Common gamma Chain Family Receptors
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
Available Resources for Common gamma Chain Family Receptors Research
At Creative BioMart, we take pride in offering a diverse range of products associated with the common gamma chain family receptors. Our product selection includes recombinant proteins, protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, and cell and tissue lysates, ensuring that researchers have access to the necessary tools for their studies. Additionally, our services can be tailored to your specific requirements, ensuring that you receive a product that perfectly suits your needs.
In addition to our comprehensive product line, we provide a wealth of information on the common gamma chain family receptors. Our resources cover a wide range of topics, including pathways, protein function, interacting proteins, related articles, research areas, and more. These resources serve as valuable references, empowering researchers to deepen their understanding of the common gamma chain family receptors and their significance in physiological processes. We are dedicated to supporting researchers by not only offering products but also providing knowledge, contributing to advancements in this field of study.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL15RA-14151H | Recombinant Human IL15RA protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| IL21R-3905H | Recombinant Human IL21R, His tagged | Human | Human Cell | His |
| IL2RA-637H | Active Recombinant Human IL2RA, His tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| IL2RB-783H | Active Recombinant Human IL2RB protein(Met1-Asp239) | Human | HEK293 | N/A |
| IL2RG-14197H | Recombinant Human IL2RG Protein, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| IL4R-586H | Recombinant Human Interleukin 4 Receptor | Human | HEK293 | N/A |
| IL7R-788H | Recombinant Human IL7R, Fc-His tagged | Human | Human Cell | Fc/His |
About Common gamma Chain Family Receptors
The common gamma chain (γc) family of cytokines comprises a group of cytokines that share the common gamma chain (γc) receptor subunit. These cytokines include interleukin-2 (IL-2), interleukin-4 (IL-4), interleukin-7 (IL-7), interleukin-9 (IL-9), interleukin-15 (IL-15), and interleukin-21 (IL-21). The common gamma chain subunit allows for functional overlap and crosstalk between these cytokines, leading to shared signaling pathways and biological effects.
Structural Features
- Common Gamma Chain (γc) Subunit: The common γc subunit is a transmembrane protein encoded by the IL2RG gene. It contains a conserved cytokine receptor homology (CRH) domain and a WSXWS motif important for receptor assembly and stability. The γc subunit is shared among the receptors for the common γc family of cytokines.
- Specific Receptor Subunits: Each cytokine in the common γc family has its own specific receptor subunits in addition to the common gamma chain. These additional subunits confer ligand specificity and determine the binding affinity for their respective cytokines. For example, IL-2R consists of IL-2Rα (CD25), IL-2Rβ, and the common gamma chain.
Biological Functions
- Immune Cell Development and Function: The common γc family of cytokines plays critical roles in the development and function of immune cells. They regulate the proliferation, survival, and differentiation of various immune cell types, including T cells, B cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and lymphoid progenitor cells. For example, IL-7 is essential for T cell development, while IL-15 is important for the development and maintenance of NK cells and memory CD8+ T cells.
- Immune Response Modulation: These cytokines regulate immune responses by modulating the differentiation and function of immune cell subsets. They influence the balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory responses and impact the production of cytokines, chemokines, and antibodies. For instance, IL-4 promotes Th2 cell differentiation and antibody production, while IL-21 is involved in B cell activation and differentiation.
- Homeostasis Maintenance: The common γc family of cytokines contributes to the maintenance of immune cell homeostasis. They support the survival, proliferation, and maintenance of memory T cells and regulate the balance between effector and regulatory T cells. Additionally, these cytokines play roles in tissue homeostasis and repair processes.
- Implications in Diseases: Dysregulation of the common γc family of cytokines and their receptors can contribute to the pathogenesis of various diseases. Defects in the common gamma chain itself lead to X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency (X-SCID), a severe immune deficiency disorder. Dysregulated signaling of these cytokines has also been implicated in autoimmune diseases, allergic conditions, and certain types of cancer.
Understanding the concept, structural features, and biological functions of the common γc family of cytokines provides insights into their crucial roles in immune regulation, development, and disease pathogenesis. Targeting these cytokines and their receptors presents therapeutic opportunities for modulating immune responses and treating immune-related disorders.
