Recombinant Human CREB1
| Cat.No. : | CREB1-26H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human CREB produced inE.Coliis a non-glycosylated, polypeptide chain containing amino acids and 2-328 having a molecular mass of 81 KD. This protein is the full-length form and is produced as a maltose binding protein (MBP) fusion protein with a poly His-tag.CREB is purified by proprietary chromatographic techniques. |
| Availability | November 17, 2025 |
| Unit | |
| Price | |
| Qty |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Citation
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | E.coli |
| Tag : | Non |
| Protein Length : | 2-328 a.a. |
| Description : | CREB (cAMP response element-binding) proteins are transcription factors which bind to certain sequences called cAMP response elements (CRE) in DNA and thereby increase or decrease the transcription of certain genes. CREB is highly related (in structure and function) to CREM (cAMP response element modulator) and ATF-1 (activating transcription factor-1) proteins. CREB has many functions in many different organs although most of its functions have been studied in relation to the brain. CREB is also thought to be involved in the growth of some types of cancer. In humans. |
| Physical Appearance : | Lyophilized freeze dry powder. |
| Purity : | Greater than 95% as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Formulation : | CREB is supplied as lyophilized freeze dry powder without additives. |
| Biological Activity : | CREB is phosphorylatable in vitro, using either recombinant Protein Kinase A, or Rsk immunoprecipitated from stimulated cells. This phosphorylation can be monitored by ELISA using CREB [pS133] phosphoELISA or by Western blotting using an anti-CREB [pS133] phosphorylation site specific antibody in conjunction with chemiluminescence detection methods. Optimization of the cell stimulation protocol, cell lysis procedure, and reaction conditions may be required for each specific application. Please note: Kinase activity may vary depending on the substrate and reaction conditions. |
| Storage : | Store at 4°C if entire vial will be used within 1-2 weeks. Store, frozen at -20°C for longer periods of time. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Publications : |
Modulating cAMP responsive element binding protein 1 attenuates functional and behavioural deficits in rat model of neuropathic pain. (2019)
|
| Gene Name | CREB1 cAMP responsive element binding protein 1 [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Synonyms | CREB1; cAMP responsive element binding protein 1; CREB; MGC9284; OTTHUMP00000206660; transactivator protein; active transcription factor CREB; cAMP-response element-binding protein-1; CREB-1 |
| Gene ID | 1385 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_004379 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_004370 |
| MIM | 123810 |
| UniProt ID | P16220 |
| Chromosome Location | 2q34 |
| Pathway | Antigen processing and presentation; Huntington"s disease; Melanogenesis; Prostate cancer |
| Function | RNA polymerase II transcription factor activity, enhancer binding; double-stranded DNA binding; protein dimerization activity; sequence-specific DNA binding; specific RNA polymerase II transcription factor activity; transcription cofactor activity |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| CREB1-6915H | Recombinant Human CREB1, His & MBP tagged | +Inquiry |
| CREB1-1019R | Recombinant Rhesus monkey CREB1 Protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| Creb1-1443R | Recombinant Rat cAMP Responsive Element Binding Protein 1, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| CREB1-183H | Recombinant Human CREB1, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| CREB1-6020C | Recombinant Chicken CREB1 | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| CREB1-7289HCL | Recombinant Human CREB1 293 Cell Lysate | +Inquiry |
Removing reference mapping biases using limited or no genotype data identifies allelic differences in protein binding at disease-associated loci
Journal: BMC Medical Genomics PubMed ID: 26210163 Data: 2015/7/26
Authors: Martin L. Buchkovich, Karl Eklund, Terrence S. Furey
Article Snippet:EMSAs were performed according to the protocol included with the LightShift Chemiluminescent EMSA Kit (Thermo Scientific).EMSAs were performed according to the protocol included with the LightShift Chemiluminescent EMSA Kit (Thermo Scientific).. Briefly, each reaction containing 1x binding buffer, 1 μg poly(dIdC), and 200 ng of purified CREB1 protein (CreativeBiomart CREB1-26H) was incubated for 15 min before adding biotin-labeled probes in a total reaction volume of 20 μl and incubating for another 25 min.. Reactions were electrophoresed on 6 % DNA retardation gels (Life Technologies) in 0.5X TBE buffer (Lonza), transferred to nylon membranes (Thermo Scientific), UV cross-linked and detected with chemilluminescence (Thermo Scientific).Reactions were electrophoresed on 6 % DNA retardation gels (Life Technologies) in 0.5X TBE buffer (Lonza), transferred to nylon membranes (Thermo Scientific), UV cross-linked and detected with chemilluminescence (Thermo Scientific).
