SlyD
-
Overview
SlyD is a putative folding helper protein from the Escherichia coli cytosol, which consists of an N-terminal prolyl isomerase domain of the FKBP type and a presumably unstructured C-terminal tail. It is involved in the biosynthesis of the metal cluster in the [NiFe]-hydrogenase enzymes, and exhibits several activities including that of a peptidyl-prolyl isomerase. -
Synonyms
SlyD;FKBP-type Peptidyl-prolyl Cis-trans Isomerase;slyD;FKBP-type peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase;slyD FKBP-type peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase;
| Species | Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E.coli | slyD-8335E | Active Recombinant E.coli slyD | E.coli | N/A |
|
|
| E.coli | SlyD-329E | Recombinant E.coli FKBP-type Peptidyl-prolyl Cis-trans Isomerase | E.coli | N/A |
|
- Background
- Case Study
What is SLYD protein?
SlyD is a putative folding helper protein from the Escherichia coli cytosol, which consists of an N-terminal prolyl isomerase domain of the FKBP type and a presumably unstructured C-terminal tail. The SlyD protein has been found not only in E. coli, but also in other bacteria. This suggests that the SlyD protein may be somewhat conserved in the evolution of bacteria. The SLYD protein is consisted of 196 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 20.9 kDa.
What is the function of SLYD protein?
SlyD is a FKBP-type peptidyl-proline cis-trans isomerase in Escherichia coli that facilitates the cis-trans isomerization of proline residues in the peptide chain, thereby enabling protein folding into the correct three-dimensional structure for proper function and thereby affecting bacterial cell division.
SLYD Related Signaling Pathway
SlyD protein is a potential target for antibiotic development due to its important function in bacterial cell division. By gaining insight into the structure and function of the SlyD protein, researchers hope to develop new antibiotic drugs to fight bacterial infections.
Some studies have found that SlyD is upregulated in bacterial and parasitic infections and correlates with host immune responses and the ability of pathogens to invade and evade the immune system. These studies suggest SlyD may be a potential target for the treatment and prevention of infectious diseases.
Case study 1: Yaozhong Hu, 2017
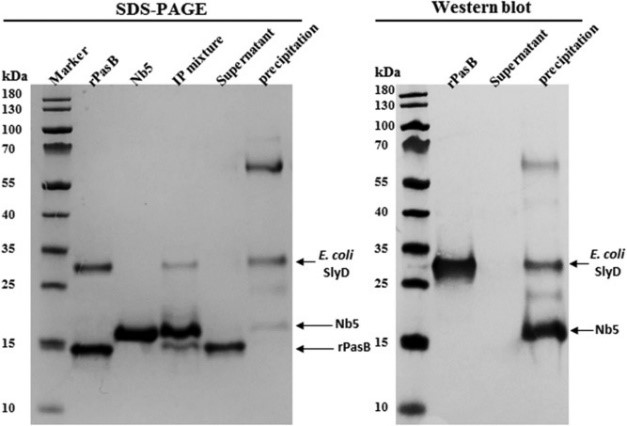
The gene for a protein domain, derived from a tumor marker was expressed in E. coli strain BL21 (DE3). The recombinant protein was purified from cell lysates through immobilized metal affinity chromatography and size-exclusion chromatography. A contaminating bacterial protein was consistently co-purified, even using stringent washing solutions containing 50 or 100 mM imidazole. Followed by mass spectrometry, the researchers identified the bacterial contaminant as FKBP-type peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase (SlyD) from E. coli. Using their SlyD-specific Nb 5 they generated an immune-complex that could be removed either by immunocapturing or by size exclusion chromatography. Both methods allow us to prepare a recombinant protein sample where the SlyD contaminant was quantitatively eliminated.
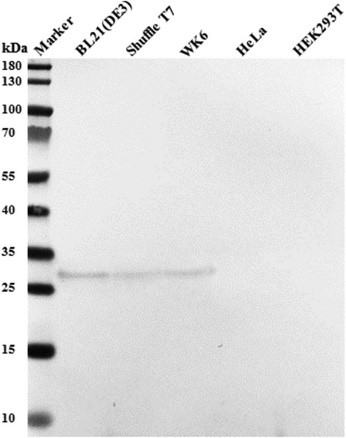
Fig1. Occurrence of SlyD recognized by Nb5 in lysates of various E. coli strains and absence of cross-reactive proteins in mammalian HeLa and HEK2937T cell lysates..
