Thu, 2023/03/02
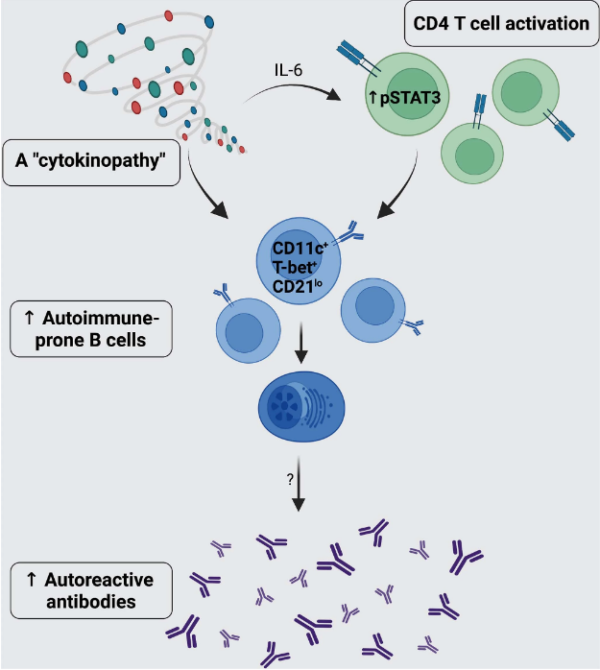
Autoimmunity in Down’s syndrome via cytokines
Fri, 2023/02/17
The combination of PD1-IL2v and anti-PD-L1 can destroy the resistance of cancer to immunotherapy
Fri, 2023/02/17
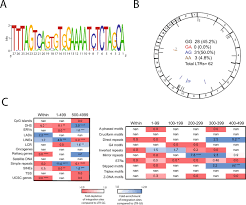
The antiviral APOBEC3 protein actually promotes HIV to enter the latent state
Fri, 2023/02/17
Restoring lost epigenetic information can make aging mammals rejuvenate

Fri, 2023/02/17
CAR-T cell therapy is expected to eliminate residual tumor cells after solid tumor surgery
Fri, 2022/12/23
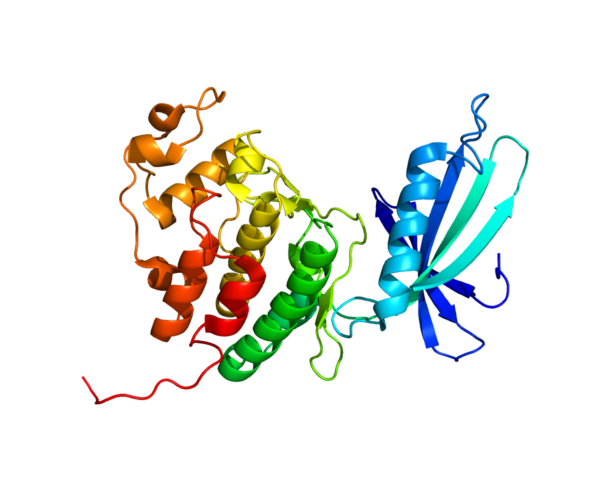
CDK4 - a master regulator of the cell cycle
Fri, 2022/12/23
Occluding the ACE2 receptor, renders all mutants incapable of infection!
Fri, 2022/12/23
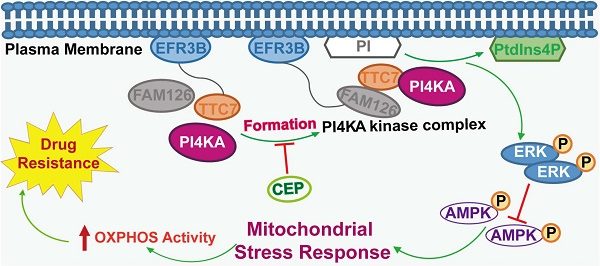
Targeting PI4KA increases chemosensitivity of refractory leukemia by regulating ERK/AMPK/OXPHOS axis
