Hedgehogs
About Hedgehogs
The Hedgehog gene was initially identified in Drosophila as a morphogen involved in segment polarity. In vertebrates, the Hedgehog family is represented by at least three members: Desert hedgehog (Dhh), Indian hedgehog (Ihh), and Sonic hedgehog (Shh). Hedgehog signaling occurs through two proteins, Patched (Ptc), a twelve-pass transmembrane protein that binds to the Hedgehog ligand, and Smoothened (Smo), a seven-pass transmembrane protein that transmits a downstream signal. In the absence of the Hedgehog ligand, Ptc inhibits Smo activity, and downstream target genes are inactivated by a processed form of the transcriptional repressor, Cubitus interruptus (Ci) in Drosophila, or Gli-1, -2, or -3 in vertebrates. Upon ligand binding to Ptc, Smo is activated, phosphorylation and cleavage of Ci/Gli is inhibited, and full-length 000000000000000000000000Ci/Gli translocates to the nucleus to activate the transcription of its target genes. Shh signaling in vertebrates is involved in diverse areas of development, including neurogenesis, hematopoiesis, bone formation, and gonad development.
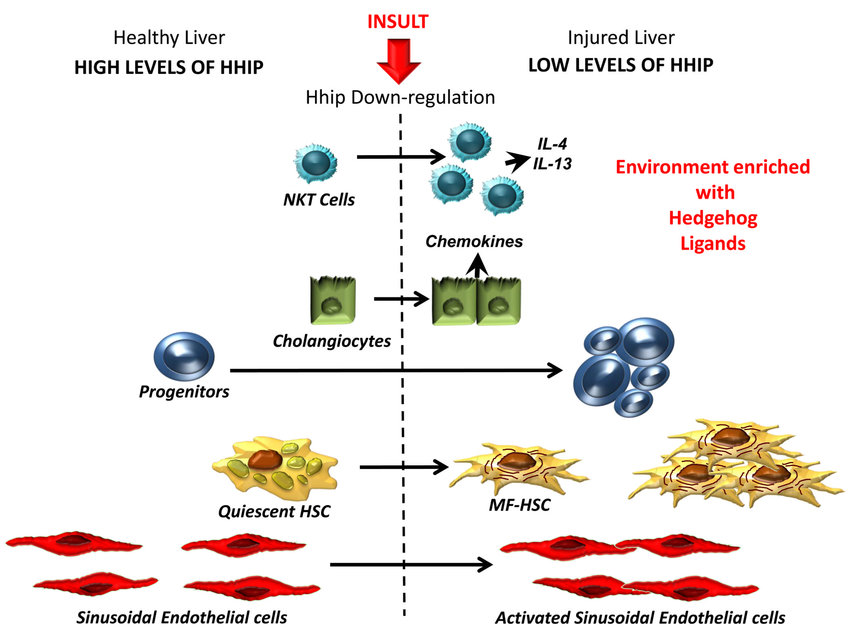 Fig.1 Differential Activity of Hedgehog Pathway in Healthy and Injured Livers. (Omenetti A, et al., 2011)
Fig.1 Differential Activity of Hedgehog Pathway in Healthy and Injured Livers. (Omenetti A, et al., 2011)
Functions of Hedgehogs
Embryonic Development
Hedgehog proteins coordinate various developmental processes, including pattern formation, cell fate determination, tissue polarity, and organogenesis. They act as morphogens, forming concentration gradients that provide positional information to developing tissues and guide the formation of complex structures during embryogenesis. Understanding the mechanisms underlying Hedgehog signaling is essential for elucidating developmental processes and addressing developmental disorders.
- Stem Cell Maintenance and Differentiation
Hedgehogs are critical regulators of stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. They play key roles in the maintenance and expansion of various stem cell populations, such as neural stem cells, hematopoietic stem cells, and intestinal stem cells. Manipulating Hedgehog signaling can direct stem cell differentiation towards specific lineages, facilitating tissue regeneration and cell replacement therapy.
- Cancer Research
Dysregulation of Hedgehog signaling is implicated in various types of cancer. Aberrant activation of the Hedgehog pathway can lead to uncontrolled cell growth, tumor progression, and metastasis. Targeting Hedgehog signaling components has emerged as a potential therapeutic strategy in cancer treatment.
Available Resources of Hedgehogs
Creative BioMart offers a wide range of resources and services to support research involving Hedgehog and its signaling pathways. These include recombinant Hedgehog proteins, antibodies, cell-based assays and gene expression analysis tools. We also provide researchers with a range of resources on each Hedgehog-related molecules/targets and research reagents, such as involved pathways, protein functions, interacting proteins, articles, and related research areas. These resources enable scientists to study Hedgehog signaling in different biological contexts and gain insight into its functional impact in development, stem cell biology and disease.
If you are interested in Hedgehogs or need related products and services, you can make price inquiries and purchases through our online ordering system. Meanwhile, you can also directly contact our professional team for consultation and cooperation
Reference:
- Omenetti A, Choi S, Michelotti G, Diehl AM. Hedgehog signaling in the liver.[J] Hepatol. 2011 Feb;54(2):366-73.


