Common gamma Chain Family Ligands
Available Resources for Common Gamma Chain Family Ligands Research
Creative BioMart proudly offers a wide range of products associated with the common gamma chain family ligands. Our extensive selection includes recombinant proteins, protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, and cell and tissue lysates, providing researchers with access to the necessary tools for their studies. Moreover, our customizable services are designed to address your specific requirements, ensuring that you receive the most suitable product tailored to your needs.
In addition to our comprehensive product line, we provide a wealth of information on the common gamma chain family ligands. Our resources cover various aspects, including involved pathways, protein function, interacting proteins, related articles, research areas, and other pertinent topics. These resources serve as invaluable references, empowering researchers to deepen their understanding of the common gamma chain family ligands and their significance in physiological processes. We are committed to supporting researchers by offering both products and knowledge, ultimately contributing to advancements in this field of study.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL15-24H | Recombinant Human IL15 protein | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| IL2-341H | Active Recombinant Human IL2 | Human | Human | N/A |
| Il21-001H | Active Recombinant Human Il21, HIgG1 Fc-tagged, mutant | Human | CHO | Fc |
| il21-4335S | Recombinant Salmon il21 Protein | Salmon | Yeast | N/A |
| IL7-507H | Active Recombinant Human IL7, His tagged | Human | Human Cell | His |
| IL9-14214H | Recombinant Human IL9, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
About Common Gamma Chain Family Ligands
The Common gamma Chain (γc) Family of cytokines comprises several ligands that share the common gamma chain receptor subunit. The common gamma chain (γc) cytokine family comprises interleukin-2 (IL-2), IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, IL-15 and IL-21, named after the γc subunit (CD132) shared by receptor complexes for these cytokines. These ligands play important roles in immune regulation, hematopoiesis, and the development and function of various immune cells.
Structural Features
- Pleiotropy: Common gamma chain family ligands exhibit pleiotropic effects, meaning they can exert diverse biological activities on different cell types. They can regulate cell proliferation, differentiation, survival, and immune responses.
- Homology: Common gamma chain family ligands share structural homology in their protein sequences, particularly in their cytokine core regions. This homology contributes to their ability to interact with the common gamma chain receptor subunit.
- Shared Receptor Subunit: All common gamma chain family ligands signal through a receptor complex that includes the common gamma chain (γc), also known as the interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain (IL-2Rγ) or CD132. This shared subunit allows for crosstalk and functional overlap among the ligands.
- Disulfide Bonds: These ligands typically contain disulfide bonds that stabilize their three-dimensional structure. These bonds are crucial for proper folding and functional activity.
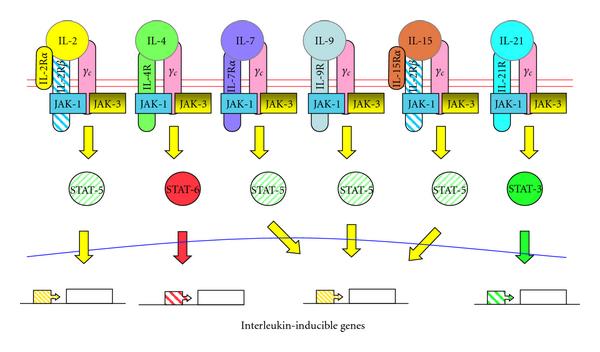 Fig.1 The family of cytokines sharing the common cytokine-receptor γc in their receptor complexes. (Meazza R, et al., 2011)
Fig.1 The family of cytokines sharing the common cytokine-receptor γc in their receptor complexes. (Meazza R, et al., 2011)
Biological Functions
- Immune Cell Development and Survival: Common gamma chain family ligands play vital roles in the development, survival, and homeostasis of immune cells. They promote the growth and differentiation of lymphocytes, including T cells, B cells, and NK cells.
- Immune Responses: These ligands regulate immune responses by modulating the balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory pathways. They can influence the differentiation of T helper cell subsets, such as Th1, Th2, Th9, and regulatory T cells, and impact antibody production and allergic responses.
- Hematopoiesis: Common gamma chain family ligands contribute to hematopoiesis, the process of blood cell formation. They are involved in the proliferation and differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells and progenitor cells, leading to the generation of various blood cell lineages.
- Tissue Homeostasis: Some common gamma chain family ligands are involved in maintaining tissue homeostasis. For example, IL-7 supports the survival and maintenance of memory T cells, while IL-9 contributes to tissue repair and remodeling.
- Autoimmune and Allergic Diseases: Dysregulation of common gamma chain family ligands and their receptors is associated with autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis, as well as allergic conditions, including asthma and atopic dermatitis.
Understanding the structural features and biological functions of common gamma chain family ligands provides insights into their roles in immune regulation and disease pathogenesis. Targeting these ligands and their receptors is a promising therapeutic approach for various immune-related disorders.
