Interleukin (IL) superfamily
Background of Interleukin (IL) Superfamily
What is IL Superfamily?
The IL (Interleukin) Superfamily is a group of cytokines with complex immunoregulatory functions. These proteins play a significant role in the body’s immune and inflammatory responses. They are produced by and direct the function of white blood cells (leukocytes) such as lymphocytes and monocytes. Cytokines in the IL superfamily include interleukin-1 (IL-1) through interleukin-37 (IL-37), each with its unique role in immune response.
The interleukin (IL) superfamily consists of protein members known as interleukins and interleukin receptors. Members of the IL superfamily participate in many processes including immunity, inflammation and hematopoiesis. IL superfamily members promote the growth of immune system cells and help regulate the immune system. The IL superfamily include the IL-1, IL-6, IL-10, IL-12, IL-17 families and other interleukins.
Interleukins are secreted by various types of cells, primarily related to T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes of the immune system. Interleukins act by binding to interleukin receptors embedded in the outer cell membrane. Once interleukins bind to their receptors, a series of chemical signals are triggered inside the cell to regulate various cell functions.
ILs and IL receptors are associated with many diseases, especially in the immune system such as autoimmune diseases. Autoimmune diseases occur when the host immune system inappropriately targets self-antigens. For example, IL-18 plays a pro-inflammatory role in most autoimmune diseases where elevated levels of extracellular IL-18 strongly correlate with disease progression. These high levels of IL-18 exert pleiotropic effects on immune cells, sustaining IFNγ production and increasing natural killer (NK) cell cytotoxicity, leading to tissue damage and necrosis. Additionally, researchers are investigating interleukin applications for cancer therapy.
Interleukins Classification and Function
IL-1
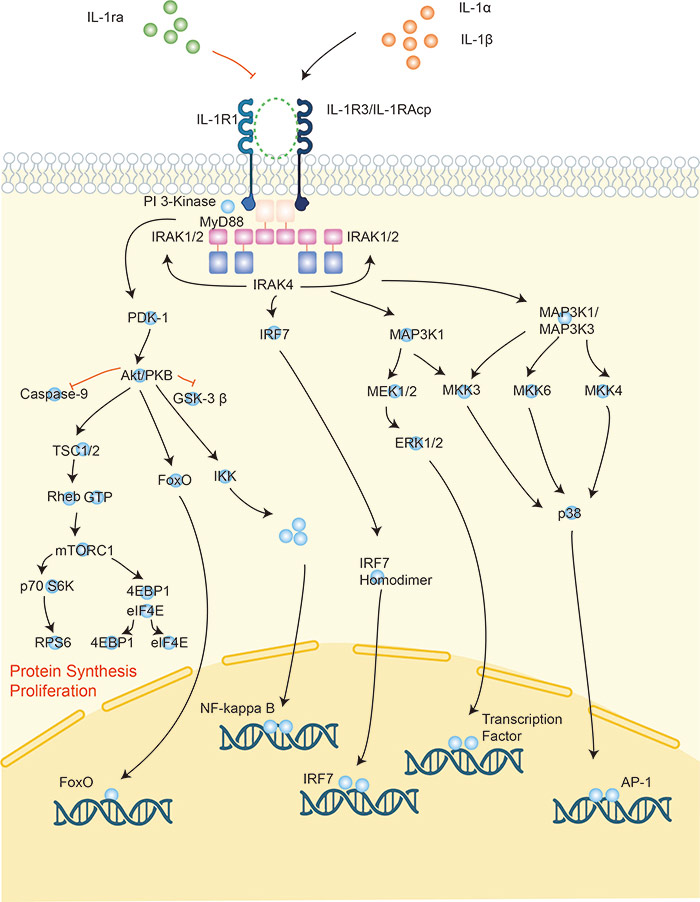
IL-1 was originally termed as the protein inducing fever and was called pyrogenic factor, which is a cytokine mainly produced by activated macrophages composed of two proteins, IL-1α and IL-1β. The IL-1 family (IL-1F) has an ancient evolutionary history. Based on amino acid sequence conservation, gene structure homology and three-dimensional structure, 11 IL-1 members have been identified, including 7 pro-inflammatory agonists (IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-18, IL-33, IL-36a, IL-36b, and IL-36g) and 4 anti-inflammatory antagonists (IL-1Ra, IL-36Ra, IL-37, and IL-38).
