Other Coagulation Cascade Molecules
About Other Coagulation Cascade Molecules
In the process of the coagulation cascade, in addition to coagulation cascade protease inhibitors, coagulation cascade proteases, and coagulation factors, there are other important molecules involved, such as:
Annexins: Annexins are a family of calcium-binding proteins that have diverse functions in the coagulation process. They are involved in platelet activation, clot formation, and fibrinolysis. Examples include ANXA2, ANXA3, and ANXA5. ANXA2, also known as annexin A2 or annexin II, has been implicated in platelet activation and clot formation. ANXA3, or annexin A3, has been associated with platelet function and thrombosis. ANXA5, or annexin A5, has anticoagulant properties and inhibits blood clot formation.
Collagen-related molecules: Collagen is an essential component of the extracellular matrix and plays a role in platelet adhesion and activation. Collagen-related molecules, such as COL25A1, COL2A1, and COL4A1, contribute to the integrity and stability of blood vessels and are involved in clot formation.
Proteins involved in platelet function, such as GP1BA, GP1BB, GP5, GP6, GP9, and P2RY12, are essential for platelet adhesion, activation, and aggregation. They help in the formation of platelet plugs and clot stabilization.
Other proteins involved in clotting or coagulation-related processes include APOH, ENPP4, F2RL1, FGA, FGB, FGL2, HPSE, MCFD2, G6B, PAWR, PF4, Plaur, PLSCR1, PROCR, PROS1, Protein S, PTGIR, TBXA2R, and THBD. These proteins participate in various steps of the coagulation cascade, including initiation, amplification, and termination of clot formation.
Physiological Functions of Other Coagulation Cascade Molecules
Fibrinogen is a soluble plasma glycoprotein that serves as a precursor for fibrin, a key component of blood clot formation. When the coagulation cascade is activated, thrombin converts fibrinogen into fibrin, which forms the mesh-like structure of the blood clot.
Platelets are cell fragments involved in blood clotting. When a blood vessel is damaged, platelets adhere to the site of injury and aggregate to form a plug and initiate clot formation. Platelets also release chemicals that promote vasoconstriction and attract more platelets to the site.
von Willebrand factor (vWF) is a plasma glycoprotein that plays a crucial role in hemostasis. It binds to exposed collagen at the site of vascular injury, forming a bridge between platelets and the damaged vessel wall. vWF also stabilizes factor VIII, a necessary cofactor in the coagulation cascade.
Tissue factor, also known as factor III, is a cell membrane protein expressed on various cell types, including endothelial cells and monocytes. It initiates the extrinsic pathway of the coagulation cascade by binding to factor VIIa. The formation of the tissue factor-factor VIIa complex activates the downstream coagulation factors, leading to clot formation.
Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) is a plasma protein that inhibits the initiation of the coagulation cascade. It primarily inhibits the activation of factor X by the tissue factor-factor VIIa complex. TFPI forms a complex with factor Xa and tissue factor-factor VIIa, thereby inhibiting the conversion of factor X to factor Xa. This helps regulate the clotting process and prevents the formation of unnecessary blood clots.
Antithrombin III (ATIII) is a plasma serine protease inhibitor that inhibits the activity of several coagulation factors, including thrombin, factors IXa, Xa, XIa, and XIIa. ATIII works by binding to these factors and accelerating their inactivation by blocking their active sites. It plays a crucial role in controlling clot formation and preventing excessive thrombin generation. Deficiency of ATIII is associated with an increased risk of venous thromboembolism.
Protein C is a vitamin K-dependent plasma protein that plays a crucial role in anticoagulation. Activated protein C inhibits the coagulation cascade by degrading factors Va and VIIIa, which are essential for clot formation. Protein C activation is stimulated by the thrombin-thrombomodulin complex on the surface of endothelial cells.
Protein S is a vitamin K-dependent plasma protein that acts as a cofactor for protein C. Protein S enhances the anticoagulant function of activated protein C by binding to phospholipids on the surface of endothelial cells. It also serves as a direct inhibitor of coagulation factors Va and VIIIa. Protein S deficiency is associated with an increased risk of venous thromboembolism.
