PTN
-
Official Full Name
pleiotrophin
-
Overview
Pleiotrophin (PTN) also known as heparin-binding brain mitogen (HBBM) or heparin-binding growth factor 8 (HBGF-8) or neurite growth-promoting factor 1 (NEGF1) or heparin affinity regulatory peptide (HARP) or heparin binding growth associated molecule (HB-GAM) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PTN gene.Pleiotrophin is an 18-kDa growth factor that has a high affinity for heparin. It is structurally related to midkine and retinoic acid induced heparin-binding protein. -
Synonyms
PTN; pleiotrophin; NEGF1, neurite growth promoting factor 1; HBGF8; HBNF; heparin binding growth factor 8; HBBM; OSF-1; HB-GAM; HBGF-8; HBNF-1; osteoblast-specific factor 1; heparin-binding brain mitogen; heparin-binding growth factor 8; heparin affin re;
- Recombinant Proteins
- Cell & Tissue Lysates
- Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads
- Cattle
- Chicken
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Rhesus Macaque
- Zebrafish
- E. coli
- E.coli
- HEK293
- HEK293F
- Human Cell
- Insect Cell
- Insect Cells
- Mammalian Cell
- Sf21 Insect Cell
- C
- His
- Fc
- GST
- GST|His
- His (Fc)
- Avi
- N/A
- N
- Background
- Quality Guarantee
- Case Study
- Involved Pathway
- Protein Function
- Interacting Protein
- PTN Related Articles
- PTN Related Research Area
What is PTN protein?
PTN (pleiotrophin) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 7 at locus 7q33. Pleiotrophin (PTN) also known as heparin-binding brain mitogen (HBBM) or heparin-binding growth factor 8 (HBGF-8) or neurite growth-promoting factor 1 (NEGF1) or heparin affinity regulatory peptide (HARP) or heparin binding growth associated molecule (HB-GAM) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PTN gene. PTN is an 18 kDa growth factor that has a high affinity for heparin. It is structurally related to midkine and retinoic acid induced heparin-binding protein.
What is the function of PTN protein?
PTN is a secreted growth factor that mediates its signal through cell-surface proteoglycan and non-proteoglycan receptors. It binds cell-surface proteoglycan receptor via their chondroitin sulfate (CS) groups, thereby regulates many processes like cell proliferation, cell survival, cell growth, cell differentiation and cell migration in several tissues namely neuron and bone. In addition, it may play a role in the female reproductive system, auditory response and the progesterone-induced decidualization pathway.
PTN Related Signaling Pathway
PTN binding PTPRZ1 controls oligodendrocyte precursor cell differentiation by enhancing the phosphorylation of AFAP1L2 in order to activate the PI3K-AKT pathway. Or PTN binds ALK and promotes cell survival and cell proliferation through MAPK pathway activation. It can also bind to Wnt ligands and Notch receptors to activate the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and Notch signaling pathway, respectively. When Notch signaling pathway is activated, it can promote biological processes such as neuronal development, angiogenesis and tumorigenesis.
PTN Related Diseases
PTN is abnormally expressed in a variety of tumors, including breast cancer, lung cancer, and colorectal cancer. PTN plays an important role in the proliferation and differentiation of bone cells, and its abnormal expression is associated with the occurrence of bone metabolism-related diseases such as osteoporosis and bone tumors. It is also associated with inflammatory diseases, neurological diseases and cardiovascular diseases.
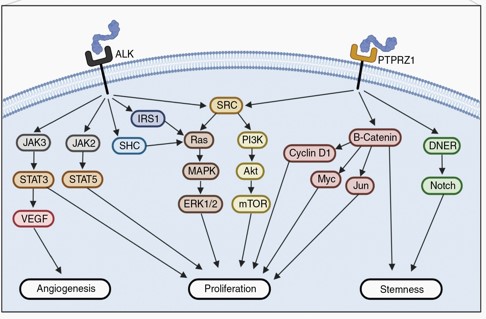
Fig1. Graphical summary of the iatrogenic induction of PTN-mediated self-renewal and proliferation in glioblastoma recurrences. (Arnon Møldrup Knudsen, 2022)
Bioapplications of PTN
More commonly, PTN is used as a therapeutic target for related diseases and drug development targets. PTN can be used for the treatment of bone diseases and the repair of fractures. In addition, PTN can promote the reconstruction of neuronal networks by promoting neuronal migration and synaptic formation, so it has been widely studied and applied to nervous system repair and regeneration.