Case study 2: Kyung-Yeon Han, 2007
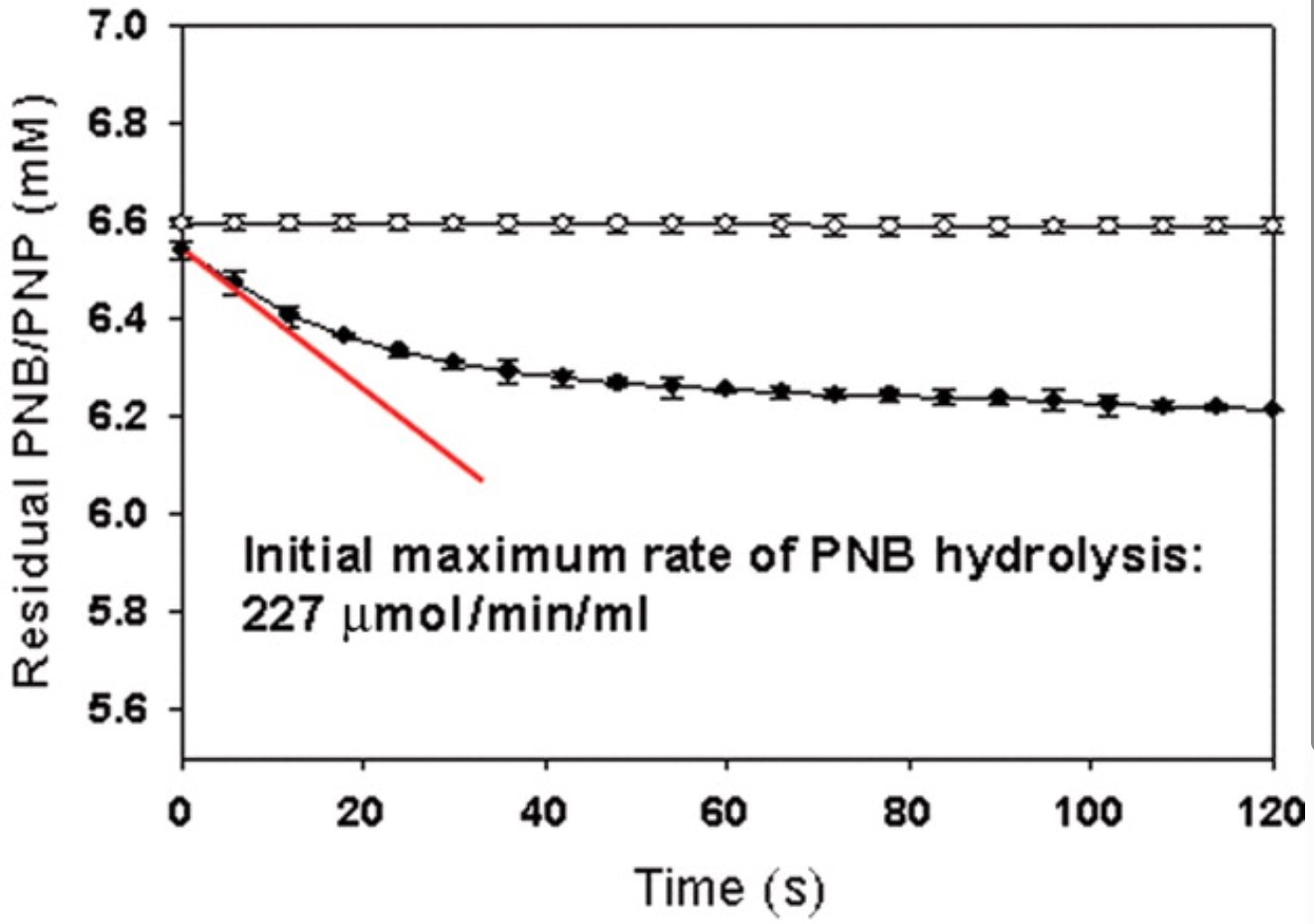
The proteome profile of Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) generated in response to heat shock stress was analyzed by two-dimensional electrophoresis (2-DE), wherein SlyD was identified. As a fusion partner, as well as solubility enhancer, SlyD facilitated folding and significantly increased the solubility of many aggregation-prone heterologous proteins in E. coli cytoplasm. SlyD was very effective in sequestering interactive surfaces of heterologous proteins associated with non-specific protein-protein interactions and the formation of inclusion bodies, most likely as a result of intrinsic folding efficiencies and/or chaperone-like activities. SlyD was also shown to be suitable for the production of a biologically active fusion mutant of Pseudomonas putida cutinase that is of considerable biotechnological and commercial interest.
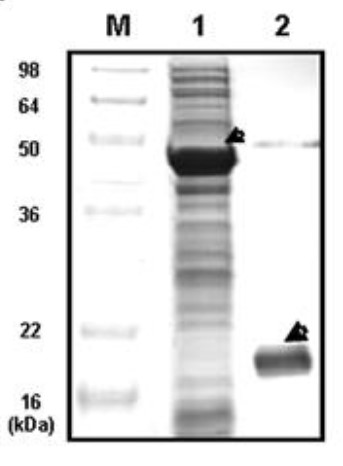
Fig3. Result of SDS–PAGE analysis, showing the solubility of recombinant G-CSF released from SlyD by enterokinase treatment.
SlyD involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways SlyD participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with SlyD were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
SlyD has several biochemical functions, for example, . Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by SlyD itself. We selected most functions SlyD had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with SlyD. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|
SlyD has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with SlyD here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of SlyD.
- Q&As
- Reviews
Q&As (6)
Ask a questionIt has a variety of associations with other proteins. For example, it may interact with histone methyltransferases and demethylases to participate in epigenetic regulation, and it may also interact with DNA methyltransferases and DNA demethylases to affect DNA methylation status.
Aberrant expression of SLYD may be associated with a variety of diseases, especially the occurrence and progression of tumors. For example, in tumors such as lung, breast, and colon cancers, SLYD expression levels may be abnormally elevated.
Levels of SLYD can be detected by methods such as immunohistochemistry, western blotting, and real-time PCR, which can assess the amount of SLYD in tissues and cells.
SLYD affects gene expression by catalyzing DNA methylation modification through the SET domain, which transfers methyl groups to bases of specific DNA sequences.
Abnormal SLYD levels may indicate a variety of conditions, particularly neoplastic diseases. For example, in tumors such as lung, breast, and colon cancers, SLYD expression levels may be abnormally elevated.
Methylation modifications of SLYD can affect the expression of specific genes, which in turn affects processes such as cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis. For example, in tumor cells, aberrant expression of SLYD may lead to abnormal methylation of genes, which in turn promotes tumor development and progression.
Customer Reviews (3)
Write a reviewSLYD was found in immunological experiments that it has good antigenicity and can induce target immune response.
High catalytic efficiency was found in enzyme experiments.
SLYD is found in biosensor preparation with high sensitivity and specificity.
Ask a Question for All SlyD Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All SlyD Products
Required fields are marked with *