The biological activities of IL-1α and IL-1β are mediated by IL-1R1 (IL-1 type I receptor), which induces a conformational change in the extracellular domain of IL-1R1 allowing it to interact with IL-1RAcP, which is essential for intracellular signal transduction, including MyD88-dependent activation of NF-κB, p38, JNK and ERK. IL-1Ra competes for binding to IL-1R1 but does not recruit IL-1RAcP or activate intracellular signaling pathways. IL-1R2 functions as a decoy receptor on the cell surface or in a soluble form (sIL-1R2) in the extracellular environment.
IL-1 is one of the important inflammatory mediators that plays a regulatory role primarily in cellular immune activation. It plays important roles in the pathogenesis of both acute and chronic inflammation induced by various stimulatory factors (including antigens, endotoxins, bacteria and viruses) and is closely related to the pathological processes of diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis and periodontitis. IL-1 also participates in hematopoietic, nervous, endocrine system responses of the body and in certain pathophysiological processes of antitumor activity. Monitoring the release of IL-1 helps understand the immune regulatory capacity of the body and provides a reliable basis for disease diagnosis, treatment efficacy observation and prognostic judgment.
IL-2
Without stimulation from various stimuli, T cells generally cannot survive long-term in vitro culture. With the addition of IL-2, T cells can undergo long-term sustained proliferation, and thus IL-2 was originally named T cell growth factor (TCGF). T cells can only express IL-2R and become the target cells of IL-2 after activation by mitogens or other stimuli. IL-2 can also induce its target cells to increase IL-2R expression. In vivo, IL-2 acts on CD4+ T cells through autocrine signaling, because activated CD4+ T cells can produce a large amount of IL-2. Expression of IL-2R on T cells is transient, usually peaking at 2-3 days after activation and disappearing around 6-10 days. As IL-2R disappears, T cells lose the ability to respond to IL-2. Therefore, to maintain normal T cell long-term growth in vitro, T cells must be continuously stimulated by mitogens or other stimuli to maintain IL-2R expression.
IL-3
IL-3 is a major early hematopoietic growth factor that plays an extremely important role in hematopoietic regulation. IL-3 mainly acts on early hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells to promote their proliferation and differentiation. In late stages, IL-3 works together with other hematopoietic growth factors such as erythropoietin (EPO), GM-CSF (granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor) and TPO (thrombopoietin) to promote the formation of colonies of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), granulocyte-monocyte progenitor cells (CFU-GM), granulocyte progenitor cells (CFU-G), macrophage progenitor cells (CFU-M), megakaryocyte progenitor cells (CFU-Meg), eosinophil progenitor cells (CFU-Eo), basophil progenitor cells (CFU-Ba) and erythroid progenitor cells (CFU-E). IL-3 also plays an important role in hematopoiesis in vivo.
IL-4
IL-4 is a pleiotropic cytokine produced by activated T lymphocytes, mast cells, and eosinophils. IL-4 activates cytotoxic T cells and is considered a prototypic cytokine produced by TH2 cells. It plays a crucial role in the development of T and B lymphocytes as well as driving humoral immune responses and antibody production. IL-4 has immunoregulatory effects on B cells, T cells, mast cells, macrophages, and hematopoietic cells.
IL-5
IL-5 is a pleiotropic cytokine also known as T cell replacing factor, eosinophil colony-stimulating factor, and eosinophil differentiation factor, mainly produced by T cells. IL-5 promotes the production of eosinophils in the bone marrow. Transgenic mice with IL-5 have a large number of eosinophils in peripheral blood, spleen and bone marrow, with detectable IL-5 in serum. IL-5 can activate eosinophils and promote their killing of tumor cells through the ADCC mechanism. It facilitates eosinophil-mediated killing of pathogens by regulating degranulation. IL-5 also promotes eosinophil superoxide anion production, prolongs the survival time of eosinophils in peripheral blood, and facilitates IgG- and IgA-induced degranulation of eosinophils. Additionally, IL-5 increases the release of neurotoxins from eosinophil precursors. Overall, IL-5 plays an important role in mucosal immunity.
IL-6
IL-6 is mainly produced by monocytes, Th2 cells, vascular endothelial cells and fibroblasts. IL-6 acts on many target cells, including macrophages, hepatocytes, resting T cells, activated B cells and plasma cells. Its biological effects are also highly complex. It was previously referred to as B cell stimulating factor-2 (BSF-2), 26kD protein, B cell differentiation factor (BCDF) or hepatocyte stimulating factor (HSF).
IL-6 exhibits antitumor effects by directly or indirectly enhancing the cytolytic activity of natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T cells. IL-6 stimulates glucocorticoid synthesis, osteoclast activity and keratinocyte growth. It can also promote hematopoiesis in the bone marrow. IL-6 alone cannot stimulate the secretion of other cytokines from responsive cells. At physiological concentrations, it exhibits relatively weak autocrine effects on immune cells. This suggests its primary immunological function is to enhance the effects of other cytokines.
