Detailed biological knowledge about the potential importance of the methylome is typically lacking for common diseases. Therefore, methylome-wide association studies (MWAS) are critical to detect disease relevant methylation sites. The most comprehensive method for determining the methylation status of every nucleotide is whole-genome bisulfite sequencing (WGBS), however, this approach is not economically viable due to the high cost of whole genome sequencing and the combination of large numbers of samples required in MWAS. At Creative BioMart, a cost-effective alternative, methyl-CpG-binding domain sequencing (MBD-Seq) is being offered to accelerate your methylome-wide association studies.
What Is Methyl-CpG-Binding Domain Sequencing?
Like the principle of methyl-DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-Seq), methyl-CpG-binding domain sequencing (MBD-Seq) is essentially a combination of affinity-based capture approach and next-generation sequencing (NGS). Affinity-based capture approach provides a cost-effective alternative because the goal of this approach is to sequence only the methylated portion of the genome. In contrast to the antibody-based method that captures DNA fragments containing any methylated cytosine, proteins with the methylated CpG binding domain (MBD) strictly bind methylated CpG loci. This more targeted method endows MBD-Seq a very useful attribute for identifying differentially methylated regions (DMRs). MBD enrichment extracts fragments with one or more methylated sites. The number of fragments covering CpG loci is then used to estimate the amount of methylation. Therefore, instead of providing methylation information at single-base resolution, MBD-Seq measures the total methylation amount of the locus, which is approximately the size of the extracted fragment (typically ~150 bp).
Features of Methyl-CpG-Binding Domain Sequencing
Our Advantages
Workflow of Methyl-CpG-Binding Domain Sequencing at Creative BioMart
During the process of MBD-Seq, genomic DNA is first fragmented, and then the methylated fragments are bound to a protein with high affinity for methylated DNA, thereby enriching the hypermethylated DNA fragments. The protein-DNA complex is then precipitated with antibody-conjugated beads that are specific to the protein tag. The unmethylated fraction is removed, and finally the methylation-enriched portion of the genome is eluted and sequenced to detect genome-wide methylation sites.
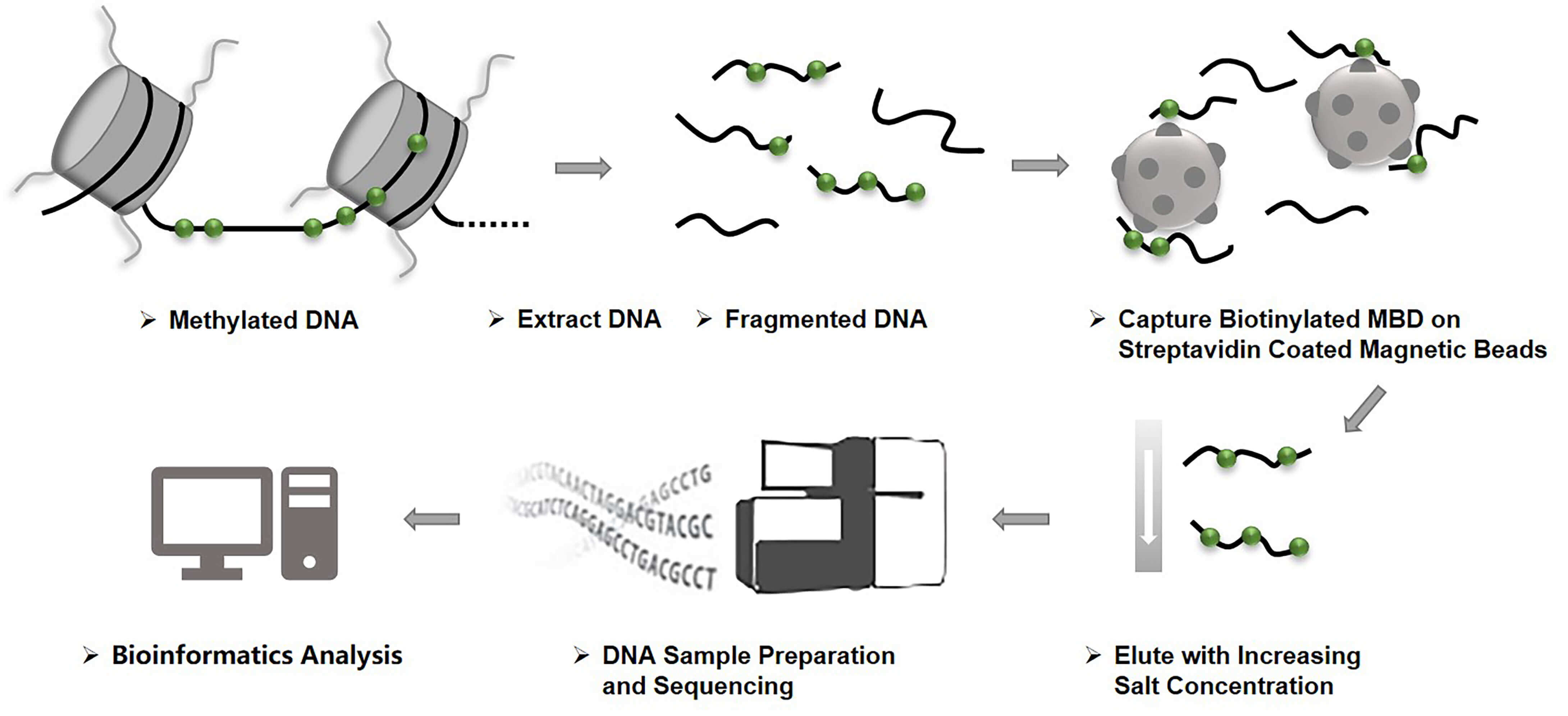
Fig 1. Workflow of MBD-Seq
It has been found that the performance of MBD-Seq is largely determined using optimal experimental protocols. At Creative BioMart, we can utilize different (combined) MBD proteins, but prefer to use MBD2 that can provide the best results. Moreover, we can make it easy to capture fragments with a small number of methylated sites by using a low-salinity elution buffer, and further enhance the sensitivity by using the shortest possible DNA fragments. Creative BioMart strictly controls every step in the MBD-Seq workflow to ensure access to unsurpassed data quality.
If you would like to use the methyl-CpG binding domain (MBD)-based capture method to enrich hypermethylated DNA fragments for other downstream applications, such as DNA methylation microarray testing, our flexible services will meet your research needs. Please feel free to contact us with any question or potential project.
Reference
1. Nair S S.; et al. Comparison of methyl-DNA immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) and methyl-CpG binding domain (MBD) protein capture for genome-wide DNA methylation analysis reveal CpG sequence coverage bias. Epigenetics. 2011, 6(1): 34-44.
2. Aberg K A.; et al. MBD-seq as a cost-effective approach for methylome-wide association studies: demonstration in 1500 case–control samples. Epigenomics. 2012, 4(6): 605-621.
USA
Enter your email here to subscribe.
Follow us on

Easy access to products and services you need from our library via powerful searching tools