Uncategorized Tuesday, 2025/12/23
Keywords: Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), F protein, G protein, RSV vaccine
The Critical Threat of RSV
Overall, the F and G proteins are suitable targets for neutralizing antibodies in RSV vaccine design due to their important functions and genetic conservation.
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) ranks among the three major respiratory viruses, circulating annually during winter and early spring. As an RNA virus transmitted through airborne routes, RSV poses significant health threats to children, older adults, and immunocompromised individuals. According to National Institutes of Health (NIH) data, nearly all children in the United States have been infected with RSV by age two, resulting in 58,000 hospitalizations of children under five each year. Globally, RSV affects 64 million people annually and causes 160,000 deaths.
Based on data from the Chinese CDC's "National Sentinel Surveillance of Acute Respiratory Infectious Diseases" (Week 49, 2025), from December 1-7, 2025, the top three pathogens detected in respiratory samples from influenza-like illness (ILI) cases were influenza virus (54.2%), rhinovirus (5.2%), and RSV (4.0%). Among hospitalized severe acute respiratory infection cases, the top three pathogens were influenza virus (22.1%), RSV (7.5%), and rhinovirus (7.1%). In summary, China has entered the high season for respiratory infectious diseases, with an overall upward trend. While influenza remains at high epidemic levels, RSV and rhinovirus also maintain considerable infection rates.
Our Related Proteins
| Cat.No. # | Product Name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSV-054R-MAB | Mouse Anti RSV Monoclonal Antibody, clone 3D9 (IVD grade) | Mouse | RSV | |||
| RSV-055R-MAB | Mouse Anti RSV Monoclonal Antibody, clone 7F5 (IVD grade) | Mouse | RSV | |||
| F-702V | Recombinant RSV-F F, His tagged | Insect Cells | RSV-F | His | ||
| Src-546R |
Active Recombinant RSV Src, GST-tagged
|
Sf9 Cells | RSV | GST |
|
|
| NP-424V |
Recombinant RSV NP protein(Met1-Leu391), His-tagged

|
E.coli | RSV | His | Met1-Leu391 |
|
| RSV-8660H | Recombinant Human RSV RSV, His tagged | Insect Cells | Human | His | 1-529 a.a. |
|
| G-475V | Recombinant RSV G Protein, His-tagged | HEK293 | RSV | His | 67-299 a.a. |
|
| G-98V | Recombinant RSV-G G, His tagged | Human Cells | RSV-G | His |
|
|
| G-292V | Recombinant RSV (A, rsb1734) G Protein, His-tagged | HEK293 | RSV | His | 66-297 a.a. |
|
| G-291V | Recombinant RSV (A, rsb1734) G Protein, His-tagged | Insect Cells | RSV | His | 66-297 a.a. |
|
What Is Respiratory Syncytial Virus?
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) belongs to the Pneumoviridae family as a single-stranded negative-sense RNA virus. Its genome contains 10 genes encoding 11 proteins, which can be divided into two major categories based on function: target proteins and non-target proteins.
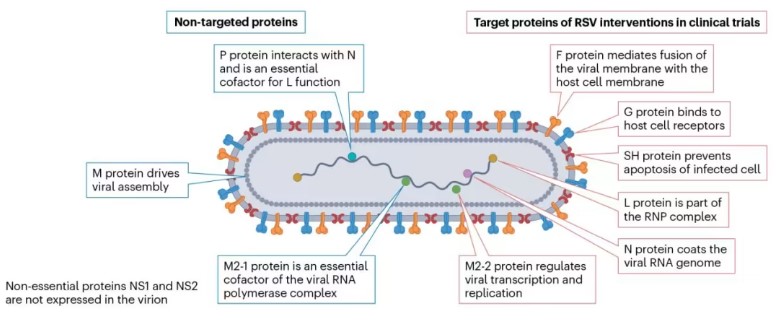
Fig1. RSV Viral Protein Composition and Functions
Among target proteins: the F protein mediates fusion between viral and host cell membranes; the G protein binds to host cell receptors; the SH protein prevents apoptosis of infected cells; the L protein is a component of the ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex; the N protein encapsulates the viral genome; and the M2-2 protein regulates viral transcription and replication.