High Purity
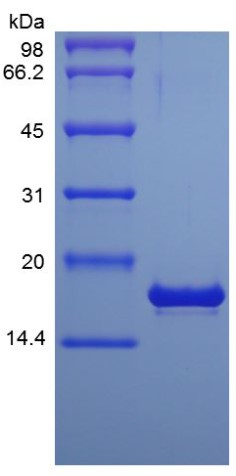
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PTN-30874TH) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
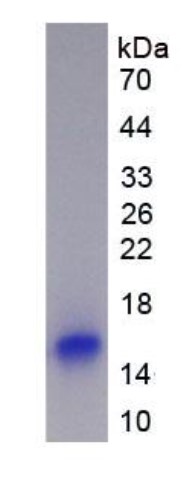
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (PTN-439H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
Case study 1: Yayun Zhang, 2023
The refined functional cell subtypes in the immune microenvironment of specific titanium (Ti) surface and their collaborative role in promoting bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) driven bone integration need to be comprehensively characterized.
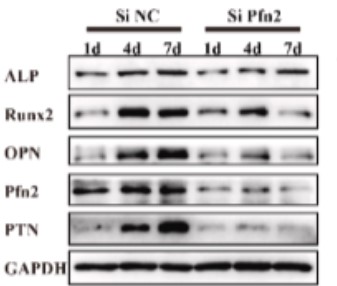
This study employed a simplified co-culture system to investigate the dynamic, temporal crosstalk between macrophages and BMSCs on the Ti surface. The M2-like sub-phenotype of macrophages, characterized by secretion of CXCL chemokines, emerges as a crucial mediator for promoting BMSC osteogenic differentiation and bone integration in the Ti surface microenvironment. The secretion of CXCL3, CXCL6, and CXCL14 by M2-like macrophages plays a pivotal role. The process activates CXCR2 and CCR1 receptors, triggering downstream regulatory effects on the actin cytoskeleton pathway within BMSCs, ultimately fostering osteogenic differentiation. PTN maintains the M2-like phenotype via the Sdc3 receptor-mediated cell adhesion molecules pathway.
The findings provide a novel insight into the intricate communication and mutual regulatory mechanisms operating between BMSCs and macrophages on the Ti surface, highlight specific molecular events governing cell-cell interactions in the osteointegration.
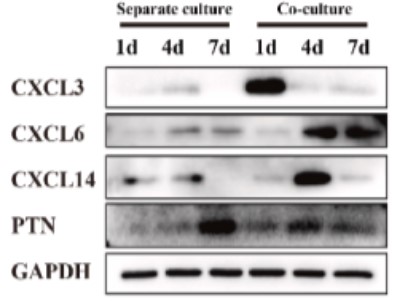
Fig1. Protein expression profiles of CXCL3, CXCL6, CXCL14, and PTN over time in separate and co-culture systems.
Case study 2: Arnon Møldrup Knudsen, 2022
Glioblastomas are highly resistant to therapy, and virtually all patients experience tumor recurrence after standard-of-care treatment. Surgical tumor resection is a cornerstone in glioblastoma therapy, but its impact on cellular phenotypes in the local postsurgical microenvironment has yet to be fully elucidated.
The team developed a preclinical orthotopic xenograft tumor resection model in rats with integrated 18F-FET PET/CT imaging. Differentially expressed genes and pathways were investigated and validated using tissue specimens from the xenograft model, 23 patients with matched primary/recurrent tumors, and a cohort including 190 glioblastoma patients. Functional investigations were performed in vitro with multiple patient-derived cell cultures. The human Pleiotrophin/PTN ELISA Kit (Invitrogen) was used according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Recurrent tumors expressed elevated levels of pleiotrophin (PTN), secreted by both tumor cells and tumor-associated microglia/macrophages. Mechanistically, PTN could induce tumor cell proliferation, self-renewal, and the stem cell program. In short, Surgical tumor resection is an iatrogenic driver of PTN-mediated self-renewal in glioblastoma tumor cells that promotes therapeutic resistance and tumor recurrence.
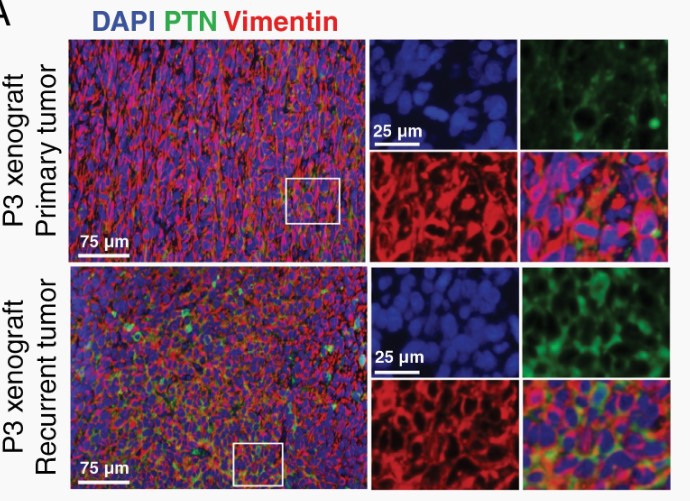
Fig3. Representative immunofluorescence images showing PTN expression in primary vs recurrent P3 xenografts.
