IL-1 Family Receptors
Available Resources for IL-1 Family Receptors Research
Creative BioMart is delighted to present a wide range of products associated with IL-1 family receptors. Our offerings include recombinant proteins, magnetic beads pre-coupled with proteins, and cell and tissue lysates, providing researchers with essential tools for their studies. Our customizable services are designed to cater to your specific requirements, ensuring that you receive the most suitable product for your research needs.
In addition to our comprehensive product line, we also offer a wealth of information on IL-1 family receptors. Our resources cover various topics such as pathways, protein function, interacting proteins, related articles, and research areas. These resources serve as valuable references that help researchers deepen their understanding of IL-1 family receptors and their significance in physiological processes. By providing both products and knowledge, we are committed to supporting researchers and contributing to advancements in this field of research.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL18R1-2254H | Recombinant Human IL18R1, Fc-His tagged | Human | Human Cell | Fc/His |
| Il18r1-3319M | Recombinant Mouse Il18r1 protein, His&hFc-tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | His&hFc |
| IL1R2-2200H | Active Recombinant Human IL1R2 protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| IL1R2-773H | Recombinant Human IL1R2 protein, Fc-tagged | Human | HEK293 | human/IgG1/Fc |
| IL1RAP-2256H | Recombinant Human IL1RAP protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| IL1RAPL1-776H | Recombinant Human IL1RAPL1, Fc tagged | Human | Human Cell | Fc |
| IL1RAPL2-778H | Recombinant Human IL1RAPL2, Fc tagged | Human | Human Cell | Fc |
| SIGIRR-3956H | Recombinant Human SIGIRR, His tagged | Human | Human Cell | His |
About IL-1 Family Receptors
The IL-1 (Interleukin-1) family receptors are a group of cell surface receptors that interact with IL-1 family ligands, transmitting signals into the cells and mediating their biological effects. These receptors are essential for the regulation of immune responses, inflammation, and various physiological processes. The IL-1 family receptors are characterized by their structural similarities and shared signaling pathways, allowing for functional overlap and complex signaling networks.
The IL-1 family includes several receptors that interact with specific ligands:
- IL-1 Receptor Type 1 (IL-1R1): IL-1α and IL-1β primarily bind to IL-1R1, initiating intracellular signaling pathways. IL-1R1 is expressed on a wide range of cell types, including immune cells, and its activation leads to the induction of inflammatory mediators, such as cytokines, chemokines, and adhesion molecules.
- IL-1 Receptor Type 2 (IL-1R2): IL-1R2 acts as a decoy receptor, binding IL-1α and IL-1β without transmitting intracellular signaling. It competes with IL-1R1 for ligand binding, thereby regulating the availability and activity of IL-1 ligands.
- IL-18 Receptor (IL-18R): IL-18 binds to IL-18R, which consists of two subunits, IL-18Rα and IL-18Rβ. The binding of IL-18 induces the recruitment and activation of intracellular signaling molecules, leading to the production of interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) and other inflammatory molecules.
- IL-33 Receptor (IL-1RL1): IL-33 binds to IL-1RL1, also known as ST2, which is expressed on various immune cells, including mast cells, eosinophils, and T helper 2 (Th2) cells. IL-33 binding activates downstream signaling pathways, promoting immune cell activation and the production of type 2 cytokines.
- IL-36 Receptor (IL-36R): IL-36 ligands (IL-36α, IL-36β, IL-36γ) interact with IL-36R, which consists of IL-36R and IL-1 receptor accessory protein (IL-1RAcP). IL-36R signaling leads to the activation of immune cells, particularly in the skin, contributing to skin inflammation and immune responses.
- IL-1 Receptor-like 1 (IL-1RL1): IL-1RL1, also known as IL-33 receptor-related protein 1 (IL-33R1), interacts with IL-33 and modulates immune responses. It is expressed on various immune cells and is involved in the activation of mast cells, eosinophils, and Th2 cells.
The IL-1 family receptors transmit signals through shared intracellular signaling pathways. Upon ligand binding, they recruit intracellular adapter proteins, such as MyD88 (myeloid differentiation primary response 88), leading to the activation of downstream signaling pathways, including NF-κB, MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase), and JAK-STAT (Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription).
