Intermediate Filaments
About Intermediate Filaments
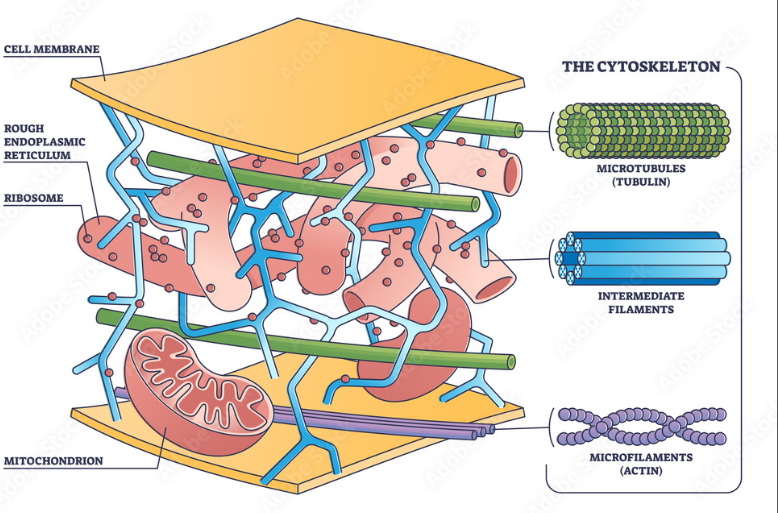
Intermediate filaments are a type of cytoskeletal filament found in the cells of all animals, including humans. They are made up of various fibrous proteins, including keratins, vimentin, desmin, and lamin. Intermediate filaments provide mechanical support and stability to cells, and they also play a role in cell adhesion, signal transduction, and maintaining cell morphology.
Unlike microtubules and actin filaments, which are dynamic and constantly undergoing polymerization and depolymerization, intermediate filaments are more stable and do not exhibit rapid turnover. This makes them well-suited for providing long-term structural support to cells. Intermediate filaments are especially prominent in cells that experience mechanical stress, such as skin cells, muscle cells, and nerve cells.
Intermediate filaments are composed of a central rod-like structure, which consists of repeating subunits called alpha-helical coiled coils. These coiled-coil subunits come together to form a dimmer, which then further associates to form protofilaments. These protofilaments bundle together to form the final intermediate filament.
There are different types of intermediate filaments found in different cell types. For example, keratins are found in epithelial cells and protect against mechanical stress and abrasion. Vimentin is found in mesenchymal cells, such as fibroblasts, and helps to maintain cell shape and resist stretching. Desmin is found in muscle cells and helps to maintain the structure and integrity of the muscle fibers. Lamins are found in the nuclear envelope of all cells and provide support and stability to the nucleus.
Mutations or abnormalities in intermediate filaments have been associated with various genetic disorders. For example, mutations in keratin genes can lead to skin disorders, such as epidermolysis bullosa, where the skin is prone to blistering and tearing. Mutations in desmin can lead to myofibrillar myopathy, a progressive muscle-wasting disease. Mutations in lamin genes can lead to a group of disorders known as laminopathies, which include diseases such as Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome, Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy, and dilated cardiomyopathy.
Biological Functions of Intermediate Filaments Proteins
- Desmin is primarily expressed in muscle cells, where it plays a crucial role in maintaining the structural integrity of muscle fibers.
- It helps to organize and stabilize the contractile apparatus within muscle cells, facilitating efficient force transmission during muscle contraction.
- Desmin mutations can lead to skeletal and cardiac muscle disorders, such as desmin-related myopathies.
GFAP (Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein):
- GFAP is predominantly found in astrocytes, a type of glial cell in the central nervous system.
- It provides structural support to astrocytes and helps maintain their shape and cytoskeletal organization.
- GFAP is involved in various functions of astrocytes, including neuronal support, regulation of blood-brain barrier integrity, and response to injury or inflammation.