IL-7
IL-7 primarily acts on lymphocytes as a target cell. It exhibits growth-promoting activity on B cell progenitors from human or mouse bone marrow, thymocytes, and mature T cells in peripheral tissues. Therefore, IL-7 plays an important role in lymphocyte development, survival and homeostasis by regulating the proliferation and differentiation of distinct lymphocyte lineages including B cells, T cells and NK cells both in the primary lymphoid organs and secondary lymphoid tissues. As a key cytokine supporting lymphopoiesis, IL-7 signaling is crucial for adaptive immune system development and function.
IL-8
IL-8 is a chemokine secreted by Th1 cells. It chemoattracts and activates neutrophils, promoting neutrophil degranulation and phagocytic activity. IL-8 is a multifunctional factor lacking species specificity in its biological functions. Originally discovered to act on neutrophils by specifically recruiting them into inflammatory tissues, inducing degranulation and reactive oxygen species production leading to respiratory burst, it also activates inflammatory cells, promotes acute phase protein synthesis, causes fever, participates in inflammatory pathological damage, and promotes the release of inflammatory mediators and fibroblast proliferation involved in chronic inflammation. Thus, IL-8 plays an important role in inflammatory responses. Further research found that IL-8 can act on different cells, promoting inflammatory processes, stimulating blood vessel formation, inducing mitosis, and regulating host immune functions. It is closely related to the occurrence and development of various inflammatory diseases, tumors, and immune diseases.
IL-9
In humans, IL-9, also known as P40, is secreted. In mice, IL-9 is also known as P40, mast cell growth enhancing factor, and T cell growth factor III. Mouse IL-9 acts on human cells, but human IL-9 has no activity on mouse cells.
IL-9 exhibits bidirectional immunological functions - it can both promote the development of certain diseases as well as suppress the development of others. Current research suggests that in hypersensitivity reactions and autoimmune diseases, IL-9 acts as a pathogenic factor. However, in parasitic infections and skin transplants, IL-9 promotes the body's clearance of pathogens and the formation of transplantation immune tolerance. IL-9 can either facilitate or inhibit various disease processes through its complex immunoregulatory roles in both humans and mice. Species specificity also exists in terms of IL-9 receptor activation between these organisms.
IL-10
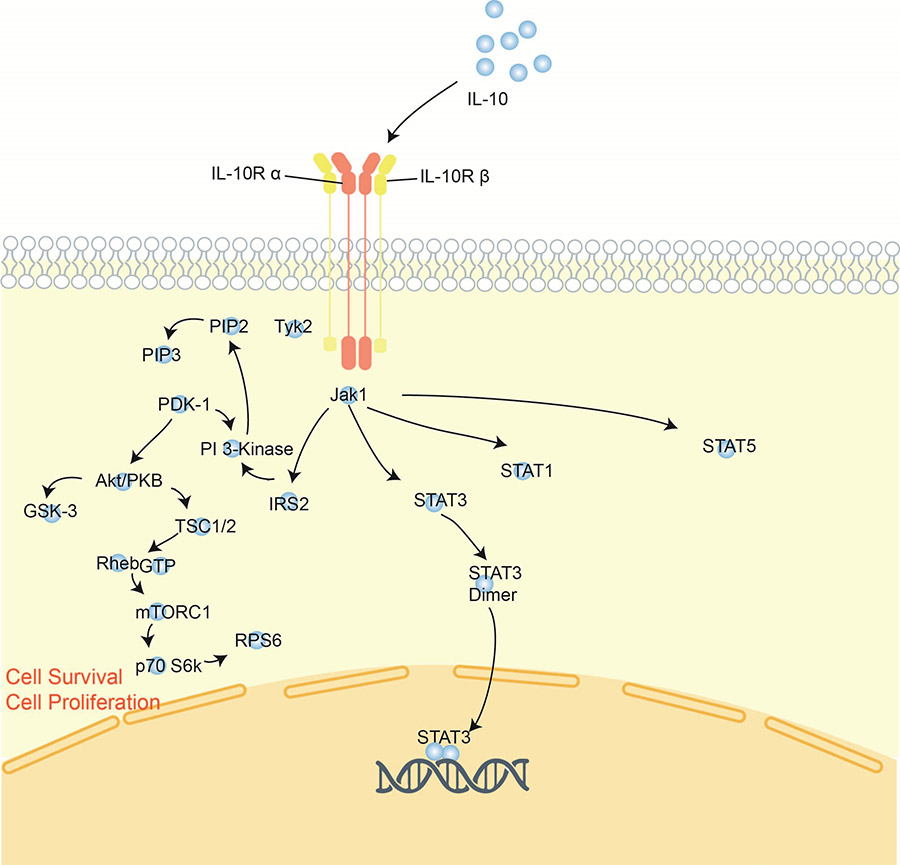
IL-10, also termed cytokine synthesis inhibitory factor (CSIF), is a pleiotropic cytokine that can exert immunosuppressive or immunostimulatory effects in multiple cell types. IL-10 produced by monocytes/macrophages can effectively regulate monocyte/macrophage function. As a cellular negative regulator of immune responses, IL-10 inhibits the production of prostaglandin E2 and pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, and IL-8. IL-10 is also able to suppress the proliferation of human Th0, Th1 and Th2-like T cell clones. Therefore, IL-10 plays an important regulatory role in dampening excessive immune activation through inhibitory effects at both the cellular and cytokine levels.
