Signal Pathway
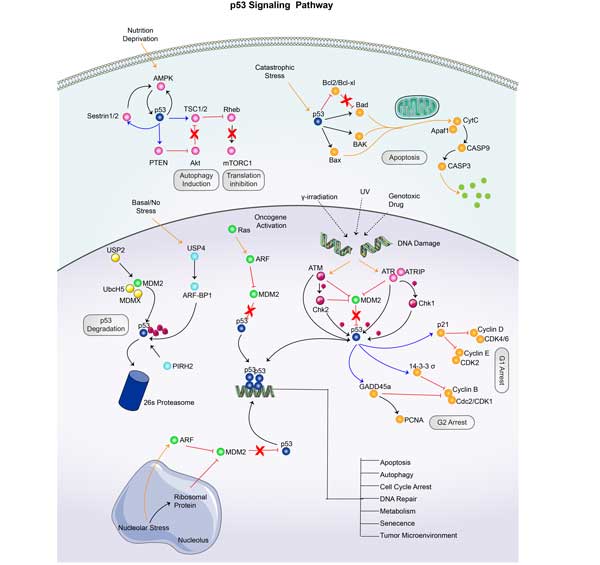
The p53 Pathway
The p53 pathway is composed of a network of genes and their products that are targeted to respond to a variety of intrinsic and extrinsic stress signals, which impact cellular homeostatic mechanisms that monitor DNA replication, chromosome segregation, and cell division (Vogelstein et al., 2000).
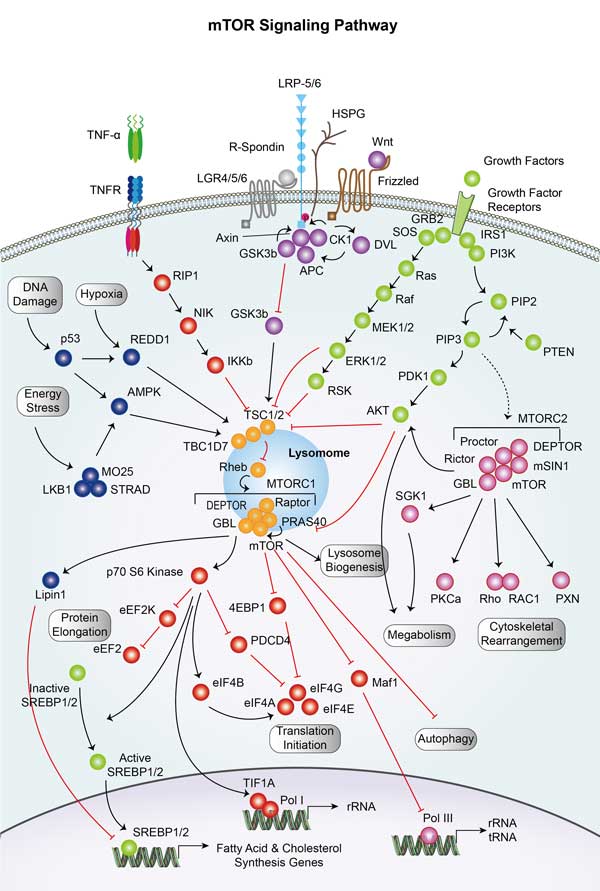
mTOR Signaling Pathway
The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway integrates both intracellular and extracellular signals and serves as a central regulator for cell metabolism, growth, proliferation, and survival.
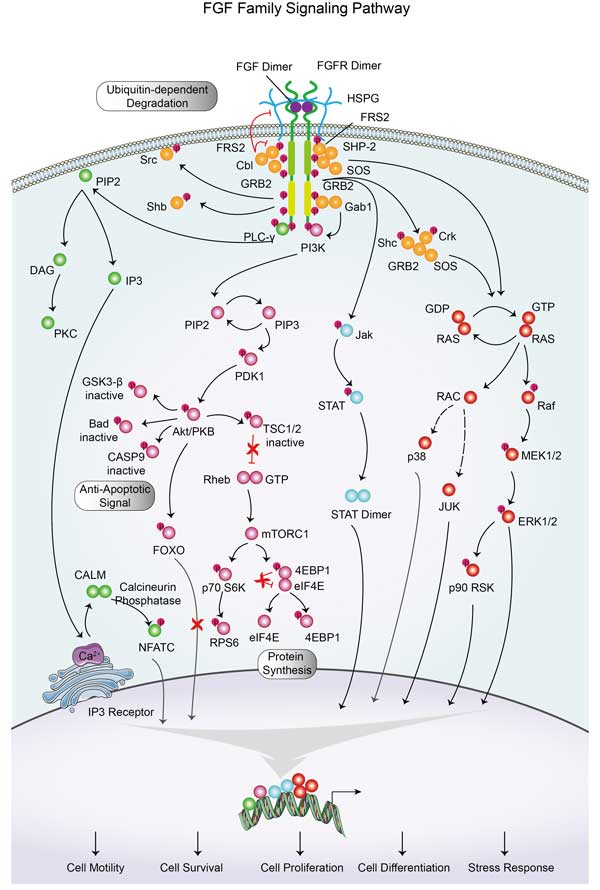
FGF Family Signaling Pathway
The signaling component of the mammalian Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) family is comprised of eighteen secreted proteins that interact with four signaling tyrosine kinase FGF receptors (FGFRs). FGF signaling generally follows one of three transduction pathways: Ras/MAP kinase, PI3/AKT, or PLCγ. Each pathway likely regulates specific cellular behaviors.
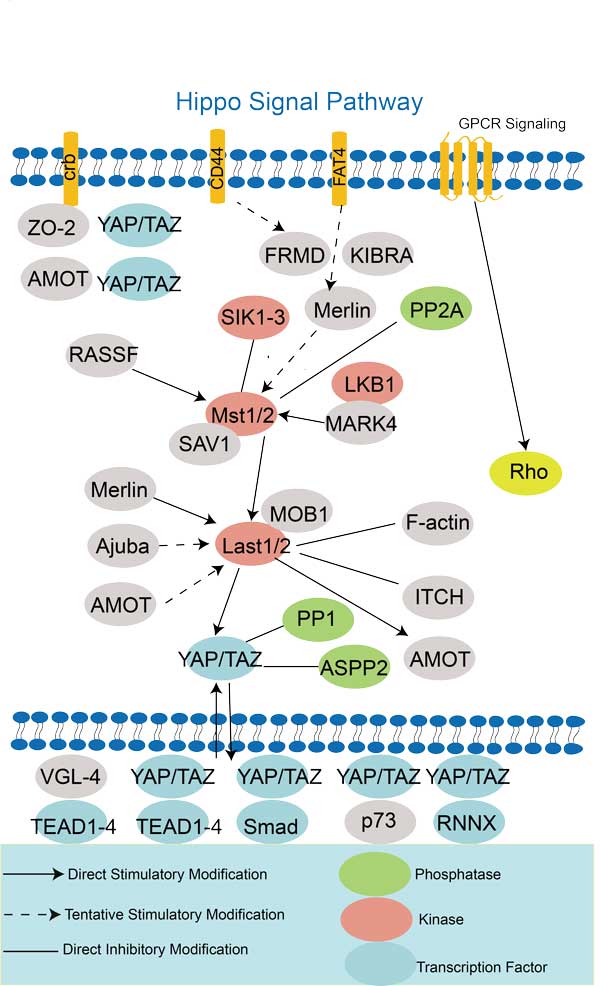
Hippo Signal Pathway
The Hippo signaling pathway is a conserved regulator of proliferation and cell survival in metazoans.
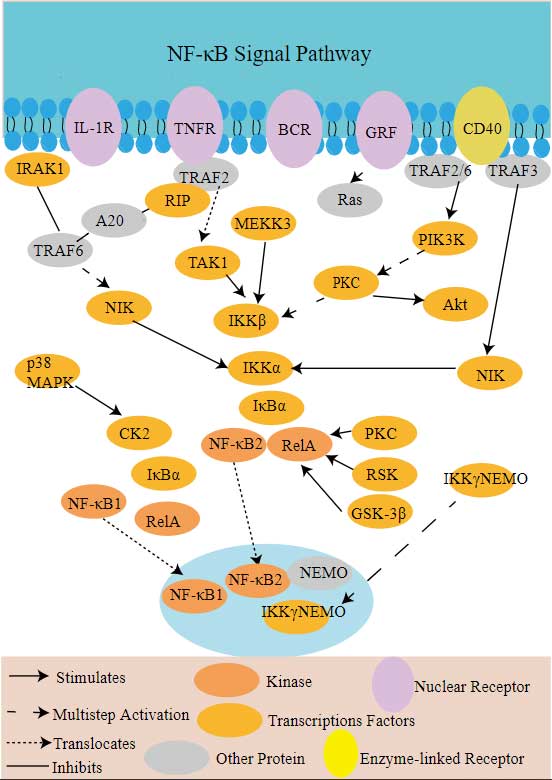
NF-κB Signal Pathway
The most basic components of NF-κB signaling pathways include receptors, signal adapter proteins, IκB kinase (IKK) complex, IκB protein and NF-κB dimer.
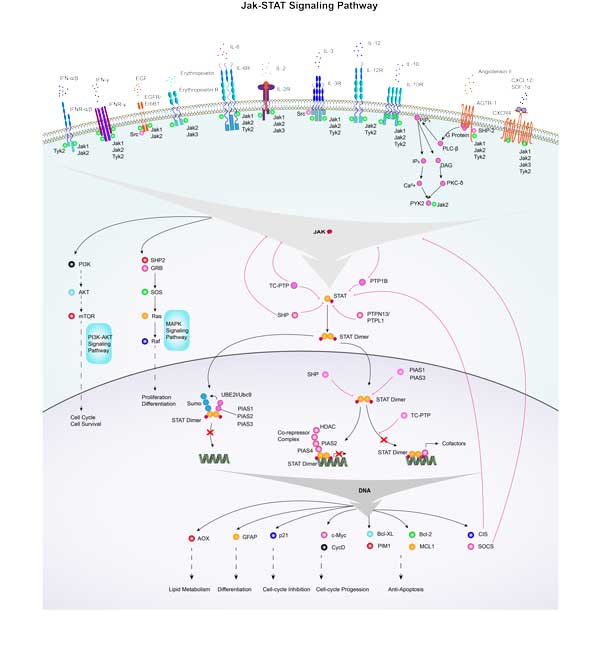
JAK-STAT Signal Pathway
JAK-STAT signal pathway is a cytokine-stimulated signal transduction pathway which consists of three major components: RTK, JAK, and STAT.
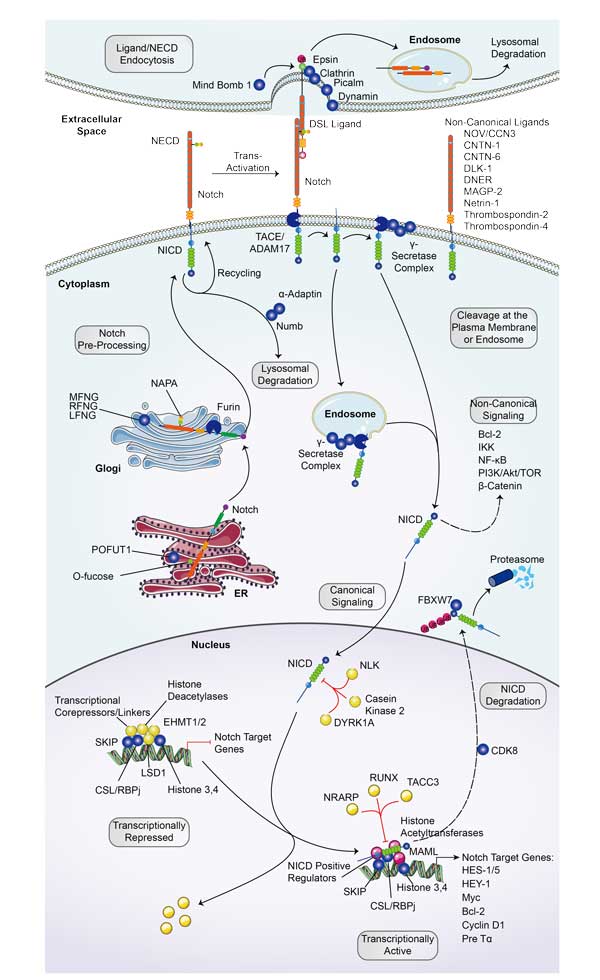
Notch Signal Pathway
In 1917, Morgan and colleagues found a gene in Drosophila, which is named Notch because of a loss of function that leads to a gap in the edge of wings. Subsequent studies found that Notch is expressed in many species from invertebrates to vertebrates.
Wnt Signal Pathway
The Wnt signal pathway is an evolutionarily conserved signal pathway that regulates cell migration, cell polarity, and neural and organ formation during embryonic development. The major signaling downstream of the Frizzled (Fz) receptor have been identified, including the canonical Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway and the non-canonical β-catenin-independent signal pathway.
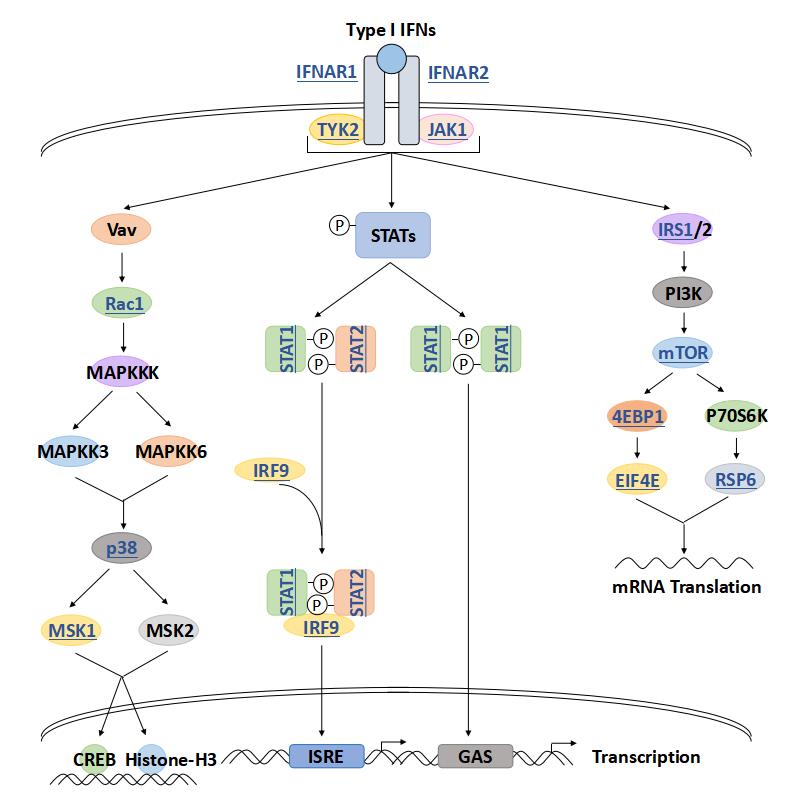
Type I Interferon Signal Pathway
Following viral infection, the human body triggers a complex regulatory system of innate and adaptive immune responses designed to defend against the virus. One of the many responses to the viral invasion is the induction of the pleiotropic cytokines, interferon (IFN)...
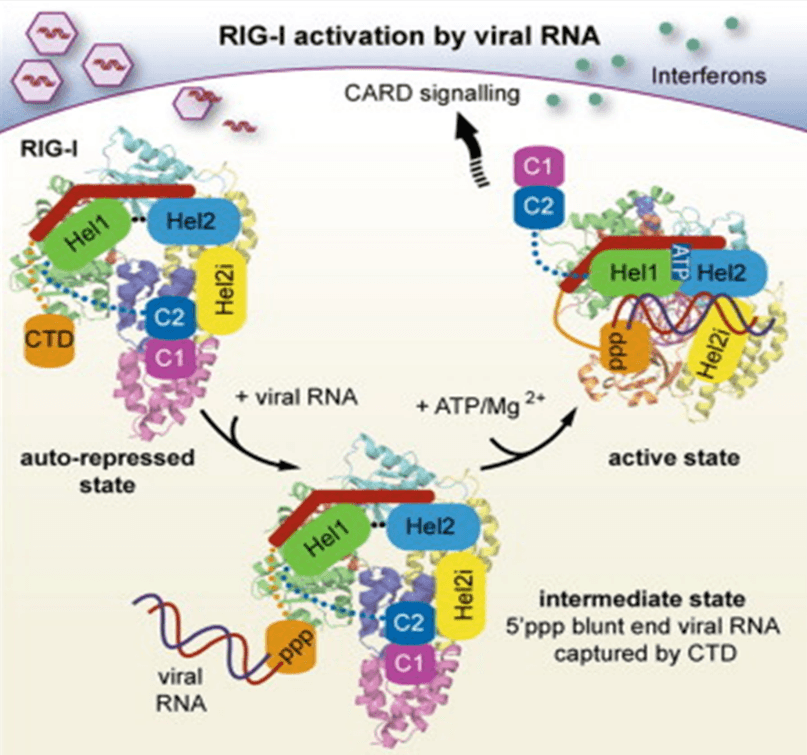
RNA Viruses Triggered Signal Pathway