- Peripherin is an intermediate filament protein mainly expressed in the peripheral nervous system, particularly in sensory and autonomic neurons.
- It contributes to the structural organization of neuronal processes, particularly in the formation and maintenance of axons.
- Peripherin is involved in neuronal development, and axon outgrowth, and may have a role in neuronal regeneration.
- Nestin is an intermediate filament protein primarily expressed in neural stem cells, progenitor cells, and certain types of cancer cells.
- It is involved in maintaining the structural integrity of these cells and plays a role in their proliferation, migration, and differentiation.
- Nestin has been used as a marker for identifying and characterizing neural stem cells and is associated with neurogenesis and tissue repair processes.
- Vimentin is a widely expressed intermediate filament protein found in various cell types, including mesenchymal cells, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and immune cells.
- It provides structural support to cells and is involved in maintaining cell shape, integrity, and resistance to mechanical stress.
- Vimentin is also associated with cellular processes such as cell migration, cell signaling, and tissue remodeling, and it has implications for cancer metastasis and inflammation.
These intermediate filament proteins play important roles in maintaining cellular structure, providing mechanical support, and contributing to the proper functioning of various cell types and tissues.
The Application Areas of Intermediate Filaments Proteins
Cell Culture and Tissue Engineering: Intermediate filament proteins, such as vimentin and desmin, are used as markers to assess the differentiation and maturation of cells in cell culture and tissue engineering studies. They provide valuable insights into the development and functionality of various cell types, helping researchers monitor and optimize cell culture conditions.
Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers: Intermediate filament proteins can serve as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in various diseases and conditions. For example, the detection of specific intermediate filament proteins, such as GFAP in brain tissue, can aid in the diagnosis and monitoring of brain injury, neurodegenerative diseases, and brain tumors.
Cancer Research and Diagnosis: Intermediate filament proteins, including vimentin and nestin, have implications in cancer research and diagnosis. Their expression patterns can provide information about the aggressiveness and metastatic potential of cancer cells. Intermediate filament proteins are often used as immunohistochemical markers in tumor pathology to aid in the classification and diagnosis of different types of cancers.
Drug Development and Targeting: Intermediate filament proteins are potential targets for drug development and therapeutic intervention. Modulating the expression or function of specific intermediate filament proteins may offer therapeutic opportunities for diseases associated with aberrant intermediate filament expression, such as certain types of muscular dystrophies or neurodegenerative disorders.
Regenerative Medicine: Intermediate filament proteins, particularly nestin, are used as markers for identifying and characterizing stem cells in regenerative medicine applications. Nestin-positive stem cells have been investigated for their potential to differentiate into various cell types and contribute to tissue repair and regeneration.
Biomaterials and Tissue Engineering Scaffolds: Intermediate filament proteins, such as vimentin and desmin, have been utilized in the development of biomaterials and tissue engineering scaffolds. Incorporating these proteins into scaffolds can enhance their mechanical properties, mimic the native tissue microenvironment, and promote cell adhesion, migration, and tissue formation.
Cell Mechanics and Biophysics: Intermediate filament proteins are studied in the field of cell mechanics and biophysics to understand the mechanical properties of cells and tissues. Their involvement in cell shape, elasticity, and response to mechanical forces provides insights into cell behavior and tissue mechanics.
These applications highlight the diverse roles and potential of intermediate filament proteins in various fields, including cell biology, diagnostics, therapeutics, regenerative medicine, and biomaterials. Continued research in these areas holds promise for advancing our understanding and utilization of intermediate filament proteins in various applications.
Available Resources for Intermediate Filaments
Creative BioMart is a foremost provider in the life sciences research sector, offering a wide array of products, custom services, and resources associated with intermediate filaments. Our product selection includes recombinant proteins, cell and tissue lysates, protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, antibodies, and related items. Additionally, we provide tailored services and an extensive range of technical resources to fulfill the specific requirements of our customers. Below is a list of molecules related to intermediate filaments, click on a molecule/target to view our extensive resources:


