IL-17 Signaling Related Molecules
Available Resources for IL-17 Signaling Related Molecules Research
At Creative BioMart, we are thrilled to present our diverse collection of products associated with IL-17 signaling-related molecules. Our extensive product portfolio includes high-quality recombinant proteins, protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, cell and tissue lysates, and more. These indispensable tools cater to the diverse needs of researchers, equipping them to conduct comprehensive studies in their respective fields. With customizable services, we ensure that you find the perfect product tailored to your specific research requirements.
In addition to our comprehensive product offering, we are dedicated to providing a wealth of information on IL-17 signaling-related molecules. Our resources cover a broad spectrum of topics, including pathways, protein function, interacting proteins, related articles, and research areas. These valuable resources serve as references for researchers seeking to enhance their understanding of IL-17 signaling-related molecules and their pivotal roles in various physiological processes. By offering an integration of products and knowledge, we actively support researchers in driving advancements within this dynamic and rapidly evolving research field.
Our Featured Products
About IL-17 Signaling Related Molecules
IL-17 signaling-related molecules play vital roles in the IL-17 signaling pathway, which is involved in various physiological and pathological processes, particularly in immune responses and inflammation. These molecules function as key components in transmitting signals from the extracellular environment to the intracellular domain, leading to the activation of downstream signaling cascades.
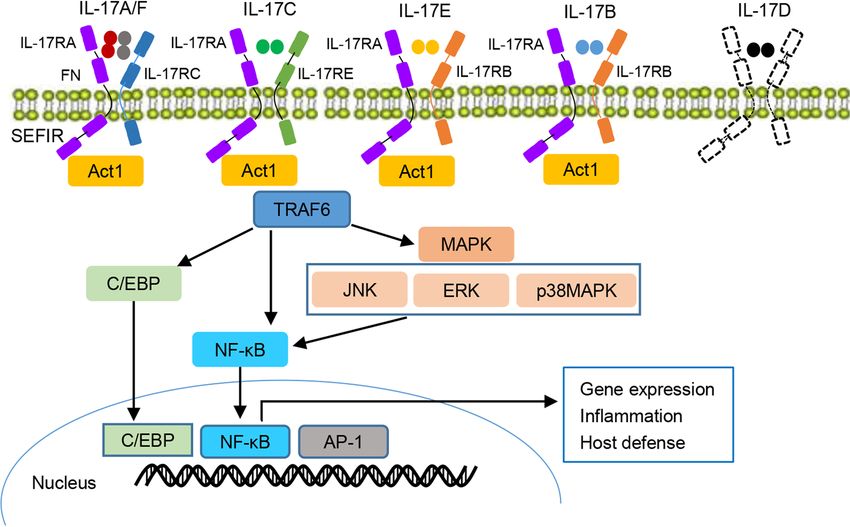 Fig.1 IL-17 cytokines, receptors, and signaling. (Nie YJ, et al., 2022)
Fig.1 IL-17 cytokines, receptors, and signaling. (Nie YJ, et al., 2022)
The IL-17 family is composed of six members, IL-17A-F, while the IL-17 receptor family is composed of five members, IL-17RA to IL-17RE (IL-17RD not shown). IL-17 signaling is activated through the binding of the IL-17 receptor complex to the adaptor protein Act1, which has been determined in IL-17C to recruit TRAF6 to drive the activation of downstream signaling pathways, MAPK, C/ EBP, and NF-κB, contributing to the target gene expression as well as mediating the host defense and inflammatory response. IL-17R interleukin 17 receptor, TRAF6 tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6, C/EBP CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein, MAPK mitogen-activated protein kinase, NF-κB nuclear factor-kappaB, Act1 NF-κB activator 1, JNK JUN N-terminal kinase. ERK extracellular signal-regulated kinase, FN fibronectin, AP1 activator protein-1
Transcription Factors
- CHUK (also known as IKKα): It is a key regulator of the NF-κB pathway and is involved in the transcription of genes related to immune responses and inflammation.