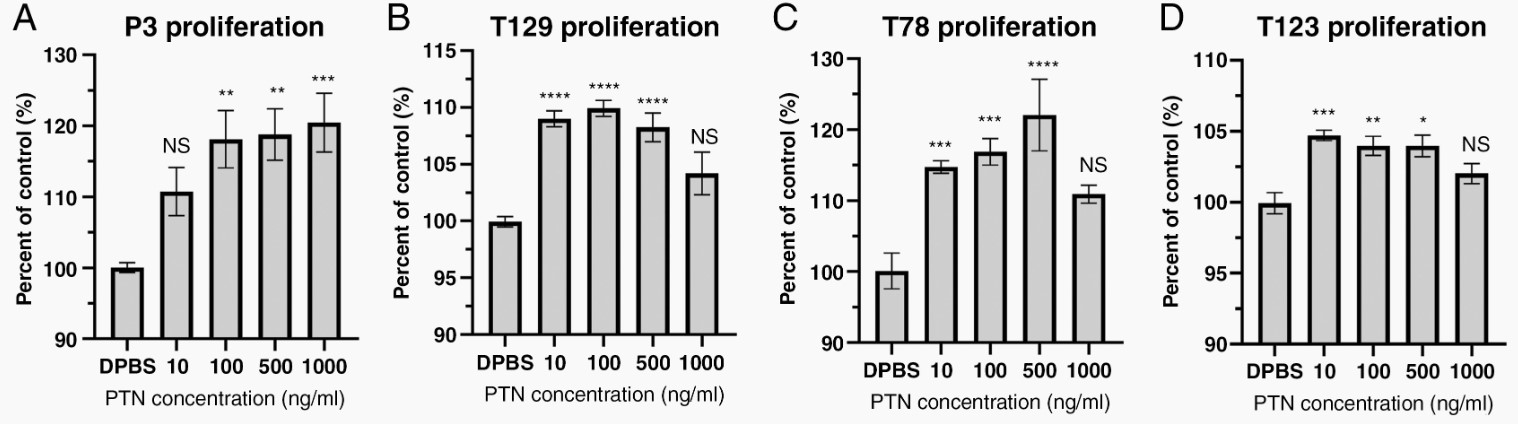
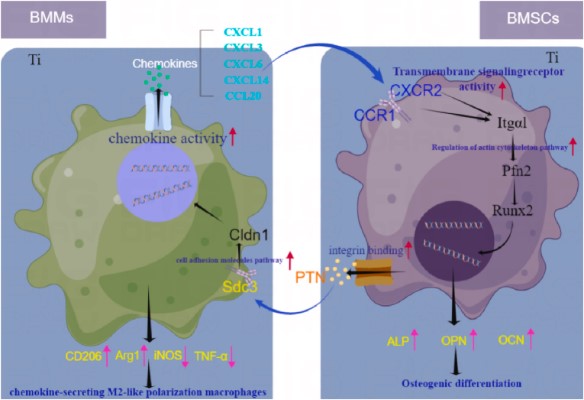
Fig1. Summary of the mechanisms underlying the interaction between BMMs and BMSCs after co-culture on titanium surfaces. (Yayun Zhang, 2023)
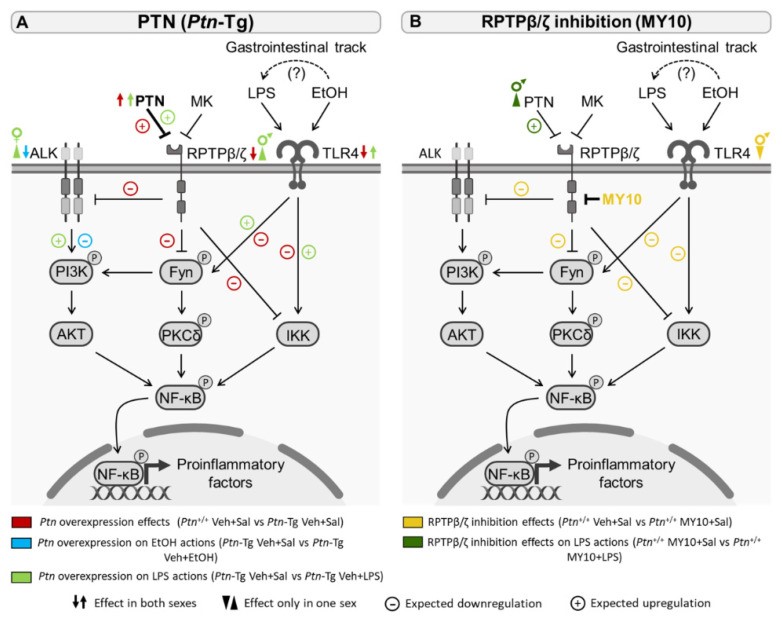
Fig2. Proposed mechanisms of the effect of Ptn overexpression on some of the principal signaling pathways implicated in ethanol and/or LPS acute response in adolescent mice. (María Rodríguez-Zapata, 2023)
PTN involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PTN participated on our site, such as Syndecan-3-mediated signaling events, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PTN were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Syndecan-3-mediated signaling events | AGRP;PTN;COL20A1 |
PTN has several biochemical functions, for example, chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan binding, growth factor activity, heparin binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PTN itself. We selected most functions PTN had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PTN. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan binding | COL20A1;PTPRF;SEMA5A;PTN |
| growth factor activity | FGF11A;Artn;PRL2C2;FGF9;FGF10A;OSM;EREG;CSF2;PDGFD |
| heparin binding | NELL2;LPL;LTF;PTPRF;PCOLCE;FN1;COL20A1;APOE;FSTL1 |
| protein phosphatase inhibitor activity | SET;PPP1R14C;PPP1R14A;SAG;KIAA0649;LMTK2;URI1;PPP1R14B;PPP1R2P3 |
PTN has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PTN here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PTN.