IL-11
IL-11 is a novel hematopoietic cytokine produced by human bone marrow stromal cells (fibroblasts) and mesenchymal cells. The human thyroid carcinoma cell line NTM-1 can also continuously secrete IL-11.
IL-11 can participate in immune responses in the body. It is involved in both primary and secondary immune responses, regulating antigen-specific antibody reactions. In vitro, IL-11 promotes IL-6-dependent plasmacytoma cell proliferation and T cell-dependent B cell development. Primitive cells can differentiate into macrophages when cultured in a medium containing IL-11 and EPO.
Therefore, IL-11 exhibits diverse immunoregulatory functions through supporting the growth and differentiation of various immune cells both directly and indirectly via other cytokines. It also plays a role in hematopoiesis and linking the immune and hematopoietic systems
IL-12
IL-12 is produced by dendritic cells (DCs), macrophages, B lymphocytes and other antigen-presenting cells (APCs). IL-12 p70 is a very important cytokine in cellular-mediated immunity. Its primary immunoregulatory role is to induce the differentiation of naïve T helper cells into the Th1 subset and promote the development and proliferation of Th1 cells. Helper T cells are indispensable for cellular and humoral immune responses mediated by B lymphocytes. Helper T cells can be classified into two subsets, Th1 and Th2. Th1 cells produce IL-2, IL-3, IFN-γ, lymphotoxin and granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF), involved in cellular immunity. Th2 cells produce IL-4, IL-5, IL-10 and IL-13 to help B cells produce antibodies and participate in humoral immunity. Therefore, as a key inductive cytokine for Th1 polarization, IL-12 plays a central role in bridging innate and adaptive immunity against intracellular pathogens and tumors
IL-13
IL-13 can be secreted by various cell types, including CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, mast cells, eosinophils, basophils and natural killer cells. IL-13 has regulatory effects on monocyte morphology and surface molecule expression. IL-13 promotes monocyte/macrophage morphological changes and accelerates monocyte/macrophage fusion to form foreign body giant cells (FBGCs). IL-13 can enhance the expression of CD23 (low affinity IgE receptor IgERn), major histocompatibility complex II (MHCII) and mannose receptors (related to phagocytosis) on human monocytes. IL-13 can also inhibit lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated monocyte/macrophage inflammatory cytokine gene transcription and protein synthesis, such as IL-1, IL-6, IL-8. Therefore, IL-13 modulates monocyte/macrophage functions important for defense responses, antigen presentation and resolution of inflammation
IL-15
IL-15 is a soluble cytokine that participates in and regulates inflammatory and immune responses in the body as a chemoattractant for various immune cells. IL-15 can stimulate the proliferation of CTLL, phytohemagglutinin (PHA)-activated T cells and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. It also acts synergistically with IL-2. IL-15 is chemotactic for T cells, and its chemotactic effect is stronger than that of IL-8 and MIP-α. Therefore, as a multifunctional cytokine, IL-15 regulates both innate and adaptive immunity through activating and attracting distinct immune cell populations involved in inflammatory responses.
IL-16
IL-16 is mainly produced by activated CD8+ T cells, and its receptor is CD4. IL-16 can chemoattract CD4+ T cells, monocytes and eosinophils. It induces the expression of IL-2R and HLAII class molecules on T cells and monocytes. Therefore, as an immunoregulatory chemokine, IL-16 plays an important role in recruiting and activating CD4+ T cells and antigen presenting cells through CD4 receptor engagement during immune responses. The sequential effects of IL-16 on different immune cell types contribute to both innate and adaptive immunity.