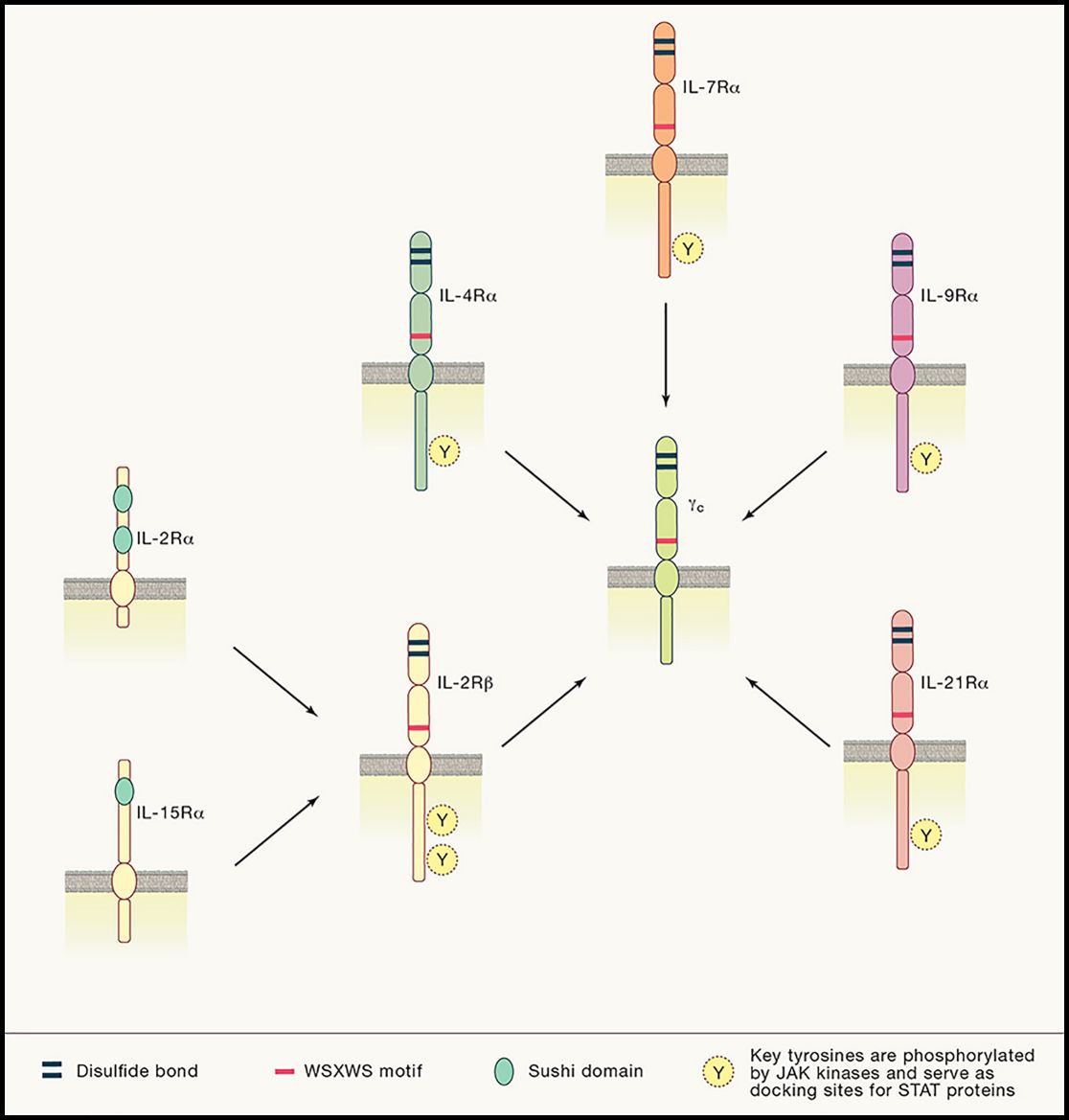 Fig.1 Schematic of γc family cytokine receptor chains. (Leonard W J, et al., 2019)
Fig.1 Schematic of γc family cytokine receptor chains. (Leonard W J, et al., 2019)
Shown are the unique receptors IL-2Rα for IL-2 and IL-15Rα for IL-15; unique receptors IL-4Rα, IL-7Rα, IL-9Rα, and IL-21Rα for their cognate cytokines; shared receptor IL-2Rβ by IL-2 and IL-15; and shared receptor γc by IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, IL-15, and IL-21. Disulfide bonds are shown in the thick dark blue bar, WSXWS motif in the thick red bar, sushi domain in the green oval, and key tyrosine residues in cytoplasmic domain are indicated as Y with the yellow circle.
Expression and Biological Functions of Common gamma Chain Family Receptors
The common γc family receptors are a group of receptors that play diverse roles in cell signaling and immune function. They share a common γ chain subunit and mediate signaling upon binding to specific ligands. Here, I will provide an overview of different types of γc receptors, their expression patterns, and biological functions in various cell types.
