Uncategorized Thursday, 2026/01/22
This study identifies CDK10 as a cancer cell-intrinsic driver of immune evasion that inhibits antitumor immunity by limiting the production of immunostimulatory nucleic acids, thereby providing a potential new target for cancer immunotherapy.
Cancer immunotherapy has revolutionized cancer treatment, but many patients do not respond. Activating innate immunity offers a promising approach to enhance therapeutic efficacy, yet the signaling kinases that directly modulate this process to augment antitumor responses remain elusive.
Zhang Jinfang from Wuhan University and Lei Xiaoguang from Peking University, as co-corresponding authors, published online in Nature Cancer a research paper titled "CDK10 suppresses nucleic acid sensors-mediated antitumor immunity." The study identifies CDK10 as a cancer cell-intrinsic driver of immune evasion that inhibits antitumor immunity by limiting the production of immunostimulatory nucleic acids, thereby providing a potential new target for cancer immunotherapy.
Immunotherapies, including PD-1 / PD-L1 and CTLA-4 immune checkpoint inhibitors, have transformed cancer treatment by enabling the immune system, particularly T cells, to recognize and eliminate tumor cells. While these therapies primarily target adaptive immunity, their success often depends on robust innate immune responses. Emerging evidence underscores the critical role of the innate immune system in enhancing these antitumor effects.
Our Related Proteins
To optimize cancer immunotherapy, conventional strategies such as radiotherapy and chemotherapy can be employed to activate innate immunity. Furthermore, targeted therapies that inhibit epigenetic and chromatin factors can drive intracellular accumulation of endogenous "viral mimicry" nucleic acids, such as double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), and R-loops. These nucleic acids activate innate immune sensors, triggering potent interferon (IFN)-driven antiviral and antitumor responses.
The TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) – IFN regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) signaling axis is a central mediator of the nucleic acid sensing pathway. Detection of cytosolic nucleic acids triggers TBK1 autophosphorylation at S172, which in turn phosphorylates IRF3 at S396. This modification induces IRF3 dimerization, nuclear translocation, and subsequent transcription of IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs), thereby orchestrating effective antiviral and antitumor immune responses. This pathway represents a critical bridge between innate nucleic acid sensing and adaptive immunity, highlighting its importance in cancer immunotherapy.
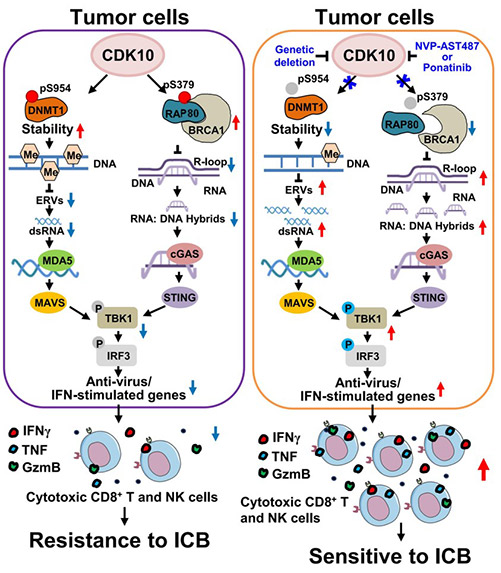
Fig1. Model of CDK10-mediated tumor immune regulation (Xu, G., et al. Nature Cancer)
Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 / 6 (CDK4/6) inhibitors also trigger innate immune responses to enhance cancer immunotherapy. CDK4/6 inhibitors, including palbociclib, ribociclib, and abemaciclib, have demonstrated clinical efficacy in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer, improving progression-free and overall survival rates.
This success has rekindled interest in targeting other members of the CDK family. CDK10 remains an enigma despite being discovered over 30 years ago. A pivotal study revealed cyclin M as an activating partner of CDK10, enabling CDK10 to phosphorylate the ETS2 oncoprotein and regulate its stability. Notably, CDK10 acts as both a tumor suppressor and oncogene, depending on cancer type.
Our Related Proteins
| Cat.No. # | Product Name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TBK1-443H |
Active Recombinant Full Length Human TBK1 Proein, GST-tagged

|
Sf9 Cells | Human | GST | Full L. 1-729 a.a. | |
| TBK1-336H | Recombinant Human TBK1 protein, GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | 590-729 a.a. | |
| TBK1-337H | Recombinant Human TBK1 protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 1-729 a.a. | |
| TBK1-732H | Recombinant Human TANK-binding Kinase 1 | Sf9 Cells | Human | Non | Full L. 1-729 a.a. | |
| TBK1-657H | Recombinant Human TBK1 Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Trp9~Val310 | |
| IRF3-61H | Recombinant Human IRF3 protein, His/T7-tagged | E.coli | Human | His&T7 | Met1~Lys360 | |
| IRF3-2297R | Recombinant Rhesus monkey IRF3 Protein, His-tagged | Mammalian Cells | Rhesus macaque | His |
|
|
| IRF3-27H | Recombinant Human Interferon Regulatory Factor 3 | E.coli | Human | Non | 1-112 a.a. |
|
| CDK4-11049H | Recombinant Human CDK4, GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | 1-303a.a. | |
| CDK4-758HF | Recombinant Human CDK4 Protein, GST-tagged, FITC conjugated | Insect Cells | Human | GST | 528 |
Beyond its role in cancer, CDK10 is also linked to severe developmental disorders. However, previous studies investigating CDK10's role in tumorigenesis have primarily relied on in vitro systems or immunodeficient models, and its function in tumor immunity and immunotherapy has not been explored.
Here, the researchers performed an in vivo kinome CRISPR screen and identified CDK10 as a key suppressor of tumor immune surveillance. Mechanistically, CDK10 phosphorylates DNMT1 and RAP80 to reduce the accumulation of double-stranded RNA and R-loops, which alleviates activation of the innate immune pathways mediated by MDA5 and cGAS.
A kinase inhibitor screen identified NVP-AST487 and ponatinib as selective CDK10 inhibitors. Genetic and pharmacological inhibition of CDK10 activates the MDA5 and cGAS pathways, cultivates an immunocompetent tumor microenvironment, and enhances cancer immunotherapy in multiple mouse tumor models. Clinically, low CDK10 expression in tumors correlates with better immunotherapy responses. These findings establish CDK10 as a key regulator of tumor immunity and a potential therapeutic target.
Related Products & Services
- Cell and Gene Therapy
- Immune Checkpoint Proteins
- ADC Target Protein
- PROTAC Targets
- Targets of CAR-T Cell Therapy
- Cancer Drug Targets
- Protein Engineering Services
- Protein Interaction Service
- Protein Expression and Purification Services
- Drug Discovery Screening
- Protein Pathway Profiling
Reference
- Xu, G., Guo, F., He, C., Wang, X., Xiang, B., Fan, L., Chen, B., Peng, J., Sun, Y., Shi, J., Xing, X., Yao, Y., Dai, P., Li, H., Xiong, W., Liu, H., Xiao, R., Qing, G., Jiang, C., . . . Zhang, J. (2026). CDK10 suppresses nucleic acid sensors-mediated antitumor immunity. Nature Cancer, 1-21. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43018-025-01100-3