IL-17
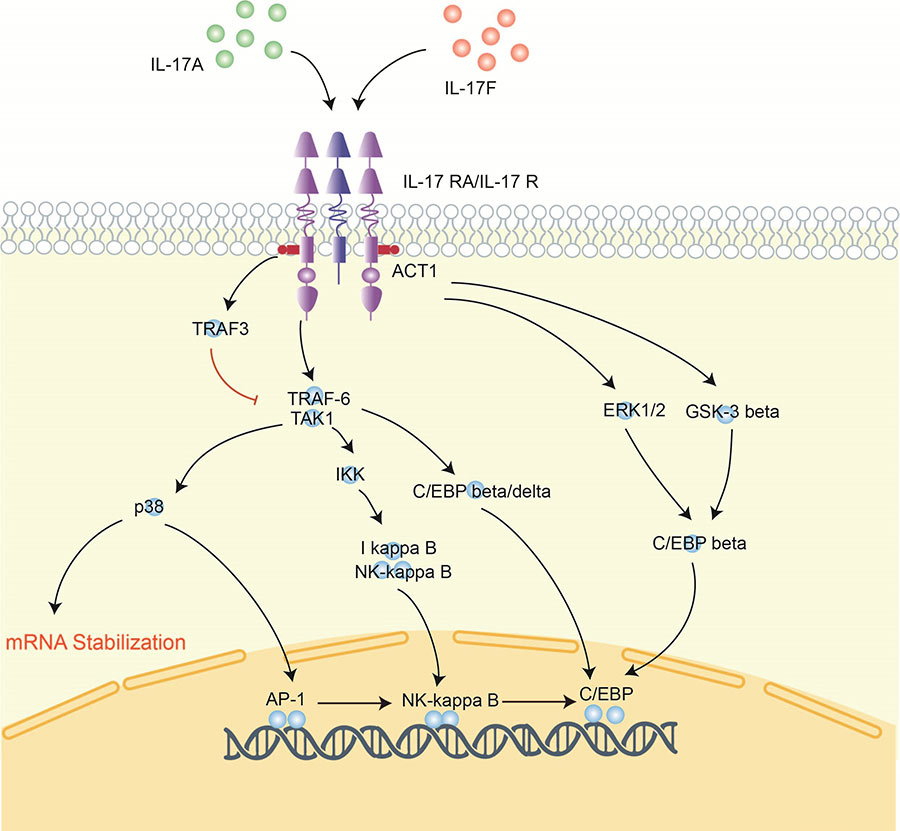
IL-17A has potent pro-inflammatory properties. It promotes the local production of chemoattractants such as IL-8, MCP-1 (monocyte chemoattractant protein-1), and Gro-α (growth-regulated α protein), facilitating the rapid accumulation of monocytes and neutrophils at sites of inflammation. In addition, IL-17A can stimulate the production of hematopoietic growth factors G-CSF and GM-CSF, inducing proliferation of myeloid cell lineages in the bone marrow. It also induces the expression of intercellular adhesion molecules (ICAM) on cells, driving T cell responses. Therefore, through inducing multiple downstream signals, IL-17A plays a key role in amplifying innate and adaptive immune responses during infection and tissue inflammation. Its pro-inflammatory properties collectively enhance pathogen clearance but prolonged signaling could potentially exacerbate immunopathology.
IL-18
IL-18 is a multifunctional cytokine that exhibits immunological functions without species specificity. Originally discovered to act on neutrophils, IL-18 specifically recruits them into inflammatory tissues, inducing degranulation and reactive oxygen species production leading to respiratory burst. It also activates inflammatory cells, promotes acute phase protein synthesis, causes fever and participates in inflammatory pathological damage. IL-18 further promotes the release of inflammatory mediators and fibroblast proliferation involved in chronic inflammation. Therefore, IL-18 plays an important role in inflammatory responses. Further research found that IL-18 can act on different cell types, promoting inflammatory processes, stimulating blood vessel formation, inducing mitosis, and regulating host immune functions. It is closely related to various inflammatory diseases, tumors, and immune diseases. In summary, through diverse cellular targets and activities, IL-18 exerts broad regulatory roles in immune and inflammatory pathways.
IL-19
IL-19 is one of the cytokines in the IL-10 family. It is highly expressed in human monocytes, B lymphocytes, and T lymphocytes, as well as inflammatory cells. IL-19 exerts its biological functions mainly through the IL-20R1/R2 receptor complex.
IL-19 and IL-20 are members of the IL-10 cytokine family. However, the precise role of IL-19 remains unclear and controversial - it could be either pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory. Some studies suggest that IL-19 may have anti-inflammatory effects similar to IL-10 and may induce phenotypic switching of lymphocytes from Th1 to Th2. However, other research shows that IL-19 up-regulates IL-6 and TNF-α production in monocytes, indicating pro-inflammatory properties.
