p38 MAP Kinases
About p38 MAP Kinases
The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases are a class of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) that respond to stress stimuli such as cytokines, UV irradiation, heat shock, and osmotic shock and are involved in cell differentiation, apoptosis, and autophagy.
p38 MAP kinase (MAPK), also called RK or CSBP (cytokinin specific binding protein), is the mammalian orthologue of the yeast Hog1p MAP kinase, which participates in a signaling cascade controlling cellular responses to cytokines and stress.
To date, four splice variants of the p38 family have been identified: p38-α (MAPK14), -β (MAPK11), -γ (MAPK12 / ERK6), and -δ (MAPK13 / SAPK4). Similar to the SAPK/JNK pathway, p38 MAP kinase is activated by a variety of cellular stresses, including osmotic shock, inflammatory cytokines, lipopolysaccharide (LPS), UV, and growth factors. Among them, p38α and p38β are universally expressed, whereas p38γ and p38δ are differentially expressed according to tissue type.
The structure of p38 kinases consists of N- and C-lobes of the kinase domain with the active site in between the ATP binding site and TGY dual phosphorylation The active site is covered by the activation loop, which undergoes dual phosphorylation resulting in conformation change, permitting access of substrates to the active site and full phosphorylation. The active site is covered by the activation loop, which undergoes dual phosphorylation resulting in conformation change, permitting access of substrates to the active site and full kinase activation.
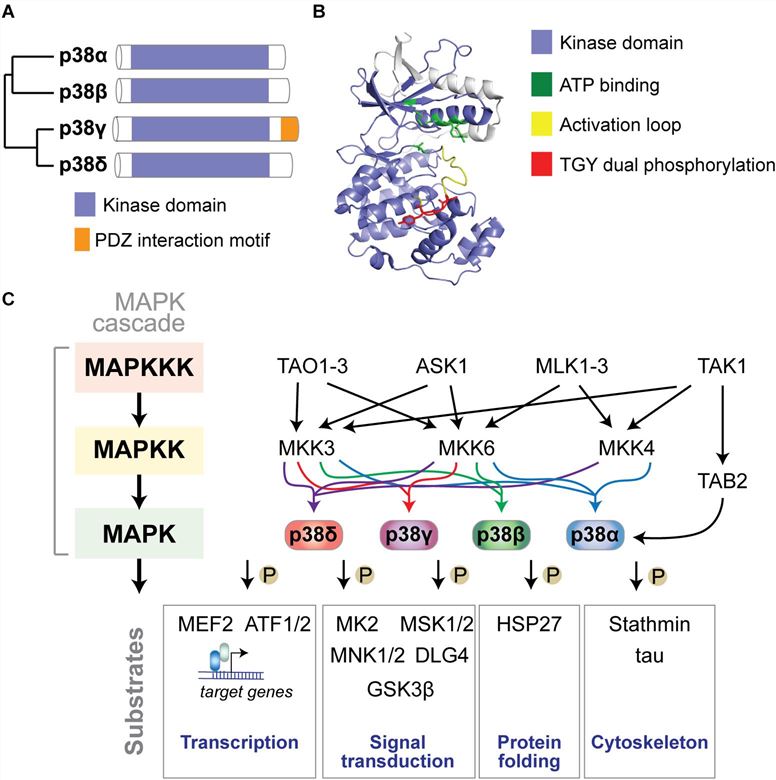 Fig.1 The p38 MAP kinase signaling pathway. (Asih P R, et al., 2020)
Fig.1 The p38 MAP kinase signaling pathway. (Asih P R, et al., 2020)
(A) Dendrogram of the four mammalian p38 MAP kinases p38α, p38β, p38γ, and p38δ.
(B) Structure of p38α showing N- and C-lobes of the kinase domain with the active site in between. ATP binding site, activation loop and TGY dual phosphorylation are highlighted. The active site is covered by the activation loop, which undergoes dual phosphorylation resulting in conformation change, access of substrates to the active site and full kinase activation. Structure was reproduced from PDB 3HVC using Pymol.
(C) Mammalian p38 kinases comprise of 4 proline-directed serine/threonine kinases - p38α, p38β, p38γ, and p38δ – encoded in 4 individual genes. p38 MAP kinases are activated by a plethora of extrinsic (extracellular) or intrinsic (intracellular) factors.