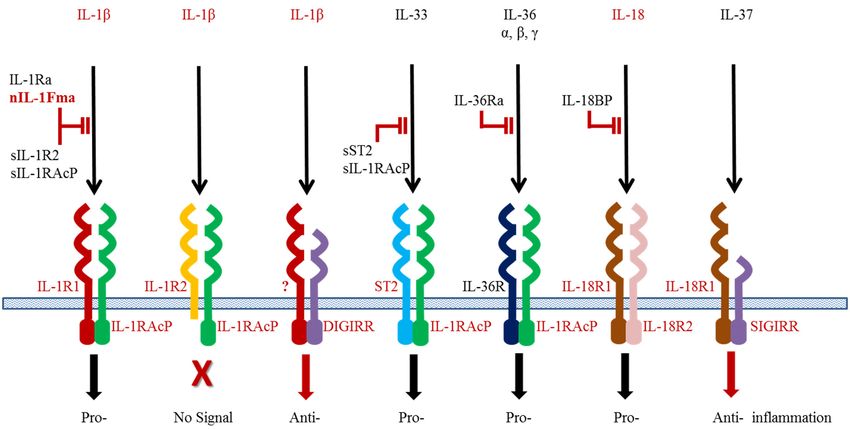 Fig.1 Interaction of the IL-1 family cytokines and receptors. (Zou J, et al., 2016)
Fig.1 Interaction of the IL-1 family cytokines and receptors. (Zou J, et al., 2016)
Signaling Pathways and Mechanisms of Action of IL-1 Family Receptors
The IL-1 family receptors transmit signals through shared intracellular signaling pathways, leading to the activation of various transcription factors and the production of inflammatory mediators. Here are the main signaling pathways and mechanisms of action employed by IL-1 family receptors:
- MyD88-Dependent Pathway: The majority of IL-1 family receptors, including IL-1R1, IL-18R, IL-33R (ST2), and IL-36R, utilize the MyD88-dependent pathway for signaling. Upon ligand binding, the receptors recruit the adapter protein MyD88 to their cytoplasmic domains. This recruitment enables the formation of a complex that triggers downstream signaling events.
- IRAK (IL-1 Receptor-Associated Kinase) Activation: Following the recruitment of MyD88, IRAKs are recruited to the receptor complex. IRAK4 phosphorylates IRAK1, which then associates with TRAF6 (TNF receptor-associated factor 6), leading to its activation. Activated IRAK1 and IRAK4 phosphorylate and activate TRAF6.
- Activation of TAK1 (Transforming Growth Factor-Beta-Activated Kinase 1): TRAF6, along with the E3 ubiquitin ligase complex, catalyzes the K63-linked polyubiquitination of TRAF6 itself and other signaling molecules. This ubiquitination event leads to the recruitment and activation of TAK1, a central kinase in IL-1 family receptor signaling.
- MAPK (Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase) Activation: TAK1 activates the MAPK signaling pathways, including ERK (extracellular signal-regulated kinase), JNK (c-Jun N-terminal kinase), and p38 MAPK. These pathways control gene expression, cytokine production, and cellular responses associated with inflammation and immune activation.
- NF-κB (Nuclear Factor-kappa B) Activation: The recruitment and activation of TAK1 also lead to the activation of the NF-κB pathway. TAK1 phosphorylates the IκB kinase (IKK) complex, which phosphorylates IκB (inhibitor of NF-κB), leading to its degradation. This releases NF-κB, allowing it to translocate into the nucleus and regulate the transcription of genes involved in inflammation and immune responses.
- Activation of Transcription Factors: The activated MAPK and NF-κB pathways induce the expression of various transcription factors, including AP-1 (activator protein-1) and IRF (interferon regulatory factor) family members. These transcription factors contribute to the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and other immune mediators.
- Negative Regulation: To prevent excessive inflammation, several negative regulators are involved in IL-1 family receptor signaling. These include IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra), which competes with IL-1 ligands for receptor binding, and IRAK-M (IL-1 receptor-associated kinase-M), which acts as a negative regulator of IRAK signaling.
The signaling pathways and mechanisms of action of IL-1 family receptors are complex and interconnected. They orchestrate immune responses, inflammation, and tissue homeostasis.