Although IL-20R1 expression has not been detected on immune cells, many studies clearly demonstrate effects of IL-19 on these cells. Most research indicates IL-19 as part of the Th2 system. In summary, while IL-19 signals through the IL-10 receptor complex, its overall immunological functions require further elucidation, as both pro- and anti-inflammatory activities have been reported depending on cellular contexts
IL-20
IL-20 is a newly discovered member of the interleukin-10 related cytokine family. IL-20 is able to regulate normal physiological functions of the skin by activating the STAT3 pathway in keratinocytes. This leads to upregulated expression of various cytokines and chemokines, thereby modulating early inflammatory responses in the skin. In summary, through targeting keratinocytes, IL-20 plays an important regulatory role in maintaining skin homeostasis and is involved in initiating cutaneous inflammation. Elucidating its signaling networks provides novel insights into the immunological control of skin health and disease.
IL-21
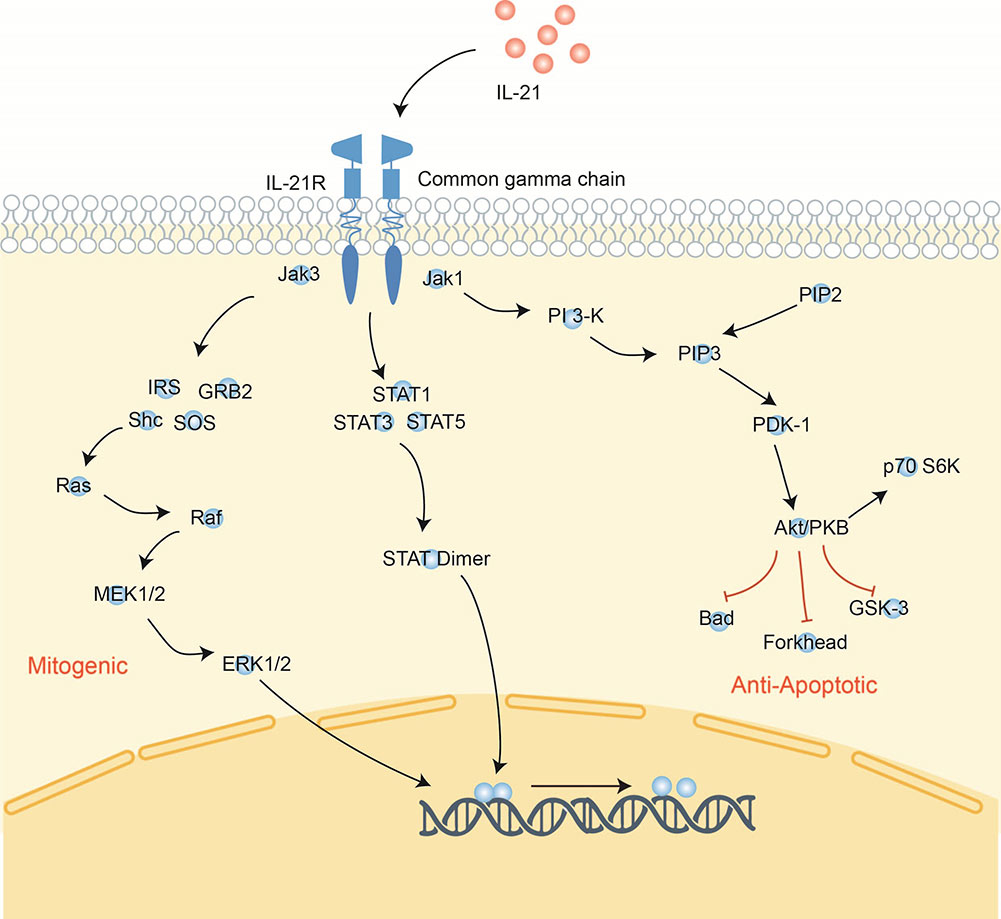
Interleukin-21 (IL-21) is a recently described cytokine that belongs to the common γ chain cytokine receptor family. Like other members of this common γ chain family, IL-21 is a four α-helical bundle type I cytokine. It signals through a receptor complex consisting of IL-21R and the common γ chain/IL-2Rγ. IL-21 is primarily produced by CD4+ T cells and natural killer T (NKT) cells, and exerts broad effects on many different cell types. IL-21 signaling in CD4 T cells is required for Th17 differentiation and generation of T follicular helper (Tfh) cells, which support B cell differentiation and antibody production in germinal centers. IL-21 also directly regulates B cell proliferation and apoptosis in a context-dependent manner and can promote immunoglobulin production and isotype switching. Additionally, IL-21 signaling enhances the cytotoxic functions of CD8+ T cells, natural killer cells and NKT cells. Therefore, IL-21 integrates both innate and adaptive immunity through regulating diverse immune cell subsets.
