecular docking and co-IP.
TRIB3 directly interacts with HNF4Α, mediating endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced degradation of HNF4Α. TRIB3 recruits a tripartite motif containing 8 (TRIM8) to form the E3 ligase complex, which catalyzes the polyubiquitination of HNF4Α linked to K48 on lysine 470. Removing the degradation of HNF4Α can weaken the effect of high-fat feed-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
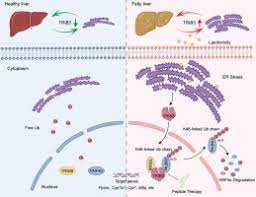
In addition, TRIB3 function obtained variation p.Q84R is associated with slow progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients, leading to decreased HNF4Α levels and more severe hepatic steatosis in mice. Importantly, using CPP to interfere with the TRIB3-HNF4Α interaction can restore HNF4Α levels and improve the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver in mice.
In this study, the researchers identified P-26 T3H2 as an effective inhibitor of TRIB3-HNF4Α interaction, representing an ideal strategy for developing targeted therapies for non-alcoholic fatty liver by stabilizing HNF4Α. Of clinical significance, researchers have confirmed that even in the context of TRIB3 p.Q84R mutation, P-T3H2 improves the progression of NAFLD, and this mutation appears more frequently in NAFLD patients.
Given the lack of strategies targeting transcription factors, data suggests that eliminating the interaction between TRIM8-TRIB3-HNF4Α may be a novel approach to treating non-alcoholic fatty liver and even other liver diseases by stabilizing the HNF4Α protein. Given the poor absorption of peptides in the intestine, further exploration of oral drugs that can occupy the binding pocket of HNF4Α ligand binding regions may be necessary for our findings to be clinically evaluated.
Related Products and Services
Protein Expression and Purification Services
Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) Service
Principle and Protocol of Co-Immunoprecipitation
Reference
Meng-Chao Xiao et al. TRIB3-TRIM8 complex drives NAFLD progression by regulating HNF4α stability. J Hepatol. 2024 Jan 16:S0168-8278(24)00036-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.12.029.