Interleukin-2 Receptor (IL-2R)
Expression: The IL-2R consists of three subunits: IL-2Rα (CD25), IL-2Rβ (CD122), and γc (CD132). While IL-2Rα is expressed on activated T cells, IL-2Rβ and γc are constitutively expressed on many lymphocyte subsets, including NK cells and memory CD8+ T cells.
Biological Functions: IL-2R signaling is vital for T cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation. It plays a crucial role in immune response regulation and is implicated in autoimmune diseases and cancer.
Interleukin-4 Receptor (IL-4R)
Expression: The IL-4R consists of two subunits: IL-4Rα and γc. IL-4Rα is expressed on various cell types, including T cells, B cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells. γc is shared with other receptors and is constitutively expressed on lymphocytes.
Biological Functions: IL-4R signaling is involved in regulating adaptive immunity and allergic responses. It promotes Th2 cell differentiation, B cell activation, and immunoglobulin class switching.
Interleukin-7 Receptor (IL-7R)
Expression: The IL-7R consists of two subunits: IL-7Rα and γc. IL-7Rα is expressed on various lymphoid cells, including T and B cells, while γc is shared with other receptors and is constitutively expressed on lymphocytes.
Biological Functions: IL-7R plays a vital role in lymphocyte development, survival, and homeostasis. It is critical for T cell and B cell receptor rearrangement and maturation. IL-7 signaling also influences memory T cell formation and maintenance.
Interleukin-9 Receptor (IL-9R)
Expression: The IL-9R consists of two subunits: IL-9Rα and γc. IL-9R expression varies depending on the cell type. It is typically found on T cells, mast cells, and eosinophils. γc is also shared with other receptors and is constitutively expressed on lymphocytes.
Biological Functions: IL-9R signaling contributes to allergic inflammation and the regulation of immune responses. It is involved in mast cell and eosinophil activation, as well as the maintenance and function of T helper cell subsets.
These common gamma chain family receptors play crucial roles in immune regulation, cell growth, and differentiation in various cell types. Their expression patterns and biological functions highlight their significance in shaping immune responses and maintaining immune homeostasis. Further research continues to uncover the complexities of γc receptor signaling and their potential as therapeutic targets in immunological disorders and cancer.
Common gamma Chain Family Receptors in Disease
- A significant body of research has elucidated the critical role of γc receptors in immune system development. γc receptors, such as IL-2R, IL-4R, IL-7R, and IL-9R, play indispensable roles in lymphocyte differentiation, survival, and function. Deficiencies or abnormalities in these receptors have been associated with severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) and other immunological disorders.
- Numerous studies have discovered the involvement of γc receptors in autoimmune diseases. Dysregulation of IL-2R signaling, for instance, has been linked to the development of autoimmune disorders like type 1 diabetes and multiple sclerosis. IL-4R signaling abnormalities have been associated with allergic diseases and asthma.
- Research has demonstrated the relevance of γc receptors in cancer progression. Dysregulated IL-2R and IL-4R signaling have been implicated in promoting tumor growth and immune evasion mechanisms within the tumor microenvironment. Targeting γc receptors and their downstream signaling pathways has emerged as a potential therapeutic strategy in certain cancers.
- The functional significance of γc receptors has led to their identification as potential therapeutic targets. In-depth studies on these receptors and their signaling pathways have opened avenues for developing novel strategies to modulate immune responses, improve immune-related diseases, and augment anti-cancer therapies.
Relevant in Stem Cell Research: γc receptors play a crucial role in hematopoietic stem cell development and differentiation. Understanding the signaling mechanisms mediated by γc receptors is essential for stem cell-based therapies and regenerative medicine.
These research findings underscore the relevance of γc receptors in various physiological processes, immunological disorders, cancer progression, and therapeutic interventions. Further investigation in this field continues to expand our understanding of the complex roles played by γc receptors, guiding the development of innovative strategies for disease treatment and immune modulation.
At Creative BioMart, we are committed to serving as a trusted partner for researchers, fostering their progress and success in investigating the common gamma chain family receptors. If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
Related References:
- Lin JX, Leonard WJ. The Common Cytokine Receptor γ Chain Family of Cytokines. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018;10(9):a028449.
- Leonard W J, Lin J X, O'Shea J J. The γc family of cytokines: basic biology to therapeutic ramifications[J]. Immunity, 2019, 50(4): 832-850.
- McGuire H M. The role of interleukin-21 in type-1 diabetes[D]. UNSW Sydney, 2010.