Applications
Interleukin (IL) proteins play critical roles in the immune system, so their applications are primarily in medical research, diagnostics, and treatment, particularly in relation to immune system-related diseases.
Therapeutic applications: Certain types of interleukin, such as IL-2 and IL-11, are used as therapeutics. For instance, IL-2 is used for treating kidney cancer and metastatic melanoma, as it helps stimulate the growth of certain types of immune cells. IL-11 is used to treat thrombocytopenia (a low level of platelets in the blood) in cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy.
Immunomodulation: Interleukins, like IL-10 and IL-4, can be used in moderation of the immune response. They are experimented to treat conditions like multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and other autoimmune diseases.
Vaccine Development: Some interleukins are used in the development of vaccines. They are used as adjuvants, substances that enhance the body's immune response to an antigen. For example, IL-12 is being studied for its potential use as an adjuvant in vaccines against various pathogens, including HIV.
Anti-Cancer Therapy: Some interleukins have been found to have tumor-suppressing properties. A classic example is the use of IL-2 in the treatment of certain cancers. More recent research is looking at interleukins like IL-15 and IL-21 for their potential anti-cancer properties.
Diagnostics: Levels of specific interleukins can be used as diagnostic markers for certain conditions. For instance, high levels of IL-6 are associated with systemic inflammation, and can be used to predict outcomes in diseases like sepsis and lung injury.
Treatment of Skin disorders: Topical application of some interleukins can potentially relieve symptoms and treat skin disorders like psoriasis and eczema.
In addition, interleukins are often used in research studies to better understand the functioning of the immune system and the complex interplay between different types of immune cells.
Case Study
Case 1: Chawla AS, Khalsa JK, Dhar A, et al. A role for cell-autocrine interleukin-2 in regulatory T-cell homeostasis. Immunology. 2020 Jul;160(3):295-309. doi: 10.1111/imm.13194. Epub 2020 Apr 14. PMID: 32187647; PMCID: PMC7341549.
Activated T-cells make both interleukin-2 (IL2) and its high-affinity receptor component CD25. Regulatory CD4 T-cells (Treg cells) do not make IL2, and the IL2-CD25 circuit is considered a paracrine circuit crucial in their generation and maintenance.
When the researchers re-visited experiments with mixed bone marrow chimeras using a wide range of ratios of wild-type (WT) and IL2-/- genotype progenitors, they found that, as expected, thymic Treg cells were almost equivalent between WT and IL2-/- genotypes at ratios with WT prominence. Research data indicate that cell-intrinsic autocrine IL2 plays significant roles in Treg generation and maintenance.
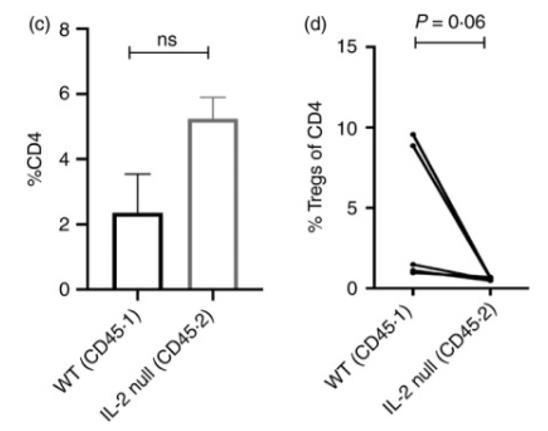
Fig1. (c,d) For in vivo Treg generation, naïve CD4 T‐cells (CD4+ CD25− CD44lo) cells from both WT and IL2−/− donor partners were isolated from mixed bone marrow chimeras and mixed in a 1:1 ratio and transferred into Rag−/− mice along with congenic WT Tregs. After 2 months, spleen cells from the Rag−/− recipients were analysed for (c) CD4 expansion and (d) Treg induction from these donor populations.
Case 2: Li E, Yang X, Du Y, et al. CXCL8 Associated Dendritic Cell Activation Marker Expression and Recruitment as Indicators of Favorable Outcomes in Colorectal Cancer. Front Immunol. 2021 May 7;12:667177. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.667177. PMID: 34025668; PMCID: PMC8138166.
CXCL8 (IL-8) may also be a potential therapeutic target in cancer. CXCL8 is a potent chemotactic factor for neutrophils, myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) and monocytes, which are considered immunosuppressive components in cancer-bearing hosts. In this article, researchers identified the TME-related gene CXCL8 in a high-ImmuneScore population that contributed to better survival in colorectal cancer (CRC) patients from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database.