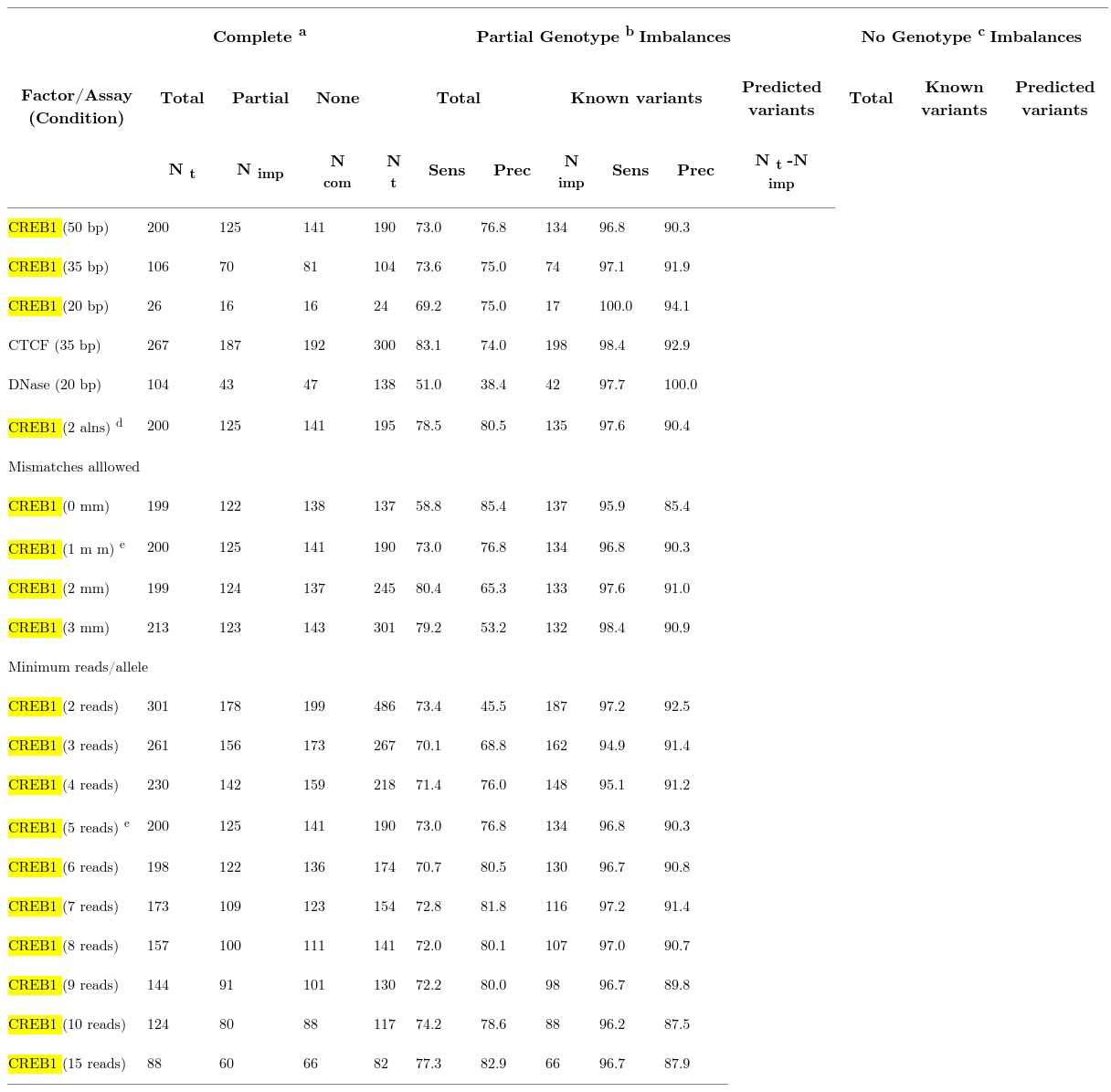
Allelic imbalance detection accuracy in alignments using partial or no genotypes compared to complete genotypes
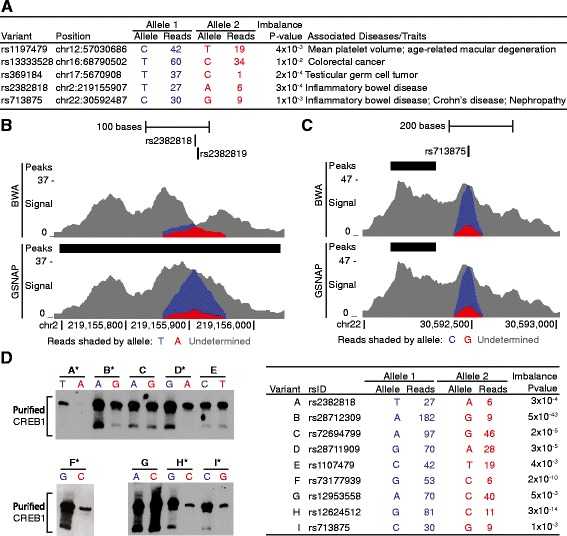
Validation of allelic imbalance detected at GWAS loci and other predicted sites. a We detected significant allelic imbalance (binomial P < 0.01) in
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews (0)
- Q&As (0)
Ask a Question for All CREB1 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All CREB1 Products
Required fields are marked with *