Mechanism of Action of p38 MAP Kinases
The classic activation of p38 follows a three-tiered mechanism. Stimuli of p38 activation are cellular stressors such as oxidative stress, inflammatory stimuli/cytokines, UV radiation, and osmotic pressure at cell membranes. Upstream stimuli activate a MAP kinase kinase kinase (MAPKKK) such as ASK1, TAK1, MLK, or TAO kinases, which in turn phosphorylate and activate a MAPKK, such as MKK3, MKK4, or MKK6, which in turn phosphorylates p38 kinases on Threonine and Tyrosine residues in the activation loop. Dual phosphorylation of p38 can be detected by phospho-specific antibodies as a marker of activated p38. Dual-phosphorylated p38 is fully active and targets downstream phosphorylation substrates to alter their structure, activity, function, localization, or interaction with other biomolecules. An alternative activation mechanism of p38α downstream of TAK1 involves direct interaction with TAB2 followed by auto-phosphorylation of p38α.
Classic downstream targets of p38 kinases include transcription factors (e.g., ATF-1/2 and MEF2), chaperones (e.g., HSP27), cytoskeletal regulators (stathmin, tau), and other signaling factors (e.g., MAPKAP kinase 2/3, MSK1/2, MNK1/2, DLG4, and GSK3β). Feedback inhibition of p38 kinases occurs through dephosphorylation by MAP kinase phosphatases (e.g., MKP1), limiting the activity of upstream kinases, or transcriptional feedback.
Functions of p38 MAP Kinases
The p38 MAP kinase has multiple functions within the cell, and it is involved in the regulation of many cellular processes and biological functions. Here are some of the major functions of p38 MAP kinase:
- Inflammation Regulation
p38 MAP kinase plays an important role in the inflammatory response. Once activated, it can induce the production of inflammatory mediators such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β). It is involved in the activation of inflammatory cells and the regulation of inflammatory signaling pathways and is essential for the development and regulation of inflammatory responses.
- Cellular Stress Response
p38 MAP kinase is an important regulator of cellular stress response. It can be activated by a variety of external stimuli, such as oxidative stress, environmental stress, heat shock, and DNA damage. Activated p38 MAP kinase can regulate the cellular stress response, prompting cells to adapt to and fight against adverse environmental conditions.
- Cell Cycle Regulation
p38 MAP kinase is involved in the genetic stability of the cell cycle, cell cycle checkpoints, as well as cell proliferation and differentiation. p38 MAP kinase activation induces the expression of cell cycle inhibitory factors, which inhibit the progression of the cell cycle.
- Apoptosis
p38 MAP kinase can influence cell survival and death decisions by regulating the phosphorylation status of apoptosis-related proteins. In some cases, activation of p38 MAP kinase promotes apoptosis, while in other cases it inhibits apoptosis.
In addition to these functions, p38 MAP kinase is involved in a variety of other biological processes, such as cell migration, cell differentiation, cell adhesion, and intracellular signaling. Although the functions of p38 MAP kinase may overlap in some cases, its role in many physiological and pathological processes remains a very critical area of research.
Available Resources for p38 MAP Kinases
p38 MAP kinase plays an important role in cell signaling, stress response, inflammation, and disease development. The in-depth study of its function and regulatory mechanism can help to reveal the pathogenesis of related diseases and is expected to provide targets and therapeutic strategies for the development of new drugs. Creative BioMart offers a variety of p38 MAP kinases-related research products, such as recombinant proteins, cell and tissue lysates, and protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, as well as customizable services and other resources to support your research in the field of p38 MAP kinases or p38 pathway. The following p38 MAP kinases are displayed, click to view all related molecules/targets and research reagents. For further information or to purchase products, please contact us. We are committed to providing the highest quality resources and support for your research to help you succeed.
References:
- Asih P R, Prikas E, Stefanoska K, et al. Functions of p38 MAP kinases in the central nervous system[J]. Frontiers in molecular neuroscience, 2020, 13: 570586.
- Zarubin T, Han J. Activation and signaling of the p38 MAP kinase pathway[J]. Cell research, 2005, 15(1): 11-18.
- Han J, Wu J, Silke J. An overview of mammalian p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases, central regulators of cell stress and receptor signaling[J]. F1000Research, 2020, 9.
- Cuenda A, Rousseau S. p38 MAP-kinases pathway regulation, function and role in human diseases[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Research, 2007, 1773(8): 1358-1375.


