The immune system acts as a guardian of the host by initiating an immune response to harmful pathogens and tumor cells. However, overreaction is the cause of chronic or excessive inflammation and autoimmune diseases. Immune checkpoints play a key role in regulating the size of immune responses, thereby maintaining immune homeostasis and self-tolerance. However, tumor cells can also use immune checkpoints to evade immune surveillance, suppress anti-tumor immune responses, and…
Month: March 2023
The Role of the Third Intracellular Ring of GPCR in GPCR Signal Conduction Mechanism
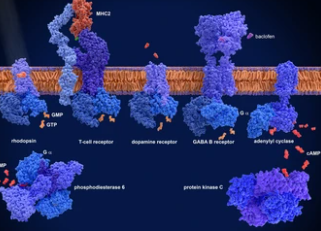
In a new study, American researchers have discovered the role of the third intracellular loop of GPCR in the GPCR signal transduction mechanism, indicating the possibility of adopting more targeted drug discovery methods and developing new drugs. More than one-third of the drugs approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) function by targeting G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). The human body has over 800 types of GPCRs,…
The Base Editor Is Expected to Be Used for the Treatment of CD3Δ Severe Combined Immunodeficiency
In a new study, researchers from research institutions such as the University of California, Los Angeles, discovered that advanced genome editing technology may be able to be used for a rare and fatal genetic disease, D3 delta severe combined immunodeficiency, CD3δ SCID, for a one-time treatment. The relevant research results were published online in Cell, with the title “Human T cell generation is restored in CD3δ severe combined immunodeficiency through…
Understand the mechanism of action of CFTR to better treat cystic fibrosis
In a new study, researchers from St. Jude’s Children’s Research Hospital and Rockefeller University in the United States combined their expertise to gain a better understanding of a protein called cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR). Mutations in CFTR cause cystic fibrosis, a fatal disease that cannot be cured. The relevant research results were published online in the journal Nature, with the title “CFTR function, physiology and pharmacology at single…
Interferon-gamma (IFNG) drives regulatory T cells to restrain DC1-mediated priming of cytotoxic T cells against lung cancer
Immunotherapy – drug therapy that stimulates the immune system to attack tumors – has a good effect on some types of cancer, but its effect on lung cancer is mixed. A new study helps to clarify why the immune system responds so weakly to lung cancer, even after treatment with immunotherapy drugs. In this study on mice, researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology found that bacteria found naturally…
ROR2 may be a potential biomarker of prostate cancer
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the main cause of cancer-related deaths in men. Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) is still the standard systemic treatment, but patients always progress to metastatic castrated tolerant prostate cancer (mCRP C). Most of these tumors will react to the further treatment of androgen signaling inhibitors (ASIs), but inevitably will produce drug resistance. Changes in androgen receptor (AR) and interaction pathway contribute to the sustained activity of…
AMPK activation is a promising strategy to reduce the risk of melanoma
Skin cancer is the most common cancer in the United States, with about 5 million cases every year. Melanoma is less common than other types of skin cancer, including basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), but it causes most of the death of skin cancer. The risk of melanoma is related to environmental factors, such as ultraviolet radiation (UVR) and genetic background. It is noteworthy that…
Autoimmunity in Down’s syndrome via cytokines
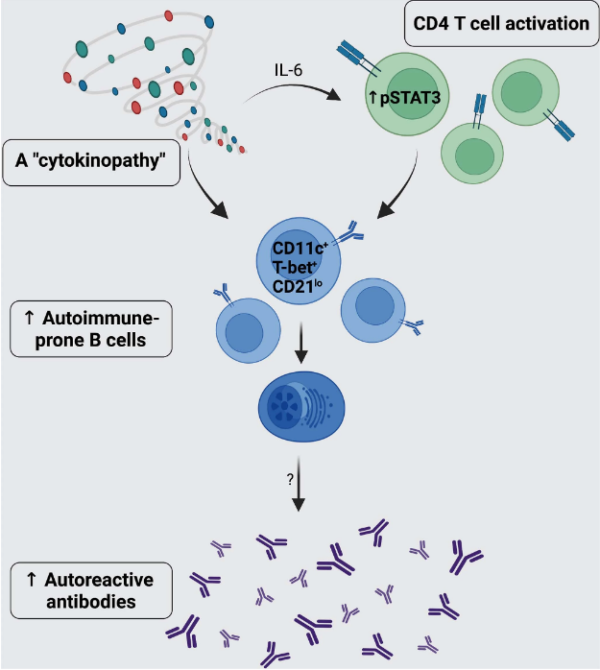
In a new study, researchers from the Icahn Medical College in Mount Sinai, the United States, determined which parts of the immune system of patients with Down’s syndrome had problems, which led to autoimmune diseases. Relevant research results were published online in the journal Nature. This new study complements the findings of these authors published in the journal of Immunity in October 2022, that is, the frequency of viral…
