Neurexins and Neuroligins
About Neurexins and Neuroligins
Neurexins and neuroligins are two families of proteins that play critical roles in synaptic function and neurotransmission in the brain. They are transmembrane proteins located on opposite sides of the synaptic cleft, facilitating cell-cell adhesion and communication between neurons.
Neurexins are presynaptic proteins found on the axon terminals of neurons. They exist in various isoforms and can interact with partners to form heterophilic or homophilic trans-synaptic adhesion complexes. Neurexins serve as scaffolding proteins at the synapse, linking the extracellular matrix to the intracellular cytoskeleton, and play a crucial role in synaptic development, maintenance, and plasticity. Additionally, they are involved in synaptic transmission by modulating the release of neurotransmitters and regulating the number and properties of synapses.
Neuroligins, on the other hand, are postsynaptic proteins located on the dendritic spines of neurons. Like neurexins, they also have various isoforms and can form trans-synaptic complexes with neurexins, establishing a strong adhesion between pre- and postsynaptic membranes. Neuroligins are critical for the formation and maturation of synapses during development, as they facilitate the recruitment and stabilization of synaptic proteins. They contribute to the proper alignment of pre- and postsynaptic components, regulate the synaptic structure and plasticity, and are involved in the balance between excitatory and inhibitory synaptic signaling.
The interaction between neurexins and neuroligins is crucial for synapse formation, maintenance, and function. Their binding promotes synapse formation and influences synapse morphology, neurotransmitter release, and synaptic strength. This interaction is specific and highly regulated, and alterations in neurexin-neuroligin signaling have been implicated in various neurological and psychiatric disorders, including autism spectrum disorders, schizophrenia, and intellectual disability.
Biological Functions of Neurexins and Neuroligins
Neurexins and neuroligins are cell adhesion molecules that play a crucial role in synaptic function and connectivity in the brain. They work together to form trans-synaptic complexes that bridge pre- and postsynaptic membranes, facilitating the formation and maintenance of synapses. The biological functions of neurexins and neuroligins include:
Synaptic Adhesion: Neurexins and neuroligins interact with each other in a calcium-dependent manner, forming a tight bond between the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes. This adhesion is essential for synapse formation and stabilization.
Synaptic Differentiation: Neurexins and neuroligins help organize the pre- and postsynaptic specializations at synapses. They recruit and interact with other synaptic proteins, such as scaffolding molecules and neurotransmitter receptors, contributing to the proper assembly and localization of synaptic components.
Synaptic Transmission: Neurexins and neuroligins can modulate neurotransmitter release and synaptic strength. They interact with components of the presynaptic machinery, such as voltage-gated calcium channels, regulating the release of neurotransmitters from the presynaptic terminal.
Synaptic Plasticity: Neurexins and neuroligins are involved in the dynamic remodeling of synapses, which underlies learning and memory processes. They regulate the recruitment and activity of postsynaptic receptors, influencing synaptic strength and plasticity.
Neural Circuit Formation: Neurexins and neuroligins have important functions in the establishment and refinement of neural circuits. They contribute to the specificity and selectivity of synaptic connections, ensuring proper wiring of the brain during development.
Neurodevelopmental Disorders: Mutations in neurexins and neuroligins have been associated with several neurodevelopmental disorders, including autism spectrum disorders (ASDs) and schizophrenia. These mutations disrupt the normal function of synapses, leading to impaired synaptic connectivity and altered neuronal communication. This can result in difficulties with social interaction, communication, and behavior seen in individuals with ASDs. In schizophrenia, alterations in neurexin and neuroligin signaling have been linked to abnormalities in synaptic function and connectivity, which are believed to contribute to the cognitive deficits and psychiatric symptoms observed in this disorder.
The Application Areas of Neurexins and Neuroligins
Autism: Mutations in neurexin and neuroligin genes have been associated with autism spectrum disorders (ASD). Understanding the role of these molecules in synapse formation and function can help in developing targeted therapies for ASD.
Schizophrenia: Neurexins and neuroligins have also been implicated in schizophrenia, a psychiatric disorder characterized by altered synaptic connectivity. Research on the involvement of these molecules may provide insights into the underlying mechanisms of the disease and potential therapeutic targets.
Neurodevelopmental Disorders: Neurexins and neuroligins are critical for synapse development and maturation. Dysregulation of these molecules can lead to various neurodevelopmental disorders, such as intellectual disability and epilepsy. Studying their function can aid in understanding the pathophysiology of these disorders and developing interventions.
Neurological Diseases: Neurexins and neuroligins have been linked to several neurological conditions, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and Huntington's disease. Investigating their role in these diseases can provide insights into the disease progression and potentially identify therapeutic targets.
Synaptic Plasticity and Learning: Neurexins and neuroligins play a crucial role in synaptic plasticity, which underlies learning and memory processes. Understanding the mechanisms by which these molecules modulate synaptic strength and connectivity can contribute to developing interventions to enhance learning and memory formation.
Overall, further research on neurexins and neuroligins can provide valuable insights into the complex mechanisms underlying brain development, synaptic communication, and neurological disorders. Understanding the role of these molecules in normal brain function and disease pathology could pave the way for the development of targeted therapies to treat a wide range of neurological conditions.
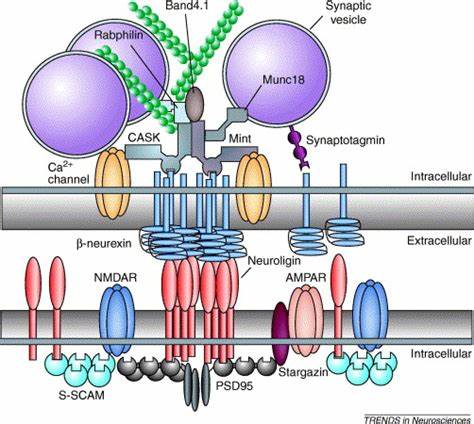 Fig.2 Molecular interactions of postsynaptic neuroligins and presynaptic β-neurexins. (Dean C, et al., 2006)
Fig.2 Molecular interactions of postsynaptic neuroligins and presynaptic β-neurexins. (Dean C, et al., 2006)
Clustered β-neurexin recruitsscaffolding proteins via its PDZ binding motiflike CASK and Mint. These two proteins bindtoeach other and could mediate therecruitment of synaptic vesicles through Munc18, the actin binding protein Band4.1and Rabphilin. CASK also binds to Ca2+-channels and 3-neurexin to synaptotagmin. Thus, B-neurexin assembles fundamentalcomponents necessary for neurotransmitterrelease through its PDZ binding motif.
Available Resources for Neurexins and Neuroligins
Creative BioMart is a leading supplier to the life science research industry dedicated to providing high-quality products and services. Our product catalog covers a broad range of recombinant proteins related to neurexins and neuroligins, cell and tissue lysates, and protein pre-coupled magnetic beads. We also offer tailored services and other extensive technical resources to meet our clients' specific needs.
Whether you have any questions about a product or require custom service, our customer service team is here to support you. Below is a list of molecules related to neurexins and neuroligins, click on a molecule/target to view our extensive resources:
You can get more details and browse our complete product catalog by visiting our website or contacting our customer service team directly. We are committed to providing reliable tools and support for scientific research to help drive progress in the life sciences.
Reference:
- Dean C, Dresbach T. Neuroligins and neurexins: linking cell adhesion, synapse formation and cognitive function[J]. Trends in neurosciences, 2006, 29(1): 21-29.


