DYRKs (Dual-specificity Tyrosine-[Y]-phosphorylation Regulated Kinases)
About DYRKs (Dual-specificity Tyrosine-[Y]-phosphorylation Regulated Kinases)
DYRKs are a class of protein kinases with dual-specific tyrosine-[Y]-phosphorylation-regulated kinase activity, belonging to the tyrosine/serine/threonine CMGC family of protein kinases, which is characterized by kinase activity on its tyrosine residues and on serine/threonine sites of other proteins, with five members (DYRK1A , DYRK1B, DYRK2, DYRK3, and DYRK4). DYRKs are widely expressed in a variety of cell types, and their activities are usually regulated by phosphorylating substrates and are involved in the regulation of biological processes such as cell proliferation, cell differentiation, cell cycle control, and neural development.
These protein kinases are involved in multiple cellular functions, including intracellular signaling, mRNA splicing, chromatin transcription, DNA damage repair, cell survival, cell cycle control, differentiation, homocysteine/methionine/folate regulation, body temperature regulation, endocytosis, neuronal development, synaptic plasticity, etc. Abnormal expression and/or activity of some of these kinases, DYRK1A in particular, is seen in many human nervous system diseases, such as cognitive deficits associated with Down syndrome, Alzheimer's disease and related diseases, tauopathies, dementia, Pick's disease, Parkinson's disease and other neurodegenerative diseases, Phelan-McDermid syndrome, autism, and CDKL5 deficiency disorder. DYRKs and CLKs are also involved in diabetes, abnormal folate/methionine metabolism, osteoarthritis, several solid cancers (glioblastoma, breast, and pancreatic cancers) and leukemias (acute lymphoblastic leukemia, acute megakaryoblastic leukemia), viral infections (influenza, HIV-1, HCMV, HCV, CMV, HPV), as well as infections caused by unicellular parasites (Leishmania, Trypanosoma, Plasmodium).
Mechanism of Action of DYRKs
The mechanism of action of DYRKs is mainly through the phosphorylation of a variety of substrate proteins within the cell. They can phosphorylate cytokines, transcription factors, and other kinase and receptor proteins, thereby affecting intracellular signaling pathways. DYRKs have a dual specificity for the phosphorylation of regulatory proteins, which means that they are capable of phosphorylating both tyrosine (Y) residues, as well as threonine (T) or threonine (S) residues, which regulate cellular signaling pathways and influence cellular function and fate.
![DYRKs (Dual-specificity Tyrosine-[Y]-phosphorylation Regulated Kinases) - Creative BioMart](/incl/images/2-8-9 dyrks-dual-specificity tyrosine-y-phosphorylation-regulated-kinases-1.jpg)
Functions of DYRKs
- Regulation of Cell Proliferation and Differentiation
DYRKs play an important role in cell proliferation and differentiation, and they are involved in the regulation of different phases of the cell cycle, including cell division and cell proliferation. DYRKs can phosphorylate and regulate several cell cycle proteins, such as cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) and cyclins, to ensure that cells divide and proliferate in the correct order. DYRKs also regulate the process of cellular differentiation, facilitating the transition of undifferentiated cells to specific cell types. This is essential for the normal development and function of tissues and organs.
- Neurodevelopmental Regulation
DYRKs are involved in the regulation of neuronal growth, branching, and connectivity, dynamic remodeling of the cytoskeleton, formation, and stabilization of synapses, and migration and localization of neurons. DYRKs are essential for the normal development of the brain and the maturation of the nervous system.
- Metabolic Regulation
DYRKs are involved in the regulation of energy metabolism, glucose metabolism, lipid metabolism, etc. DYRKs regulate the activities of several metabolic pathways and key metabolic enzymes, which have an important impact on the maintenance of overall metabolic homeostasis and energy utilization.
- Disease Control
DYRKs play a key role in the development and progression of many diseases. For example, DYRKs are associated with the development and metastasis of cancer, and their aberrant activity may lead to uncontrolled cell proliferation. DYRKs have also been implicated in the pathogenesis of neurological disorders (e.g., Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease) and congenital mental retardation, and other diseases. Therefore, DYRKs are considered as potential therapeutic targets, providing new directions for the treatment of related diseases.
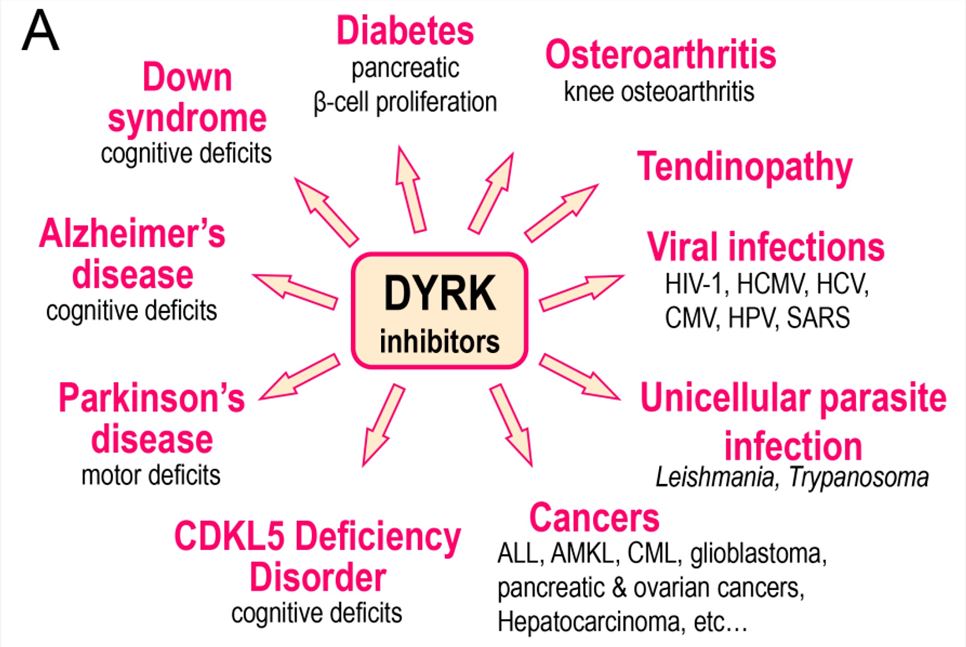 Fig.2 DYRK inhibitors (in particular inhibitors of DYRK1A) have been investigated in the indicated diseases. (Lindberg MF, et al., 2021)
Fig.2 DYRK inhibitors (in particular inhibitors of DYRK1A) have been investigated in the indicated diseases. (Lindberg MF, et al., 2021)
Available Resources for DYRKs
DYRKs are involved in a variety of biological processes including cell proliferation, cell differentiation, cell cycle regulation, and neurodevelopment, etc. Creative BioMart offers a wide range of products such as recombinant proteins, cell & tissue lysates, protein pre-coupled magnetic magnetic beads, as well as customizable services and other resources to support your research in the field of DYRKs. The following DYRKs are displayed, click to view all related molecules/targets and research reagents. For further information or to purchase products, please contact our customer service team. Thank you for your interest in Creative BioMart and we look forward to providing you with excellent research support!
References:
- Lindberg MF, Meijer L. Dual-Specificity, Tyrosine Phosphorylation-Regulated Kinases (DYRKs) and cdc2-Like Kinases (CLKs) in Human Disease, an Overview. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(11):6047.
- Correa-Sáez, A., Jiménez-Izquierdo, R., Garrido-Rodríguez, M. et al. Updating dual-specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation-regulated kinase 2 (DYRK2): molecular basis, functions, and role in diseases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 77, 4747–4763 (2020).
- Santos-Durán, Gabriel Nicolás, and Antón Barreiro-Iglesias. "Roles of dual specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation-regulated kinase 2 in nervous system development and disease." Frontiers in Neuroscience 16 (2022): 994256.


