Lysine and arginine residues in a histone can be mono-, di- or tri-methylated under the catalysis of histone methyltransferase (HMT), each of which could function as a primary determining factor in repression or activation of transcription, depending on the target sites. Histone methylation plays a critical role in the epigenetic regulation of gene transcription and may serve as a global epigenetic mark to explain our phenotypic diversity from cell to cell. Quantification of histone methylation has become particularly useful in studying epigenetic regulation patterns of gene expression.
Creative BioMart offers convenient package of tools for methylated histone quantification (MHQ) assay. Customized design and identification of histone methylation are involved in our MHQ service. Compared with traditional quantitative proteomics analysis, the key step in histone modification quantitative analysis is how to isolate and purify pure histone components. Our innovative biologists adopt highly sensitive ELISA methods to solve this problem, which is further combined with colorimetric technique to meet your MHQ needs.
What Is Methylated Histone Quantification (MHQ) Assay?
Methylation of H3 at lysine 4, 9, 27, 36, and 79 (H3-K4, H3-K9, H3-K27, H3-K36, H3-K79) and methylation of H4 at lysine 20 (H4-K20) are common types of histone modification, and they are involved in pathological processes. MHQ assay is a whole cell-based detection of histone methylation, which enables researchers to measure global mono-methylation or multi-methylation of H3 or H4 in situ and in vitro. Levels change of methylation caused by inhibition or activation of HMTs allows quantitative detection of global methyl histone to be significant in developing a better comprehension of epigenetic regulation of gene activation/repression and in the exploration of HMT-targeted drugs. A variety of mammalian cells including fresh and frozen tissues, and cultured adherent and suspension cells are available in this assay.
Procedure of MHQ Assay
Adherent cells are cultured in conventional 96-well microplates and cells are fixed, permeabilized and blocked after an experimental treatment. Specific methylated histone is stably spotted to the strip wells coated with corresponding antibody, and then can be recognized with a labeled detection antibody followed by the addition of color or fluorescence development reagent. The ratio of the specific methylated histone is proportional to the intensity of absorbance/fluorescence. The absolute methylated histone amount can be quantitated by comparing to the standard control through the horseradish peroxidase (HRP) conjugated secondary antibody-color development system.
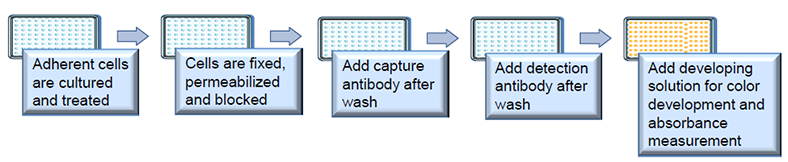
Figure 1. Workflow of MHQ assay.
Features of Our MHQ Assay
Our workflows can accommodate both of your small and large assay requirements, and our committed executive will guide you through every step of the project and constantly keep you informed of the progress. Collaborate with us to loosen the puzzle enwinding your project with a tailored solution for you. If you need to receive more detailed information on pricing and the timeline, please feel free to contact us.
References
Greer, E. L.; Shi, Y. Histone methylation: a dynamic mark in health, disease and inheritance. Nat Rev Genet. 2012, 13: 343–357.
USA
Enter your email here to subscribe.
Follow us on

Easy access to products and services you need from our library via powerful searching tools