Mechanisms of Common Gamma Chain Family Ligands in Signaling and Immune Regulation
The γc family of cytokines utilizes specific signaling mechanisms to regulate immune responses. These ligands, such as IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, and IL-9, interact with their respective receptors and activate signaling pathways that contribute to immune regulation. Here are some key mechanisms of common gamma chain family ligands in signaling and immune regulation:
- Receptor Complex Formation: Common gamma chain family ligands bind to specific receptors, which typically consist of multiple subunits. The common gamma chain (γc) functions as a shared subunit for these ligands. Ligand binding induces the assembly of receptor complexes, which are essential for downstream signaling events.
- JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway: Upon ligand binding, the associated receptor subunits, including the common gamma chain, recruit and activate Janus kinases (JAKs). JAKs phosphorylate the receptor subunits, creating docking sites for signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) proteins. Phosphorylated STATs dimerize and translocate to the nucleus, where they regulate gene expression, leading to immune cell activation, proliferation, and differentiation.
- PI3K-Akt-mTOR Pathway: Common gamma chain family ligands can also activate the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)-Akt-mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway. Activation of this pathway promotes cell survival, growth, and metabolism. It plays a critical role in regulating the proliferation and survival of immune cells, including T cells and B cells.
- MAPK Signaling Pathway: Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways, including the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and p38 MAPK pathways, are activated by common gamma chain family ligands. MAPK pathways regulate various cellular processes, such as cell proliferation, differentiation, and cytokine production, contributing to immune cell activation and function.
- STAT-Independent Signaling: In addition to the classical JAK-STAT pathway, common gamma chain family ligands can activate alternative signaling pathways that are independent of STAT proteins. These pathways involve other signaling molecules, such as phospholipase C gamma (PLCγ), nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK), leading to diverse cellular responses and immune regulation.
- Cross-Talk and Synergy: The common gamma chain family ligands and their receptors can exhibit cross-talk and synergy with other cytokine signaling pathways. For example, IL-7 and IL-15 share the common gamma chain and can synergistically enhance immune cell survival and proliferation. This cross-talk and synergy contribute to the complexity and fine-tuning of immune responses.
- Negative Regulation: To maintain immune homeostasis, common gamma chain family ligands are subject to negative regulation by various mechanisms. This includes the action of suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins, which inhibit JAK-STAT signaling, and other negative regulators that modulate the intensity and duration of cytokine signaling to prevent excessive immune activation.
Understanding the mechanisms of common gamma chain family ligands in signaling and immune regulation provides insights into the complex processes involved in immune cell activation, proliferation, and differentiation. Dysregulation of these pathways can contribute to immune-related disorders, and targeting these mechanisms holds therapeutic potential for modulating immune responses in various diseases.
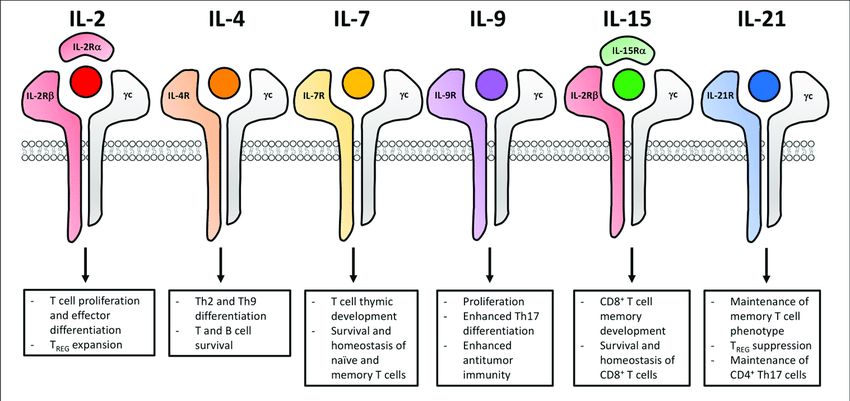 Fig.2 Common γ chain cytokine signaling impacts the functional fate of T cells for adoptive cell transfer. (Dwyer C J, et al., 2019)
Fig.2 Common γ chain cytokine signaling impacts the functional fate of T cells for adoptive cell transfer. (Dwyer C J, et al., 2019)
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
Related References
- Kinter AL, Godbout EJ, McNally JP, et al. The common gamma-chain cytokines IL-2, IL-7, IL-15, and IL-21 induce the expression of programmed death-1 and its ligands. J Immunol. 2008;181(10):6738-6746.
- Meazza R, Azzarone B, Orengo AM, Ferrini S. Role of common-gamma chain cytokines in NK cell development and function: perspectives for immunotherapy. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011;2011:861920.
- Dwyer C J, Knochelmann H M, Smith A S, et al. Fueling cancer immunotherapy with common gamma chain cytokines[J]. Frontiers in immunology, 2019, 10: 263.