- FOS: Part of the AP-1 transcription factor complex, it regulates gene expression involved in immune cell activation and inflammatory responses.
- RELA: A component of the NF-κB family of transcription factors, it plays a crucial role in regulating immune reactions and inflammation.
- JUN: Another member of the AP-1 transcription factor complex, it cooperates with FOS to regulate the expression of genes involved in immune responses.
Inhibitors of NF-κB (IκB)
- NFKBIB (also known as IκBβ) and NFKBIA (also known as IκBα): These molecules sequester NF-κB in the cytoplasm, preventing its translocation to the nucleus and subsequent activation of immune and inflammatory target genes.
Protein Kinases
- IKBKE (also known as IKKε): It is involved in the activation of NF-κB and plays a role in immune responses and inflammation.
- MAP3K7 (also known as TAK1): Acts as a MAP kinase kinase kinase (MAP3K), initiating signaling cascades involved in immune and inflammatory responses.
- MAPK11, MAPK12, MAPK13, and MAPK14: These members of the MAP kinase family participate in various cellular processes, including immune cell activation and inflammatory signaling.
- ERK1 (also known as MAPK3) and MAPK3: These proteins are part of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) family, which regulates cell proliferation, differentiation, and immune responses.
- GSK3B: Regulates several downstream signaling pathways connected to immune responses and inflammatory processes.
Signal Transducers
- TRAF6 and TRAF3: These adapter proteins are essential for mediating signaling between IL-17 receptors and downstream pathways, leading to the activation of NF-κB and other immune-related genes.
These IL-17 signaling-related molecules work in concert to regulate gene expression and propagate signaling events, orchestrating immune responses and inflammation. Understanding their functions and interactions is critical for deciphering the complex mechanisms underlying IL-17-related biological processes.
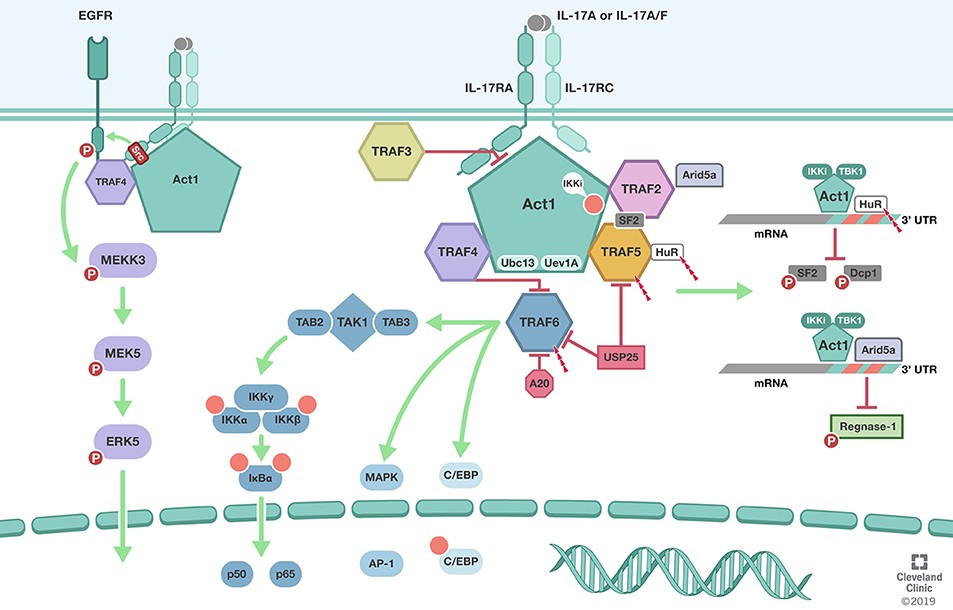 Fig.2 TRAFs in IL-17 signaling pathway. (Swaidani S, et al., 2019)
Fig.2 TRAFs in IL-17 signaling pathway. (Swaidani S, et al., 2019)
IL-17 Family Signaling Molecules and Other Signaling Pathways
The IL-17 family of cytokines and signaling molecules plays a crucial role in the regulation of immune responses and inflammation. The interactions and regulatory mechanisms between IL-17 family signaling molecules and other signaling pathways are complex and involve multiple levels of cross-talk and feedback loops. Here's an overview of some key interactions and regulatory mechanisms:
Interleukin-17 (IL-17) and NF-κB signaling pathway
- IL-17 cytokines, including IL-17A and IL-17F, activate the IL-17 receptor (IL-17R) complex, which consists of IL-17RA and IL-17RC subunits.
- IL-17 signaling leads to the recruitment of Act1 (TRAF3IP2) and the activation of downstream signaling pathways, including NF-κB.
- Act1 interacts with TRAF6, leading to the activation of the IKK complex and subsequent NF-κB activation.
- NF-κB, in turn, regulates the expression of pro-inflammatory genes, including cytokines, chemokines, and adhesion molecules, amplifying the inflammatory response initiated by IL-17.
Interleukin-17 (IL-17) and MAPK signaling pathway
- IL-17 signaling can also activate MAPK signaling pathways, including ERK1/2, JNK, and p38 MAPK.
- IL-17-induced activation of MAPKs contributes to the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and matrix metalloproteinases.
- MAPKs can also regulate the expression and activity of transcription factors, such as AP-1, which further modulate gene expression involved in inflammation and immune responses.
Interleukin-17 (IL-17) and JAK/STAT signaling pathway
- IL-17 can engage the JAK/STAT signaling pathway in certain cellular contexts.
- IL-17 stimulation leads to the activation of JAK kinases, which phosphorylate and activate STAT transcription factors.
- Phosphorylated STATs translocate to the nucleus and regulate the expression of specific target genes involved in immune responses and inflammation.
Interleukin-17 (IL-17) and IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway
- IL-17 can induce the production of IL-6, which activates the IL-6 receptor (IL-6R)/gp130 signaling complex.
- IL-6/gp130 signaling activates JAK/STAT3 signaling, leading to the nuclear translocation of phosphorylated STAT3.
- STAT3 regulates the expression of numerous genes involved in inflammation, immune responses, and cell survival, further amplifying the effects of IL-17 signaling.
Interleukin-17 (IL-17) and TGF-β signaling pathway
- IL-17 can synergize with TGF-β signaling to promote the differentiation of naïve T cells into pro-inflammatory Th17 cells.
- TGF-β signaling induces the expression of the transcription factor RORγt, which, in combination with IL-6 and IL-23 signaling, drives the differentiation and maintenance of Th17 cells.
- Th17 cells produce IL-17 cytokines, creating a positive feedback loop that sustains the pro-inflammatory response.
These are some examples of the interactions and regulatory mechanisms between IL-17 family signaling molecules and other signaling pathways. The precise nature and outcomes of these interactions can vary depending on the specific cellular context and the presence of other cytokines and signaling molecules. The complex interplay between these signaling pathways contributes to the regulation of immune responses, inflammation, and the pathogenesis of various inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.
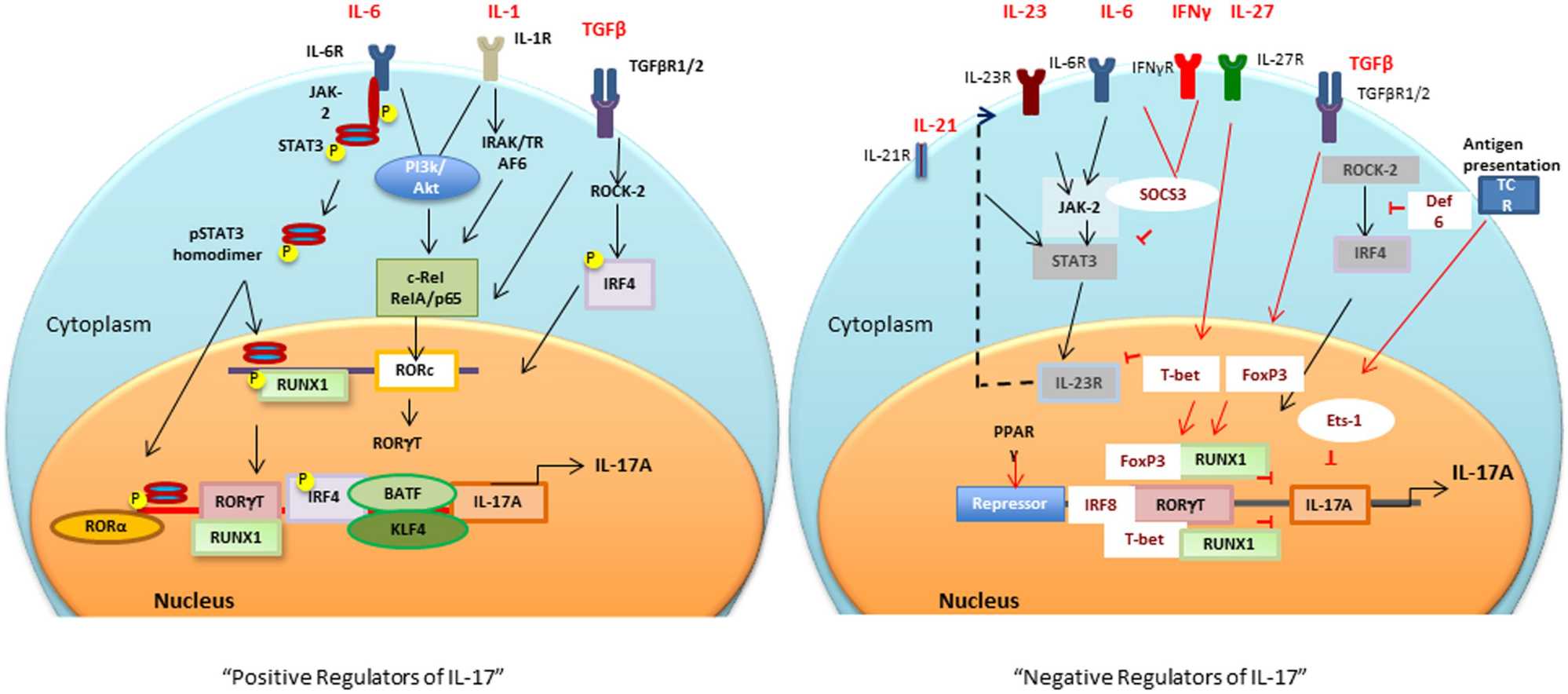 Fig.3 Positive and negative transcriptional tegulators of IL-17 induction. (Khan D, et al., 2015)
Fig.3 Positive and negative transcriptional tegulators of IL-17 induction. (Khan D, et al., 2015)
Different cytokines and antigen specific stimuli trigger (black arrows and lines) different signaling cascades for activation of RORc and consequently Il17 gene.
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
Related References:
- Nie YJ, Wu SH, Xuan YH, Yan G. Role of IL-17 family cytokines in the progression of IPF from inflammation to fibrosis. Mil Med Res. 2022;9(1):21. Published 2022 May 12. doi:10.1186/s40779-022-00382-3
- Swaidani S, Liu C, Zhao J, Bulek K, Li X. TRAF Regulation of IL-17 Cytokine Signaling. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1293. Published 2019 Jun 27. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.01293
- Khan D, Ansar Ahmed S. Regulation of IL-17 in autoimmune diseases by transcriptional factors and microRNAs. Front Genet. 2015;6:236. Published 2015 Jul 14. doi:10.3389/fgene.2015.00236


