In bacterial genomes, N6-methyladenine (m6A), N4-methylcytosine (m4C) and 5-methylcytosine (m5C) act as components of restriction-modification (RM) systems. Along with m6A and m5C, modified bases such as 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), 5-formylcytosine (5fC) and 5-carboxylcytosine (5caC) are also present in the eukaryotic genome. However, next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology lacks simple methods to determine the location of most DNA modifications, so many DNA modifications are generally ignored. The recently developed single molecule real time (SMRT) DNA sequencing technology directly detects natural epigenetic modifications through measuring kinetic changes during base incorporation. By capturing these modifications simultaneously with the sequenced data, the method eliminates the need for special sample preparation and additional sequencing.
Creative BioMart is providing SMRT sequencing service for epigenetic research to complement our NGS technology-based research methods.
What Is SMRT Sequencing?
SMRT sequencing technology applies the idea of sequencing while synthesizing. This technology utilizes four-color fluorescence labeled dNTPs and zero-mode waveguides (ZMWs) to sequence single DNA molecules. When the DNA template is captured by DNA polymerase, dNTPs with four different fluorescence enter the detection area randomly through Brownian motion and bind to the polymerase. The bonding time of the base matched with the template is much longer than that of other bases. Therefore, the matching base and free base can be distinguished by counting the duration of the fluorescence signal.
Four kinds of bases (dNTP) are labeled with four-color fluorescence respectively. In the base pairing phase, different bases will emit different fluorescent light when added, and the type of base entering can be determined according to the wavelength and peak value of fluorescent light. In addition, since the fluorescence signal is attached to the phosphate group of dNTP, when the previous dNTP is synthesized, the phosphate group is automatically detached, which ensures the continuity of detection, improves the detection speed and cooperates with the high-resolution optical detection system to realize real-time detection. Moreover, the difference in interpulse duration (IPD) between normal and modified bases can be used as a signal to detect base modification.
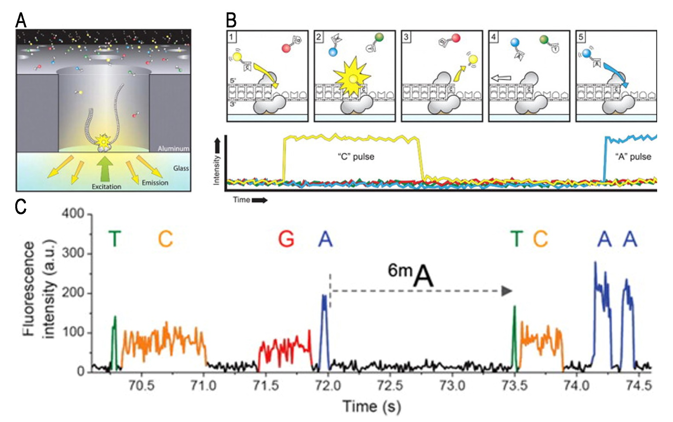
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the principle behind SMRT sequencing. (Rhoads A.; Au K F. 2015). A. A SMRTbell (gray) diffuses into a ZMW, and the adaptor binds to a polymerase immobilized at the bottom. B. Each of the four nucleotides is labeled with a different fluorescent dye (indicated in red, yellow, green, and blue, respectively for G, C, T, and A) so that they have distinct emission spectrums. C. SMRT sequencing can detect modified bases (e.g. m6A).
Features of SMRT Sequencing
| Features | Description |
| Single molecule |
|
| Extra-long read length |
|
| Direct recognition of base modification |
|
Our Advantages
Workflow of SMRT Sequencing at Creative BioMart
Figure 2. Workflow of SMRT Sequencing at Creative BioMart
Creative BioMart pursues a strong commitment to service and unparalleled data quality to help our customers achieve research goals in the rapidly evolving world of epigenetics. contact us for more information about our SMRT sequencing service.
References
1. Davis B M.; et al. Entering the era of bacterial epigenomics with single molecule real time DNA sequencing. Current Opinion in Microbiology. 2013, 16(2): 192-198.
2. Rhoads A.; Au K F. PacBio sequencing and its applications. Genomics, Proteomics & Bioinformatics. 2015, 13(5): 278-289.
USA
Enter your email here to subscribe.
Follow us on

Easy access to products and services you need from our library via powerful searching tools