SGTA; CHD3; TAF1D; UBQLN4; DNAJB11; SMAP; PSMD11; EIF3F; CACNB4; TXNDC9; PLXNB2; SGSM2; NUDT21; DFNA5; PFDN1
- Q&As
- Reviews
Q&As (7)
Ask a questionPTN plays a critical role in neurodevelopment and neuronal plasticity. During embryonic development, PTN promotes axonal outgrowth, neuronal migration, and synaptogenesis. It interacts with cell surface receptors on neurons, such as ALK, to activate downstream signaling pathways that modulate cytoskeletal dynamics and promote neurite growth. In the adult brain, PTN is involved in synaptic plasticity, memory formation, and neuronal survival. Dysregulation of PTN expression or signaling can disrupt normal neurodevelopmental processes and contribute to neurological disorders.
PTN has shown promise as a diagnostic biomarker for certain diseases. Increased PTN expression has been observed in the serum or tissue samples of patients with various cancers, suggesting its potential as a cancer biomarker. Additionally, PTN levels in cerebrospinal fluid have been associated with neurodegenerative disorders, including Alzheimer's disease. Ongoing research aims to develop sensitive and specific assays for PTN detection, which could aid in early disease diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring of treatment response in these conditions.
PTN binding to its cell surface receptors initiates downstream signaling pathways that regulate cellular functions. One of the major pathways activated by PTN is the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathway, which promotes cell survival and growth. PTN can also activate the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, including extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), leading to cellular proliferation and differentiation. Additionally, PTN can influence intracellular calcium signaling and modulate the activity of various transcription factors, ultimately impacting gene expression and cellular behavior.
The protein PTN, also known as pleiotrophin, plays a crucial role in various biological processes. It functions as a cytokine and growth factor that regulates cellular proliferation, differentiation, and migration. PTN is involved in embryonic development, tissue repair, and the maintenance of neuronal plasticity. Its interactions with cell surface receptors, such as receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase beta/zeta (RPTPβ/ζ) and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK), mediate downstream signaling cascades that influence cellular behavior and tissue homeostasis.
Dysregulation of PTN expression has been implicated in several diseases. Increased PTN levels have been observed in various types of cancer, including breast, lung, and glioblastoma, where it promotes tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis. Furthermore, aberrant PTN expression has been linked to neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer's disease, where it contributes to neuronal dysfunction and neuroinflammation. In cardiovascular diseases, PTN can promote vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and contribute to the development of atherosclerosis.
The transcriptional regulation of the PTN gene involves complex mechanisms. Several transcription factors, including AP-1, NF-κB, and SP1, have been identified as regulators of PTN expression. Additionally, epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation and histone acetylation, can modulate PTN gene activity. Furthermore, various extracellular stimuli, including growth factors and cytokines, can induce PTN expression through the activation of specific signaling pathways, such as the MAPK/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways.
Inhibition of PTN activity or downstream effectors is being investigated as a potential therapeutic approach. Small molecule inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies targeting PTN or its receptors are being developed to block PTN signaling and mitigate its pathological effects. Additionally, strategies to modulate PTN expression through gene therapy or targeted delivery of RNA-based therapeutics are being explored. The efficacy of these approaches is being evaluated in preclinical and clinical studies to determine their potential for treating PTN-related diseases.
Customer Reviews (3)
Write a reviewBy utilizing this experimental reagent, I save a significant amount of time and effort, enabling a seamless workflow.
Using this reagent, I can rapidly obtain high-quality experimental data.
Following the implementation of this protein reagent, the reproducibility of my experiments has significantly improved, leaving me highly satisfied.
Ask a Question for All PTN Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All PTN Products
Required fields are marked with *