Among non-target proteins: the P protein interacts with the N protein and serves as an essential functional cofactor for the L protein; the M protein drives viral assembly; and the M2-1 protein is a critical cofactor required for the viral RNA polymerase complex.
The F Protein: A Primary Vaccine Target
Research shows that RSV invasion requires host cell binding to both the F and G proteins. Both proteins are highly glycosylated transmembrane proteins. The F protein regulates the virus-cell fusion process, exhibits strong genetic and antigenic conservation, carries multiple neutralizing epitopes, and induces potent neutralizing antibody responses, making it the primary vaccine target.
The F protein undergoes conformational changes between a prefusion (pre-F) and postfusion (post-F) state. The pre-F protein demonstrates significantly higher neutralizing activity than post-F and shows high conservation across RSV A and B subtypes. Consequently, over 90% of vaccine and monoclonal antibody projects target the pre-F protein, particularly the Ø site.
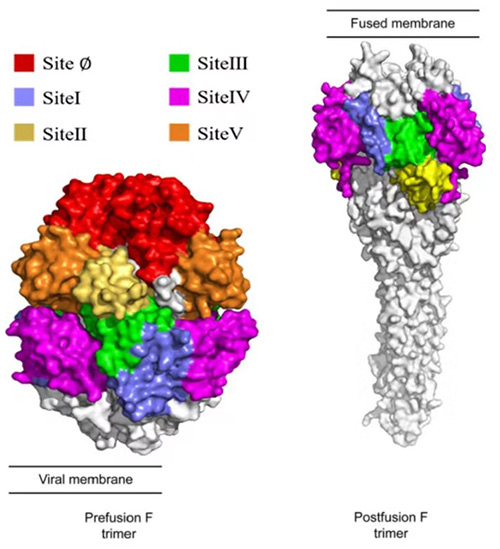
Fig2. Conformational changes of F protein before and after fusion
The G Protein: A Secondary but Important Target
The G protein is one of the most variable RSV proteins, with its sequence variation determining RSV subtypes and concentrating in the mucin-like domains at its amino and carboxyl termini. The G protein features a central conserved domain (CCD) that promotes viral attachment through interaction with cell-surface heparan sulfate receptors and carries a neutralization-sensitive epitope. Therefore, the G protein also represents a potential target for vaccine and antibody development.
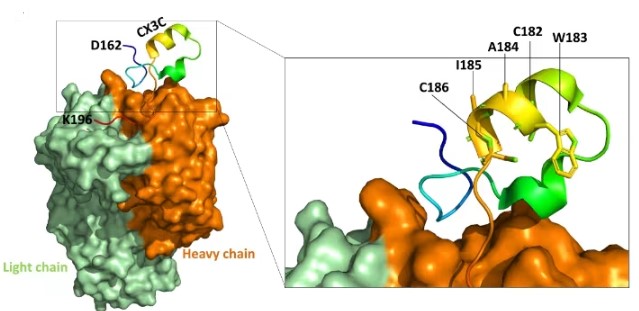
Fig3. Schematic of CCD Domain Binding with Neutralizing Antibody Fragment Fab CB017.5
The RSV Vaccine Landscape: From Research to Reality
After six decades of arduous development, RSV vaccines finally came to fruition in 2023 with GSK's Arexvy and Pfizer's Abrysvo, followed by Moderna's mRESVIA in 2024. To date, three novel RSV vaccines have been approved globally, all targeting the pre-F glycoprotein.
The RSV vaccine market is substantial, with numerous domestic Chinese companies actively developing candidates, including Adimmune and Clover Biopharmaceuticals. Clover's self-developed SCB-1019 is an adjuvant-free bivalent recombinant pre-F vaccine candidate. Phase I results showed it induced comparable neutralizing antibody levels to Arexvy in elderly subjects while demonstrating better tolerability.
Current RSV pipeline projects focus primarily on vaccines, including SP0125 (nasal spray live-attenuated vaccine), MKK900, ADV110, and SCB-1019 (recombinant protein vaccines), and IN006, STR-VO03 (mRNA vaccines).