IPS-1 TRAF3 IKKi TBK1 IRF3 IRF7 IRF3 IRF7 FADD TRADD Caspase-8/-10 NF-κB NF-κB Figure: RIG-I recognize RNA viruses by detecting short dsRNAs with 5’triphosphate ends. MDA5 recognize RNA viruses by detecting long dsRNAs. LGP2 positively regulates RIG-I and MDA5 mediated
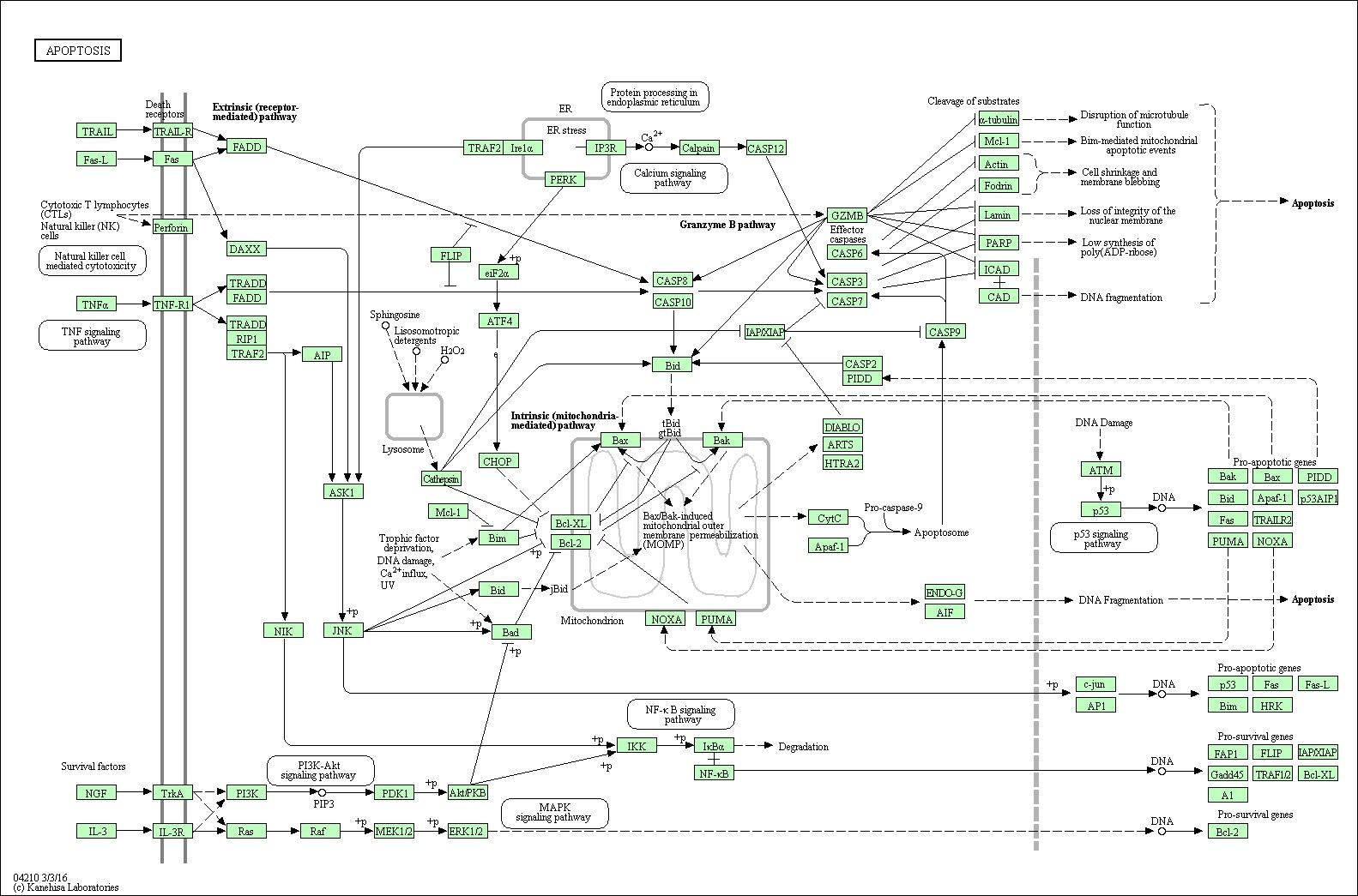
Apoptosis Signal Pathway Overview
Fig1. Apoptosis Signal Pathway Overview Apoptosis is a kind of programmed cell death (PCD) plays a fundamental role in multicellular organism development and tissue homeostasis. We might