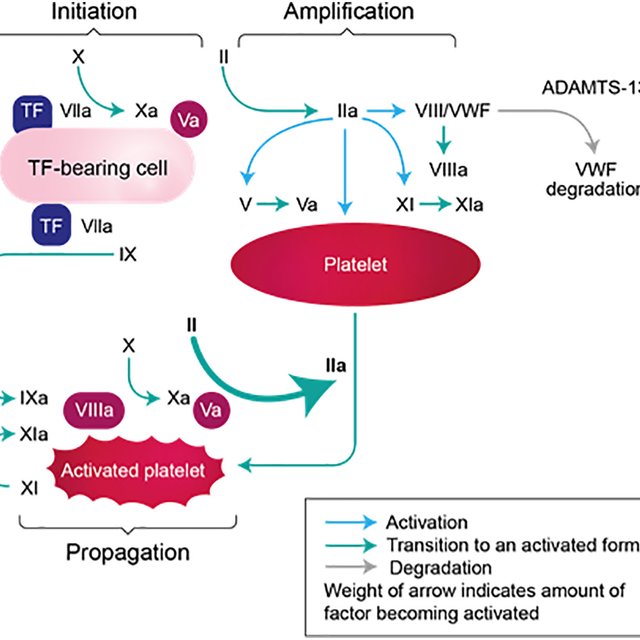 Fig.2 Phases of coagulation. TF, tissue factor; VWF, von Willebrand factor. (Samuelson Bannow B, et al., 2019)
Fig.2 Phases of coagulation. TF, tissue factor; VWF, von Willebrand factor. (Samuelson Bannow B, et al., 2019)
Available Resources for Other Coagulation Cascade Molecules
Creative BioMart offers researchers and scientists access to an extensive selection of high-quality recombinant proteins, customized services, and a diverse repository of valuable resources related to other coagulation cascade molecules.
- Recombinant Proteins: Creative BioMart furnishes a wide assortment of recombinant proteins, encompassing diverse elements of the coagulation cascade, all produced utilizing advanced recombinant DNA technology. These proteins are expressed and purified to exacting standards, ensuring their biological functionality, crucial for studying the functions, interactions, and mechanisms of other coagulation cascade molecules.
- Personalized Services: Creative BioMart offers tailored services designed to meet specific research requirements, including protein expression, purification, labeling, modification, and characterization.
- Extensive Resource Repository: Creative BioMart possesses a comprehensive selection of resources relating to additional coagulation cascade molecules, encompassing pathways, protein function, interacting proteins, articles, research domains, and more.
Our Featured Products
- Recombinant Human COL2A1, His tagged
- Recombinant Human COL2A1, His-tagged
- Recombinant Human COL25A1, His-tagged
- Recombinant Human ANXA2, GST-tagged
- Recombinant Human ANXA3, GST-tagged
- Recombinant Human GP1BA Protein, His-tagged
- Recombinant Human GP1BB protein, His-tagged
- Recombinant Human GP5 protein, His-tagged
- Recombinant Human P2RY12, GST-tagged
- Recombinant Human APOH, GST-tagged
- Recombinant Human APOH, GST-tagged
- Recombinant Human FGL2, GST-tagged
- Recombinant Human FGL2 protein, His-tagged
- Recombinant Human PF4, GST-tagged
- Recombinant Human PF4 protein
- Active Recombinant Human PLAUR protein, His/Avi-tagged, Biotinylated
- Active Recombinant Human GP1BB Protein (26-147aa), C-His-tagged
- Recombinant Human PLAUR protein, His-tagged
- Recombinant Human PLAUR Protein (23-305 aa), GST-tagged
- Recombinant Human PLAUR Protein, His-tagged
- Recombinant Human PLSCR1, GST-tagged
- Recombinant Human THBD, His-tagged
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
Reference:
- Samuelson Bannow B, Recht M, Négrier C, et al. Factor VIII: Long-established role in haemophilia A and emerging evidence beyond haemostasis. Blood Rev. 2019;35:43-50.