RSV Vaccine Candidates in Clinical Development
| Vaccine Candidate | Developer | Clinical Phase | Target Population | Technology Platform | Key Features / Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
APPROVED VACCINES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Arexvy (RSVPreF3) |
GSK |
FDA Approved (2023) |
Adults ≥60 yrs (also pregnant women) |
Recombinant pre-F protein + AS01E adjuvant |
First approved RSV vaccine; showed >82% efficacy |
|
Abrysvo (RSVpreF) |
Pfizer |
FDA Approved (2023) |
Adults ≥60 yrs, pregnant women |
Bivalent recombinant pre-F protein |
Maternal immunization approved; 81% efficacy in elderly |
|
mRESVIA (mRNA-1345) |
Moderna |
FDA Approved (2024) |
Adults ≥60 yrs |
mRNA encoding pre-F protein |
First mRNA RSV vaccine; 83.7% efficacy |
|
PHASE 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SP0125 |
Sanofi |
Phase 3 |
Infants & young children |
Live-attenuated nasal spray vaccine |
Intranasal administration; seeks to induce mucosal immunity |
|
IVX-A12 (VLP) |
Icosavax (AstraZeneca) |
Phase 3 |
Adults ≥60 yrs |
Virus-like particle (VLP) with pre-F + hMPV |
Combination RSV/hMPV vaccine; acquired by AstraZeneca in 2024 |
|
PHASE 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
ADV110 |
Adivaccine (Adimmune) |
Phase 2 |
Adults 60-80 yrs |
Recombinant pre-F protein with adjuvant |
Chinese company; focuses on elderly population |
|
MKK900 |
Meikang Biotech |
Phase 2 |
Adults ≥60 yrs |
Recombinant pre-F with novel adjuvant |
Adjuvanted subunit vaccine |
|
IN006 |
Senxen Biotech |
Phase 2 |
Adults ≥60 yrs |
mRNA encoding pre-F |
mRNA platform; potentially multivalent |
|
PHASE 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SCB-1019 |
Clover Biopharmaceuticals |
Phase 1 |
Adults ≥60 yrs |
Recombinant pre-F trimer (adjuvant-free) |
No adjuvant; Phase I showed comparable antibodies to Arexvy with better tolerability |
|
SCB-1022 |
Clover Biopharmaceuticals |
Phase 1 |
Adults ≥60 yrs |
Recombinant pre-F + hMPV |
Combination RSV/hMPV vaccine using Trimer-Tag platform |
|
SCB-1033 |
Clover Biopharmaceuticals |
Phase 1 |
Adults ≥60 yrs |
Recombinant pre-F + hMPV + PIV3 |
Triple combination vaccine (RSV/hMPV/PIV3) |
|
STR-V003 |
Starray Pharma |
Phase 1 |
Adults ≥60 yrs |
Self-amplifying mRNA (saRNA) |
Next-generation mRNA technology |
Key Insights from the Development Landscape
Market Dynamics:
- The global RSV vaccine market is projected to exceed $10 billion by 2030
- All approved vaccines target the pre-fusion (pre-F) protein conformation
- Combination vaccines (RSV + hMPV + PIV3) represent the next frontier
Technology Trends:
- mRNA platforms (Moderna, Senxen) offer rapid development and potential multivalency
- Adjuvant-free subunit vaccines (Clover's SCB-1019) may provide better tolerability profiles
- Live-attenuated vaccines (Sanofi's SP0125) aim to induce mucosal immunity for pediatric use
Related Products & Services
- Viral Infections Targets
- S protein
- N protein
- G protein
- F protein
- Protein Engineering Services
- Protein Interaction Service
- Protein Expression and Purification Services
- Drug Discovery Screening
- Protein Pathway Profiling
Reference
- Annefleur C. Langedijk and Louis J. Bont. Respiratory syncytial virus infection and novel interventions. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-023-00919-w
- Xirui Qiu, et al. Development of mRNA vaccines against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Cytokine and Growth Factor Reviews, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2022.10.001
- David A Foley and Linny K Phuong, RSV: an update on prevention and management. Aust Prescr. 2025. doi: 10.18773/austprescr.2025.018
- Yu, et al. RSV Vaccines: Targeting Prefusion F and G Proteins from Structural Design to Clinical Application. Vaccines 2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13111133