take it as a regulated cellular suicide mechanism. Abnormal regulation of this process is associated with a
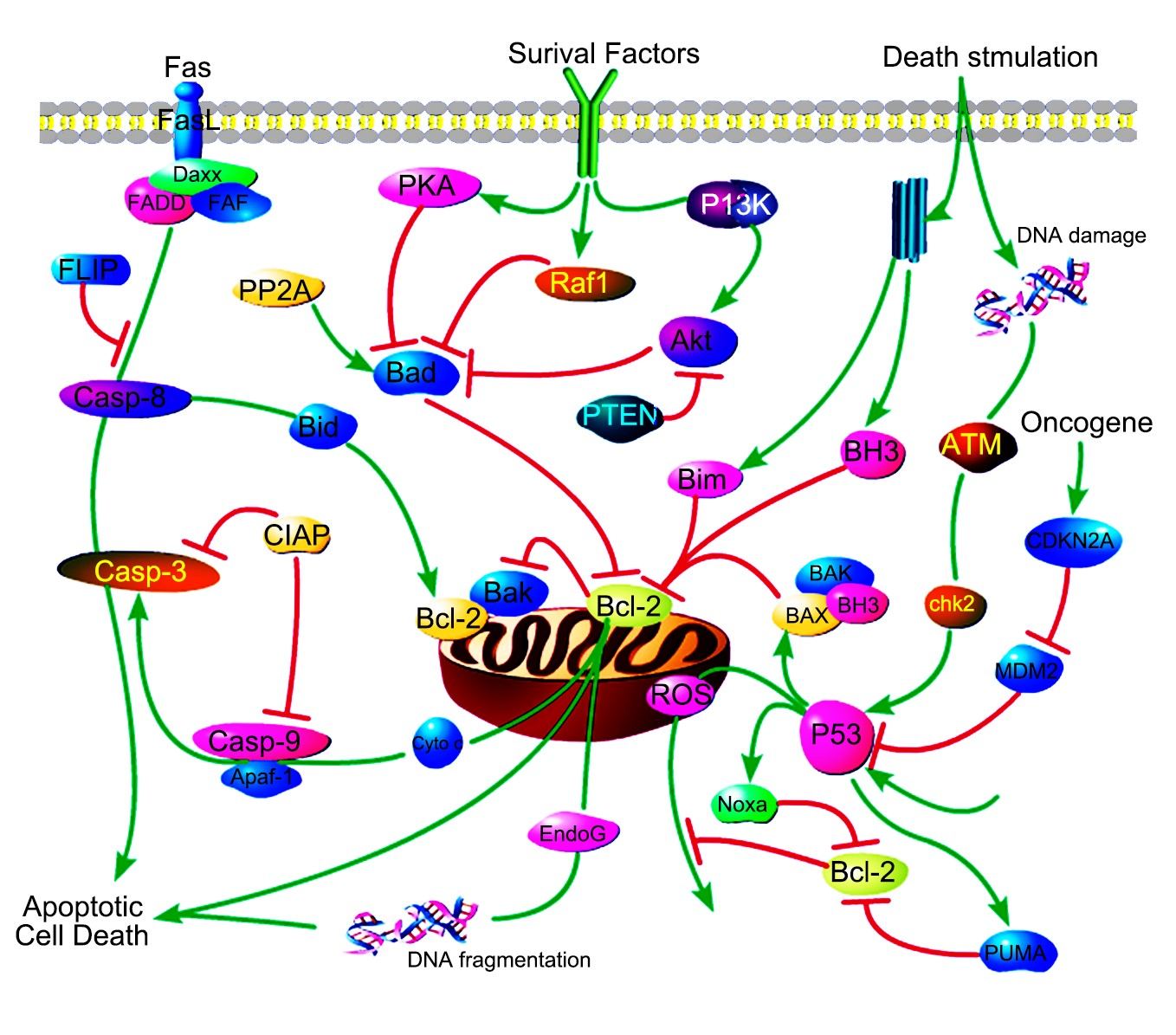
Mitochondrial Control of Apoptosis
Apoptosis is a highly regulated programmed cell death (PCD), it is vital to the development and homeostasis of multicellular organisms. Among various organelles, mitochondria play a central role in the regulation of apoptotic cell death. Under a certain death stimuli, different apoptogenic