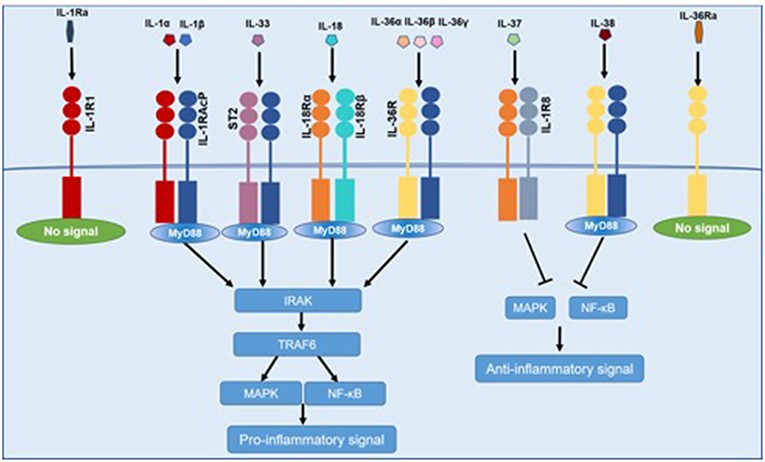 Fig.2 Common signaling pathway for IL-1 family cytokines. (Xu D, et al., 2019)
Fig.2 Common signaling pathway for IL-1 family cytokines. (Xu D, et al., 2019)
IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-18, IL-33, and IL-36 bind to IL-1R family members, recruiting MyD88, IRAK4, TRAF6, which resulted in the activation of NF-κB and MAPK and then promoting the transcription of several inflammatory genes. IL-37 and IL-38 exert anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK signaling. IL-1Ra and IL-36 Ra cannot recruit the signaling chain.
Role of IL-1 Family Receptors in Immunomodulation
IL-1 family receptors play a vital role in immunomodulation, regulating immune responses and maintaining immune homeostasis. They contribute to the fine-tuning of immune activation, the resolution of inflammation, and the balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory signals. Here are some key roles of IL-1 family receptors in immunomodulation:
- Immune Cell Activation and Cytokine Production: IL-1 family receptors, such as IL-1R1, IL-18R, and IL-33R (ST2), are expressed on various immune cells, including macrophages, dendritic cells, and lymphocytes. Activation of these receptors triggers intracellular signaling cascades, leading to the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1β, IL-18, and IL-33, as well as other immune modulators. These cytokines further regulate the activation and function of immune cells, shaping the immune response.
- Inflammatory Response Regulation: IL-1 family receptors are involved in the regulation of inflammatory responses. They contribute to the initiation and amplification of inflammation through the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. However, they also participate in the negative regulation of inflammation through the induction of anti-inflammatory molecules, such as IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) and IL-36 receptor antagonist (IL-36Ra). These antagonists compete with pro-inflammatory ligands for receptor binding, dampening the inflammatory signals and promoting the resolution of inflammation.
- T Cell Differentiation and Function: IL-1 family receptors influence the differentiation and function of T cells, which are key regulators of immune responses. For instance, IL-18R signaling promotes Th1 cell differentiation, leading to the production of cytokines, such as interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), that drive cellular immune responses against intracellular pathogens. IL-33R signaling contributes to the activation and function of Th2 cells, which are involved in allergic and type 2 immune responses. The balance between different T cell subsets is critical for immune homeostasis, and IL-1 family receptors contribute to this regulation.
- Modulation of Innate Immunity: IL-1 family receptors are involved in the regulation of innate immune responses. They enhance the antimicrobial functions of phagocytes, such as macrophages and neutrophils, promoting the clearance of pathogens. Additionally, IL-1 family receptors contribute to the activation of natural killer (NK) cells, stimulating their cytotoxic activity against infected or transformed cells.
- Tissue Repair and Remodeling: IL-1 family receptors, particularly IL-33R, have roles beyond inflammation in tissue repair and remodeling. They contribute to tissue healing processes by promoting the activation and recruitment of immune cells involved in tissue repair, such as fibroblasts and myofibroblasts.
- Allergic and Type 2 Immune Responses: IL-1 family receptors, including IL-33R, are critical in allergic and type 2 immune responses. They activate immune cells, such as mast cells, eosinophils, and type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s), contributing to the initiation and amplification of allergic inflammation.
The precise role of IL-1 family receptors in immunomodulation can vary depending on the specific ligand-receptor interaction and the cellular context. Their activities are tightly regulated to maintain immune homeostasis, prevent excessive inflammation, and promote appropriate immune responses against pathogens. Dysregulation of IL-1 family receptor signaling can contribute to the development of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, highlighting the importance of understanding their immunomodulatory functions for therapeutic interventions.
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
Related References:
- Boraschi D, Italiani P, Weil S, Martin MU. The family of the interleukin-1 receptors. Immunol Rev. 2018 Jan;281(1):197-232.
- Xu D, Mu R, Wei X. The Roles of IL-1 Family Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2025
- Boraschi D, Tagliabue A. The interleukin-1 receptor family. Semin Immunol. 2013;25(6):394-407.
- Dinarello CA. Overview of the interleukin-1 family of ligands and receptors. Semin Immunol. 2013;25(6):389-393.
- Zou J, Secombes CJ. The Function of Fish Cytokines. Biology (Basel). 2016;5(2):23.