Their data suggested that targeting the CXCL8-CXCR2 axis might impede DC activation or recruitment, and this axis could be considered a favorable factor rather than a target for critical antitumor effects on CRC.
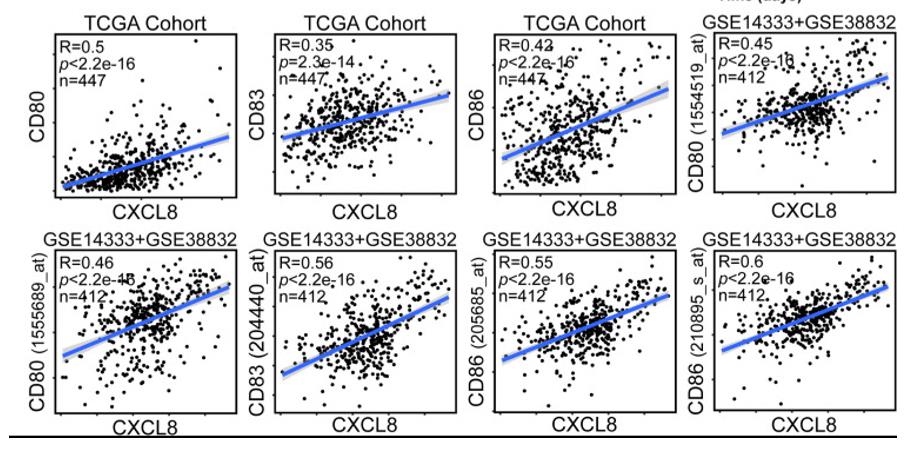
Fig1. CXCL8 expression correlates with activated dendritic cells and their gene expression. Scatterplots representing the relationships between the expression of the dendritic cell activation genes CD80, CD83, and CD86 compared with CXCL8 expression in the TCGA cohort and GSE14333 and GSE38832 cohorts.
Case 3: Nakamizo S, Dutertre CA, Khalilnezhad A, et al. Single-cell analysis of human skin identifies CD14+ type 3 dendritic cells co-producing IL1B and IL23A in psoriasis. J Exp Med. 2021 Sep 6;218(9):e20202345. doi: 10.1084/jem.20202345. Epub 2021 Jul 19. PMID: 34279540; PMCID: PMC8292131.
Inflammatory skin diseases including atopic dermatitis (AD) and psoriasis (PSO) are underpinned by dendritic cell (DC)-mediated T cell responses. Currently, the heterogeneous human cutaneous DC population is incompletely characterized, and its contribution to these diseases remains unclear. In this article, researchers performed index-sorted single-cell flow cytometry and RNA sequencing of lesional and nonlesional AD and PSO skin to identify macrophages and all DC subsets, including the newly described mature LAMP3+BIRC3+ DCs enriched in immunoregulatory molecules (mregDC) and CD14+ DC3. They found that CD14+ DC3s increased in PSO lesional skin and co-produced IL1B and IL23A, which are pathological in PSO.
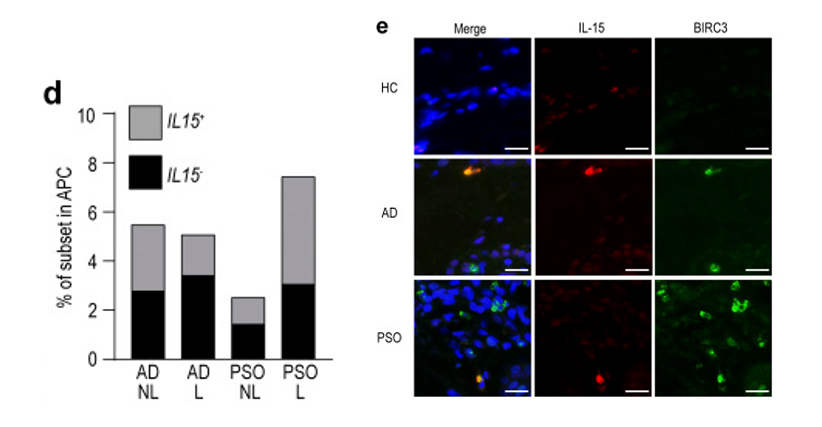
Fig1. mregDCs produce IL-15 and are more abundant in AD skin. (d) Proportion of IL15-producing cells in AD and PSO skin. (e) Immunolabeling for IL-15 and BIRC3 in normal (n = 8), AD (n = 9), and PSO (n = 9) skin. Blue: DAPI, red: IL-15, green: BIRC3. Scale bar = 20 µm.



