Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a common neurodegenerative disease, which has become a serious problem worldwide. The typical clinical features of Parkinson’s disease include motor manifestations such as bradykinesia, static tremors, and postural instability. Although several physiological processes are related to the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease, some studies have reported the central role of mitochondrial dysfunction in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease.
Recently, researchers from the Department of Health Sciences at the Graduate School of Donga University in South Korea published a paper in the journal Theranostics titled “Intranasal delivery of mitochondrial protein humanin rescues cell death and promotes mitochondrial function in Parkinson’s disease”. This study supports the new role of the mitochondrial protein humanin in mitochondrial function and neuronal survival against Parkinson’s disease. Among them, humanin therapy is sufficient to stimulate the expression of mitochondrial genes.
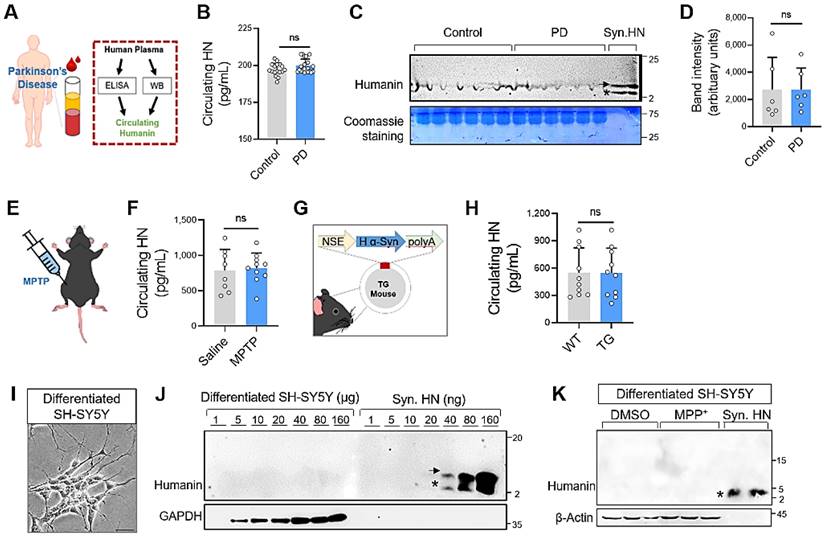
Mitochondrial dysfunction is a critical factor in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease (PD). Therefore, many aspects of mitochondrial function have been studied as potential therapeutic targets. In this study, researchers proposed a new strategy to promote mitochondrial function and prevent Parkinson’s disease through the mitochondrial-derived polypeptide (MDP) humanin (HN) encoded in the mitochondrial genome.
In order to test the potential of humanin as a potential biomarker for Parkinson’s disease, researchers measured the protein levels of circulating humanin in the plasma of Parkinson’s disease patients and transgenic or neurotoxic Parkinson’s disease mouse models. The next step for researchers is determining whether HN peptide therapy can regulate its activity or expression. Using a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease, the researchers assessed how HN enters the brain through Nasal administration. Researchers further revealed the possible mechanism of HN peptide therapy for Parkinson’s disease through in vitro and in vitro Parkinson’s disease models.
Although the expression of intracellular HN is not related to PD, HN treatment can induce the expression of intracellular HN and promote mitochondrial biogenesis to induce the expression of mitochondrial genes. After Nasal administration, HN peptide has neuroprotective and behavioral recovery effects on animal models of Parkinson’s disease.
Interestingly, HN peptide after Nasal administration was found in the brain, mainly through the Trigeminal nerve pathway. In mechanism, HN induces the activation of Phosphatidylinositol -3-kinase/Protein kinase B (PI3K/AKT) signaling pathway, thus promoting mitochondrial biogenesis, leading to the upregulation of mitochondrial genes including human protein.
This study elucidates that exogenous HN peptides protect PD by promoting mitochondrial biogenesis and stimulating the expression of mitochondrial genes, including humanin. Therefore, enhancing mitochondrial function with HN peptides may be a promising method for treating Parkinson’s disease.
Related Products
Recombinant Human Mitochondrial Ribosomal Protein L28, T7-tagged
Recombinant Human mitochondrial ribosome recycling factor, His-tagged
Recombinant Human GrpE-like 1, Mitochondrial (E. coli), His-tagged
Recombinant Human Creatine Kinase, Mitochondrial 1A, His-tagged
Recombinant Human 5′,3′-Nucleotidase, Mitochondrial, His-tagged
Reference
Kyung Hwa Kim. Intranasal delivery of mitochondrial protein humanin rescues cell death and promotes mitochondrial function in Parkinson’s disease. Theranostics. 2023 May 29;13(10):3330-3345. doi: 10.7150/thno.84165.